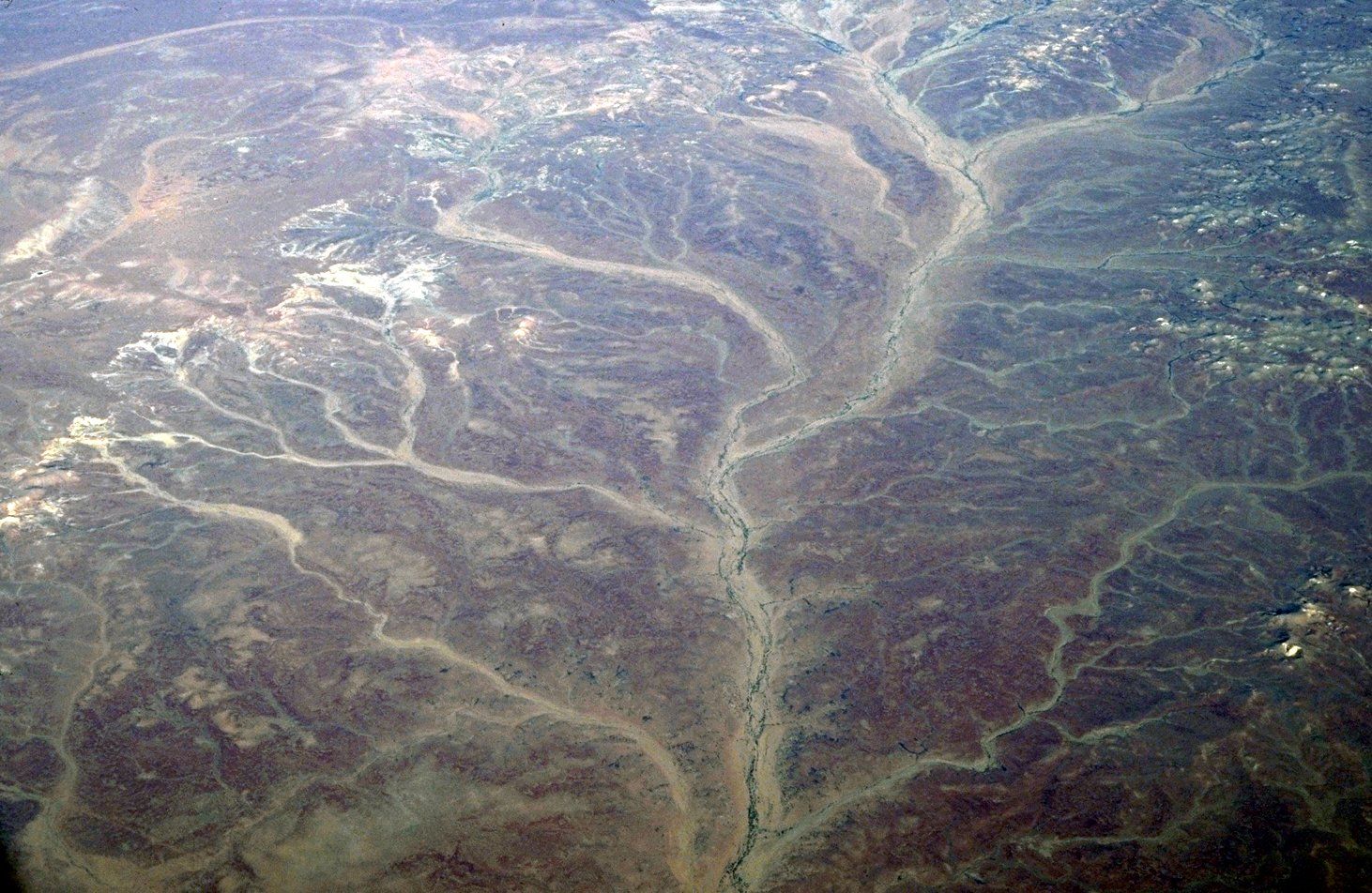
When it comes to understanding the various patterns of drainage systems, one of the most fascinating and visually striking is the dendritic drainage pattern. Derived from the Greek word “dendron,” meaning tree, this pattern resembles the branches of a tree spreading out in all directions. While this pattern may seem common, there are a number of surprising facts about dendritic drainage that many people may not be aware of.In this article, we will explore 18 intriguing facts about dendritic drainage patterns, shedding light on their formation, distribution, and significance. From their origins in geological processes to their influence on landscape features, these facts will leave you with a deeper appreciation for the intricate nature of dendritic drainage patterns.
Key Takeaways:
- Dendritic drainage patterns, like nature’s tree branches, efficiently distribute water and resources, benefitting landscapes and supporting diverse habitats.
- These patterns reveal geological history, impact agriculture, and inspire aesthetically pleasing landscapes, making them vital and fascinating features of our earth’s geography.
