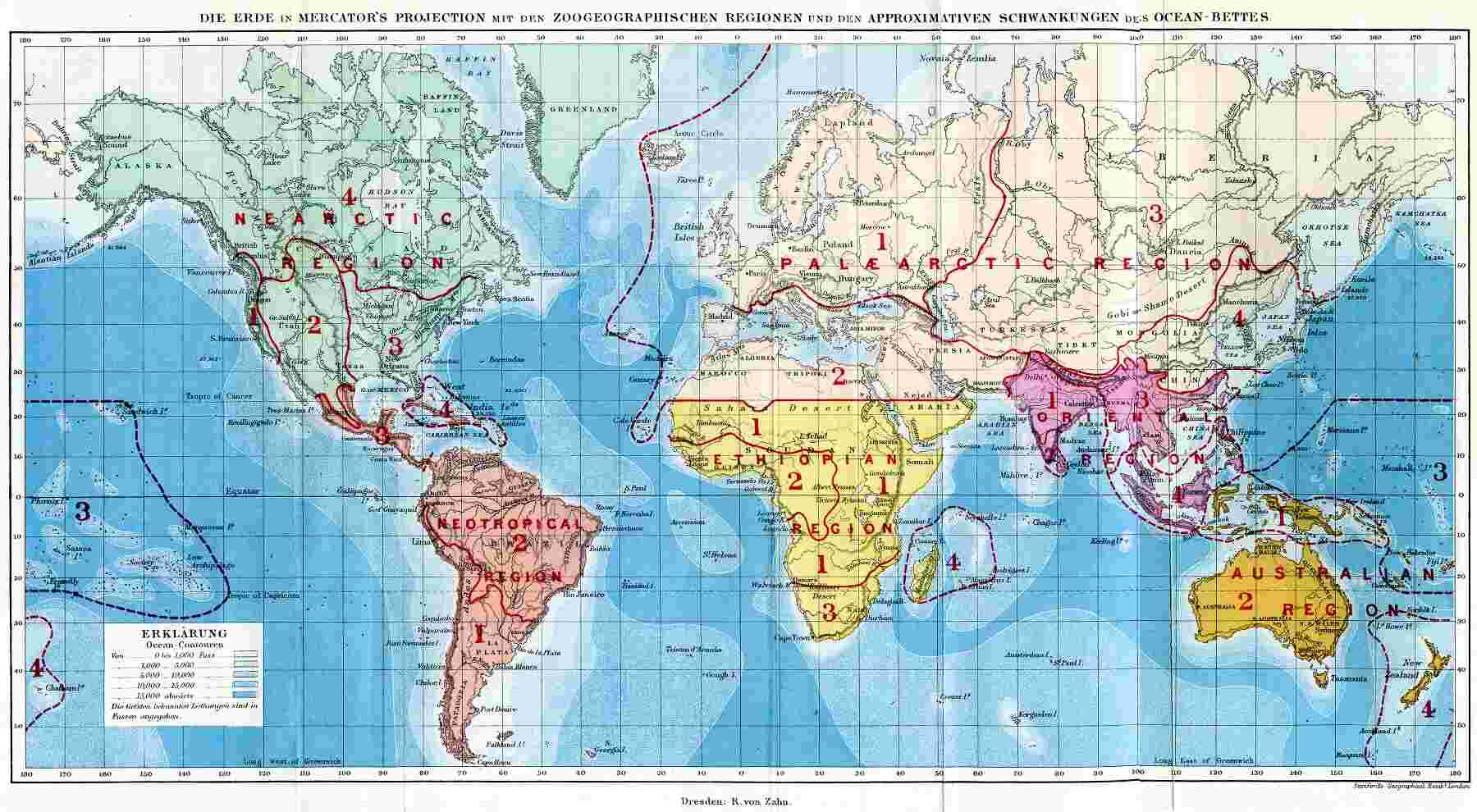
Welcome to the fascinating world of biogeographic regions! These unique areas of the planet are characterized by their distinct ecosystems, flora, and fauna. Biogeographic regions play a crucial role in understanding the distribution patterns of different species and the factors that shape their evolution.
From the lush rainforests of the Amazon to the frozen tundras of the Arctic, each biogeographic region has its own story to tell. In this article, we will explore 16 captivating facts about these remarkable regions, shedding light on their biodiversity, conservation efforts, and the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
So, get ready to embark on a journey through the diverse landscapes and rich biological heritage of biogeographic regions. Brace yourself for a thrilling adventure that will leave you with a deeper appreciation for the world’s natural wonders!
Key Takeaways:
- Biogeographic regions are like treasure troves of unique plants and animals, found nowhere else on Earth. From the Great Barrier Reef to the African savanna, they’re nature’s special showcases!
- These regions, like the Amazon rainforest and the Galapagos Islands, are like living classrooms of evolution and biodiversity. They’re like nature’s own storybooks, filled with fascinating tales of life and adaptation!
Diverse Ecosystems: A Haven of Life
Biogeographic regions are characterized by their rich and diverse ecosystems, making them a haven for a wide variety of plant and animal species.
An Intersection of Land and Water
Biogeographic regions often span across both land and water, encompassing terrestrial, freshwater, and marine ecosystems. This dynamic combination contributes to their incredible biodiversity.
Unique Species Found Nowhere Else
Biogeographic regions are home to numerous endemic species, which are found nowhere else on Earth. These unique organisms have evolved in isolation, adapting to their specific habitats over time.
