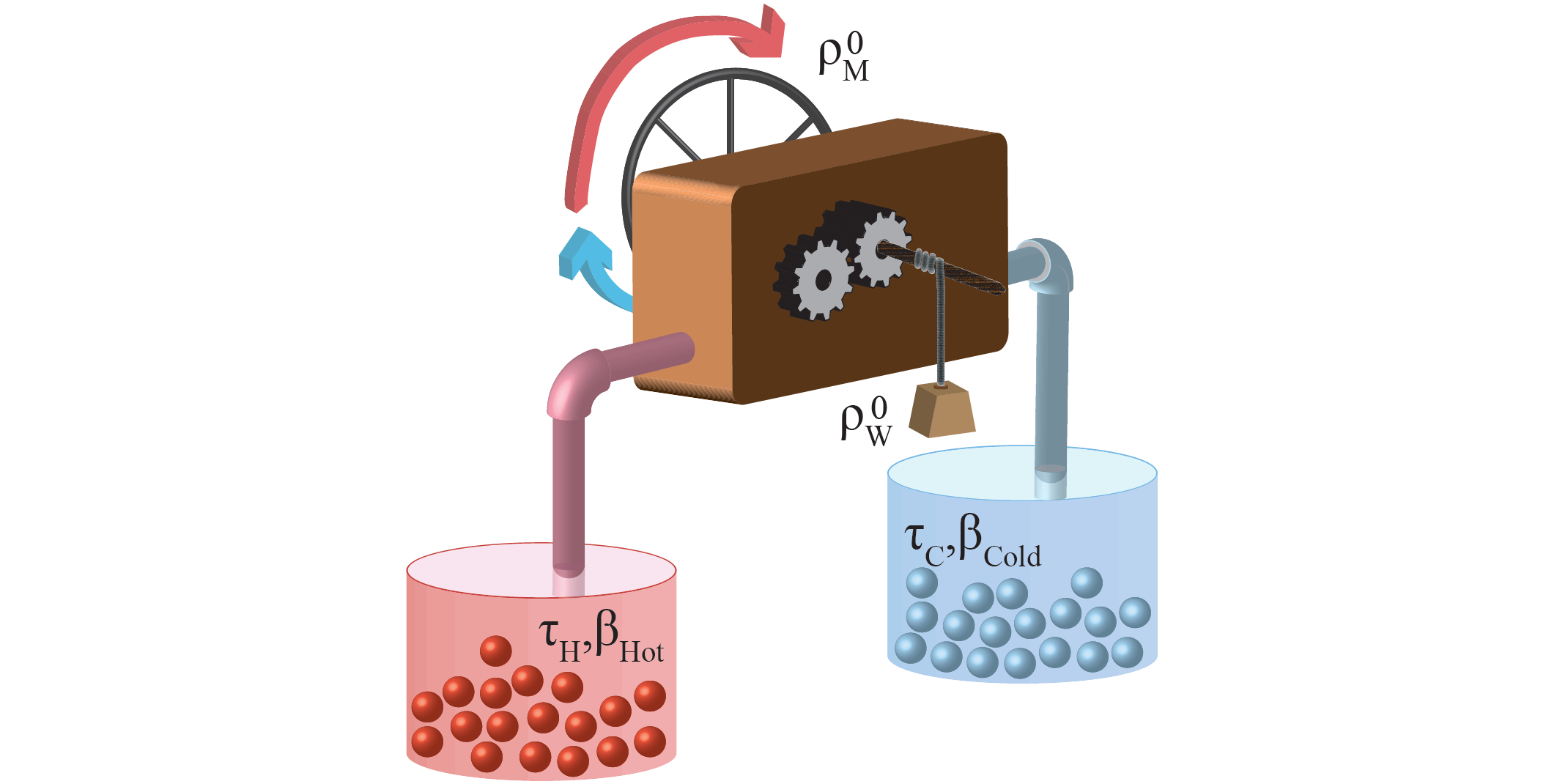
Heat engines are fascinating machines that have played a crucial role in shaping the modern world. They are devices that convert thermal energy into mechanical work, and their principles underlie the functioning of everything from steam engines to car engines. Understanding how heat engines work can provide us with insights into the fundamental laws of thermodynamics and the efficient conversion of heat into useful work.
In this article, we will explore 10 intriguing facts about heat engines that will pique your curiosity and broaden your understanding of this pivotal area of physics. From the historical significance of the steam engine to the cutting-edge advancements in renewable energy, we will delve into the inner workings, applications, and future prospects of these remarkable machines.
Key Takeaways:
- Heat engines have been around for centuries and are used in cars, power plants, and even household appliances. They convert heat energy into mechanical work, following the laws of thermodynamics.