Nature’s Tree-Like Pattern
The dendritic drainage pattern resembles the branches of a tree, with the main river channel representing the trunk and the smaller tributaries representing the branches.
Widespread Distribution
The dendritic drainage pattern is the most common drainage pattern found across the globe. It can be observed in various landscapes, from mountains to plains.
Formation Process
This pattern is formed through the erosion and weathering of rocks, creating a network of channels that follow the path of least resistance.
Efficient Water Flow
The dendritic drainage pattern allows for efficient water flow as it evenly distributes water across the landscape, minimizing the risk of flooding.
Area Coverage
This drainage pattern covers large areas and is commonly associated with flat and gently sloping terrains.
Tributary Confluence
The dendritic pattern is formed when smaller tributaries merge into larger rivers, creating a complex network of interconnected waterways.
Resilience to Erosion
The dendritic drainage pattern is resistant to erosion due to its widespread network of channels, allowing water to flow freely without causing significant damage.
Connection to Geological Structure
The formation of dendritic drainage patterns is influenced by the underlying geological structure of the area, such as the presence of fault lines and rock types.
Indicator of Mature Landscapes
The presence of dendritic drainage patterns often indicates a mature landscape that has undergone a long history of erosion and development.
Shape of Drainage Basins
The shape of the drainage basins associated with dendritic patterns is elongated and has a dendritic shape, resembling the pattern itself.
Efficiency in Resource Distribution
The dendritic pattern efficiently distributes resources, such as nutrients and sediment, across the landscape, benefitting plant and animal life.
Exploration of New Areas
Scientists study dendritic drainage patterns as a tool for exploring new areas and understanding the underlying geological processes at work.
Relationship to Climate Change
The alteration of dendritic drainage patterns may provide insights into the impact of climate change and how it affects water flow and distribution.
Geological Time Scale
By examining the dendritic patterns and their evolution, geologists can gain valuable information about the geological time scale and changes over millions of years.
Influence on Agriculture
The dendritic pattern plays a role in agricultural practices as it determines the drainage characteristics of an area, affecting irrigation and crop productivity.
Habitat Creation
Due to the presence of small tributaries and wetlands, dendritic drainage patterns create diverse habitats that support a wide range of plant and animal species.
Role in Civil Engineering
Engineers utilize knowledge of dendritic drainage patterns to design effective drainage systems for cities and infrastructure projects, ensuring proper water management.
Aesthetically Pleasing Landscapes
The gentle and harmonious flow of water in dendritic drainage patterns creates visually appealing landscapes, captivating the viewer with their natural beauty.
As these 18 surprising facts about dendritic drainage patterns reveal, this natural phenomenon is not only vital for the sustainable flow of water but also holds immense scientific and aesthetic significance in our ever-changing world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the dendritic drainage pattern is a fascinating aspect of geography that has its own unique characteristics. From its prevalence in regions with uniform rock types to its ability to efficiently transport water, dendritic patterns play a crucial role in shaping landscapes. Understanding the various factors that contribute to the formation of dendritic patterns helps us appreciate the complexity and beauty of the natural world.
FAQs
Q: What is a dendritic drainage pattern?
A: A dendritic drainage pattern is a river system that resembles the branching pattern of a tree. It is formed when streams and rivers flow downhill, eroding the landscape and following the path of least resistance, resulting in a network of interconnected channels.
Q: Where is the dendritic drainage pattern most commonly found?
A: The dendritic drainage pattern is commonly found in regions with a uniform and consistent rock type. This includes areas with sedimentary or volcanic rock formations. It is less common in areas with diverse rock types or significant tectonic activity.
Q: What are the advantages of a dendritic drainage pattern?
A: The dendritic drainage pattern is advantageous because it efficiently transports water. The branching network of streams and rivers allows for a uniform and widespread distribution of water throughout a given area. Additionally, it promotes faster runoff and reduces water pooling, which aids in preventing flooding.
Q: Are there any disadvantages to the dendritic drainage pattern?
A: One potential disadvantage of the dendritic drainage pattern is its susceptibility to erosion. Because the channels branch out in multiple directions, erosion can occur in various areas, leading to the widening and deepening of channels. This can have negative effects on the surrounding landscape and ecosystems.
Q: Can human activities affect dendritic drainage patterns?
A: Yes, human activities such as urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture can impact dendritic drainage patterns. Alterations to the natural landscape, such as construction of dams or diversion of rivers, can disrupt the natural flow of water and alter the pattern of drainage in an area.
Q: How do dendritic drainage patterns contribute to the formation of river valleys?
A: The dendritic drainage pattern plays a crucial role in the formation of river valleys. As streams and rivers erode the landscape, they create V-shaped valleys along their courses. Over time, these valleys deepen and widen, resulting in the characteristic features of river valleys that we observe in many landscapes.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.