The Great Barrier Reef: Nature’s Masterpiece
The Great Barrier Reef, located in the biogeographic region of the Coral Triangle, is the largest coral reef system in the world. It is home to an astonishing array of marine life, including colorful coral, tropical fish, and majestic sea turtles.
The Amazon Rainforest: The Lungs of the Earth
The Amazon rainforest, located in the Neotropical biogeographic region, is the largest tropical rainforest in the world. It plays a vital role in regulating the global climate and is home to countless species, many of which have yet to be discovered.
The African Savanna: Land of the Big Five
The African savanna, found in the Afrotropical biogeographic region, is famous for its iconic wildlife. It is home to the renowned Big Five: lion, leopard, elephant, rhinoceros, and buffalo.
The Galapagos Islands: A Living Laboratory
The Galapagos Islands, located in the biogeographic region of the Eastern Pacific, are renowned for their unique biodiversity and their role in Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution. These islands offer a fascinating glimpse into the intricate relationships between species.
Pacific Northwest: Towering Forests and Majestic Wildlife
The Pacific Northwest, situated in the Nearctic biogeographic region, is characterized by its lush temperate rainforests and diverse wildlife. From towering Douglas fir trees to majestic orcas, this region is a nature lover’s paradise.
The Arctic Tundra: A Harsh and Fragile Landscape
The Arctic tundra, located in the Palearctic biogeographic region, is a vast and unforgiving landscape. Its extreme cold temperatures and short growing seasons make it a challenging environment for plant and animal life.
The Mediterranean: A Mosaic of Cultures and Biodiversity
The Mediterranean region, found in the Palearctic biogeographic region, is not only known for its rich cultural heritage but also for its exceptional biodiversity. From the olive groves of Greece to the diverse marine life in the Mediterranean Sea, this region is teeming with life.
The Hawaiian Islands: Evolutionary Hotspots
The Hawaiian Islands, located in the biogeographic region of Oceania, have evolved in isolation for millions of years. This unique isolation has resulted in a stunning array of endemic species found nowhere else on Earth.
The Cerrado: Brazil’s Forgotten Biodiversity Hotspot
The Cerrado, located in the Neotropical biogeographic region of Brazil, is one of the world’s most overlooked biodiversity hotspots. It is home to an incredible diversity of plants and animals, many of which are endemic to this region.
The Himalayas: Majestic Peaks and Hidden Treasures
The Himalayan region, spanning across multiple biogeographic regions, is known for its towering peaks and breathtaking landscapes. It is also home to a wide range of unique and fascinating species, including the elusive snow leopard.
The Great Lakes: A Freshwater Wonder
The Great Lakes region, situated in the Nearctic biogeographic region, is a sprawling freshwater ecosystem. These interconnected lakes support a diverse array of fish species and provide important habitat for migratory birds.
The Boreal Forest: Earth’s Northern Green Belt
The boreal forest, found in the Palearctic and Nearctic biogeographic regions, is the world’s largest land biome. It stretches across northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia, harboring an incredible diversity of plants and wildlife.
The Australian Outback: A Land of Extremes
The Australian Outback, located in the Australasian biogeographic region, is a vast and arid landscape. Despite its harsh conditions, it is home to a unique assemblage of plants and animals, including kangaroos, koalas, and the iconic Ayers Rock.
These captivating facts about biogeographic regions highlight their immense ecological and cultural importance. From the stunning biodiversity of the Amazon rainforest to the evolutionary wonders of the Galapagos Islands, these regions provide a glimpse into the wonders of our natural world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world’s biogeographic regions are truly captivating in their diversity and ecological importance. From the rich biodiversity of the Amazon rainforest to the unique species found in the Galapagos Islands, these regions hold a wealth of natural wonders waiting to be discovered.
Understanding and protecting these biogeographic regions is essential for preserving our planet’s biodiversity and ensuring a sustainable future. By studying the unique ecosystems and species within these regions, we can gain valuable insights into the intricate web of life on Earth.
Whether you’re an avid nature enthusiast or simply curious about the world we live in, exploring the fascinating facts about biogeographic regions is a journey worth taking. So grab your map, pack your bags, and embark on an adventure to witness the incredible beauty and complexity of our planet’s biogeographic regions.
FAQs
1. What is a biogeographic region?
A biogeographic region is a geographic area that is characterized by distinct ecological and evolutionary features. It is defined based on the distribution of plant and animal species and their interactions within the area.
2. How many biogeographic regions are there?
There are a total of 35 recognized biogeographic regions globally. Each region has its unique set of environmental conditions and species compositions.
3. What factors determine the boundaries of biogeographic regions?
The boundaries of biogeographic regions are determined by various factors, including geographical barriers such as mountains or oceans, climate patterns, and the distribution of different species.
4. Why are biogeographic regions important?
Biogeographic regions play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and understanding the natural history of different species. They provide insight into the evolution and adaptation of organisms to specific environmental conditions.
5. Can different biogeographic regions overlap?
Yes, it is possible for different biogeographic regions to overlap. These areas are known as “transition zones” and are characterized by a mix of species from both regions.
6. Are biogeographic regions static?
No, biogeographic regions are not static. They can change over time due to natural events like climate change, as well as human-induced factors such as habitat destruction and introduction of invasive species.
7. Can biogeographic regions be found in the ocean?
Yes, biogeographic regions also exist in the ocean. These regions are based on factors like temperature, ocean currents, and the presence of specific marine species.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