- Engineers are constantly working to improve the efficiency of heat engines, and ongoing research aims to make them more efficient and environmentally friendly in the future.
The concept of heat engines has been around for centuries.
Heat engines are not a recent invention; in fact, their fundamental principles were first explored by ancient Greek and Roman scholars. The study of heat engines has evolved over time, leading to the development of various types and designs.
Heat engines are devices that convert heat energy into mechanical work.
A heat engine operates by taking in thermal energy from a high-temperature source, converting a portion of that energy into mechanical work, and releasing the remaining energy as waste heat. This process is governed by the laws of thermodynamics.
They are used in a wide range of applications.
Heat engines are utilized in various industries and everyday life. They power automobiles, generate electricity in power plants, propel spacecraft, and even drive household appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners.
Heat engines can be classified into different types.
There are several types of heat engines, including internal combustion engines, steam engines, and gas turbines. Each type has its own unique operating principles and applications.
Efficiency is a crucial factor in heat engine design.
The efficiency of a heat engine refers to the percentage of input energy that is converted into useful work. Engineers constantly strive to improve the efficiency of heat engines to maximize energy conversion and minimize waste heat.
Heat engines follow the laws of thermodynamics.
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the study of heat and its relationship to other forms of energy. Heat engines operate in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics, including the first and second laws.
Heat engines require a temperature difference to operate.
In order to convert heat into mechanical work, a heat engine needs a temperature gradient. This temperature difference is necessary for the transfer of thermal energy, allowing the engine to perform mechanical tasks.
Reciprocating and rotary engines are common types of heat engines.
Reciprocating engines, such as the internal combustion engine found in cars, use back-and-forth linear motion to convert heat energy into work. Rotary engines, like turbines, convert heat energy into rotational motion.
Heat engines have a finite efficiency limit.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, no heat engine can have an efficiency of 100%. This theoretical limit, known as the Carnot efficiency, depends on the temperature difference across the engine.
Future advancements may lead to more efficient heat engines.
Ongoing research and development in the field of heat engines aim to improve their efficiency and reduce their environmental impact. Concepts like waste heat recovery and new materials hold promise for enhancing the performance of heat engines in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat engines are fascinating devices that play a vital role in various applications, from power generation to transportation. Understanding how heat engines work and their underlying principles is crucial for advancements in technology and energy efficiency. From their historical significance to their impact on the environment, heat engines continue to be a subject of study and innovation. With ongoing research and development, we can look forward to even more efficient and sustainable heat engines in the future.
FAQs
1. What is a heat engine?
A heat engine is a device that converts thermal energy into mechanical work, typically by utilizing the temperature difference between a heat source and a heat sink.
2. How does a heat engine work?
A heat engine operates on the principle of the Carnot cycle, where heat is converted into work by a series of processes involving compression, expansion, and heat transfer.
3. What are some examples of heat engines?
Common examples of heat engines include internal combustion engines used in automobiles, steam engines used in locomotives, and gas turbines used in power plants.
4. Are heat engines efficient?
Heat engines can never be 100% efficient due to the inherent losses in the conversion of heat energy to work. The efficiency is determined by the temperature difference between the heat source and sink.
5. How do heat engines contribute to global warming?
Heat engines that burn fossil fuels release greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, which contribute to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
6. Are there any advancements in heat engine technology?
Researchers are constantly exploring new materials, designs, and processes to improve the efficiency and sustainability of heat engines. Some advancements include hybrid engines and waste heat recovery systems.
7. Can heat engines be used for renewable energy?
Yes, heat engines can be coupled with renewable energy sources such as solar or geothermal energy to produce clean and sustainable power.
8. What are the challenges in heat engine development?
Challenges in heat engine development include reducing emissions, improving efficiency, and finding alternative fuels or energy sources that are environmentally friendly.
9. How do heat engines impact transportation?
Heat engines power various modes of transportation, including cars, trucks, ships, and airplanes, enabling the movement of people and goods across long distances.
10. Can heat engines be used for space exploration?
Heat engines, such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators, have been used in space missions to convert heat from radioactive materials into electrical power for spacecraft and scientific instruments.
Intrigued by heat engines' inner workings? Delve deeper into thermodynamics with our captivating articles. Unravel the mysteries of Carnot engines, their astonishing efficiency, and theoretical limits. Explore entropy's enigmatic nature, its role in energy transfer, and the universe's inevitable march towards disorder. Lastly, embark on a thrilling journey through the Carnot cycle, its unbelievable implications for heat engine design, and the quest for maximum performance. Satisfy your curiosity and expand your knowledge with these engaging reads, guaranteed to leave you marveling at the wonders of thermodynamics.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
