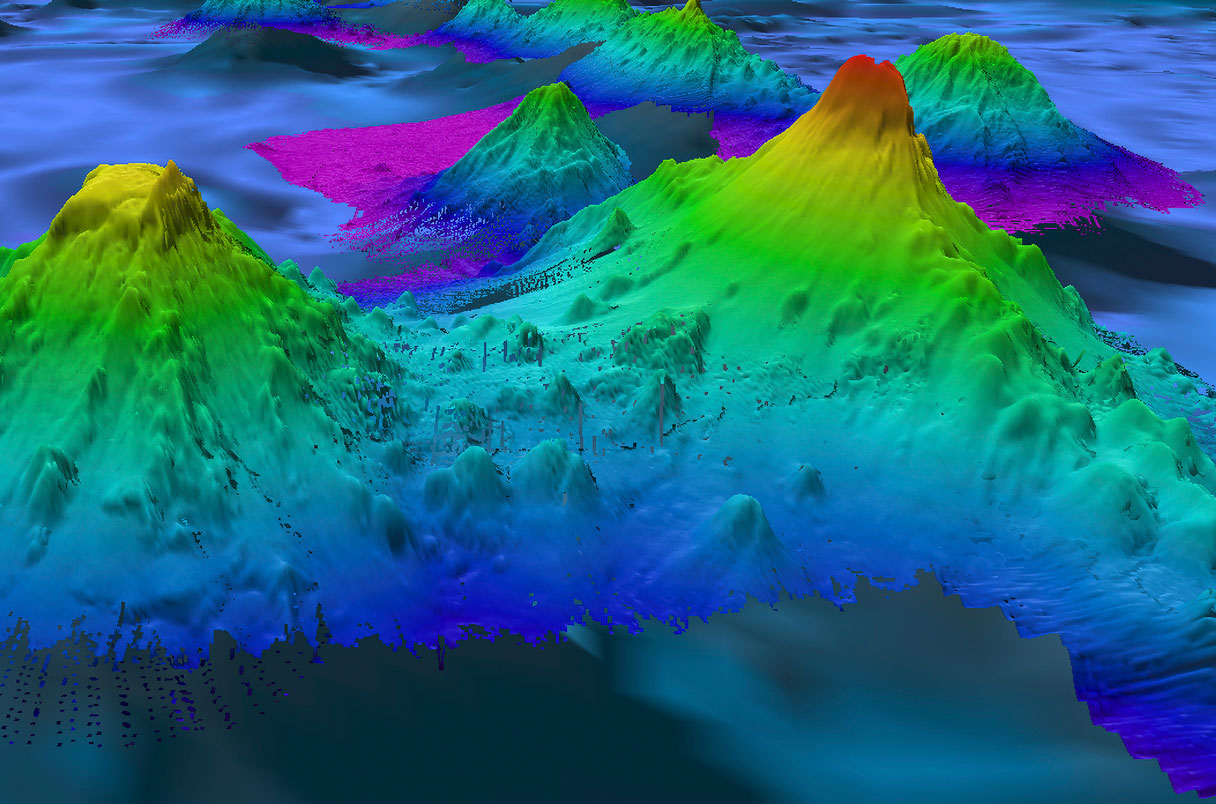
Submarine mountains, also known as underwater mountains or seamounts, are fascinating features that lie hidden beneath the vast oceans of our planet. These massive underwater peaks offer a glimpse into the mysterious depths of the Earth’s crust, showcasing a world of geological wonders that are often left unexplored.
In this article, we will unveil 10 extraordinary facts about submarine mountains that will leave you in awe of their magnitude and significance. From their formation to their ecological importance, these underwater giants are a testament to the power and complexity of our planet’s geology.
So, get ready to dive deep into the depths of the ocean as we unravel the secrets of these remarkable underwater mountains!
Key Takeaways:
- Submarine mountains are massive underwater formations, home to diverse ecosystems, and play a crucial role in ocean currents, making them a fascinating subject for scientific research and exploration.
- These extraordinary underwater mountains hold clues to Earth’s history, are potential sources of valuable minerals, and are a hotspot for marine life, making them a treasure trove for future exploration and study.
Submarine Mountains are massive underwater formations
Submarine mountains, also known as seamounts, are large underwater mountains that rise from the ocean floor. These majestic geological formations can reach heights of several thousand meters and can be found in all of the world’s oceans.
There are thousands of submarine mountains in the world
It is estimated that there are over 100,000 seamounts across the globe. Many of these mountains remain unexplored and undiscovered, making them a fascinating subject of study for scientists and researchers.
Submarine mountains are home to diverse ecosystems
Despite being underwater, seamounts support a rich array of marine life. These mountains act as oases in the deep sea, providing habitats for a wide variety of species including corals, sponges, fishes, and even deep-sea hydrothermal vent communities.
Some submarine mountains are taller than Mount Everest
While Mount Everest is the tallest mountain on land, there are submarine mountains that surpass its height. For example, the seamount known as Tamu Massif in the Pacific Ocean is believed to be the largest single volcano on Earth and is estimated to be taller than Mount Everest.
Submarine mountains can be volcanic or non-volcanic
Seamounts can be formed through volcanic activity, where hot magma rises from the Earth’s mantle and solidifies to create underwater mountains. However, some submarine mountains are formed through non-volcanic processes like tectonic movements or erosion.
Submarine mountains have unique geological features
Submarine mountains often exhibit distinct geological features such as steep slopes, rugged cliffs, and deep canyons. These features are the result of millions of years of geological processes and are fascinating to study.
Submarine mountains play a role in ocean currents
The presence of submarine mountains can significantly influence ocean currents by creating turbulence and altering the flow of water. This, in turn, affects the distribution of nutrients and marine life in surrounding areas.
Submarine mountains hold clues to Earth’s history
The study of submarine mountains provides valuable insights into the Earth’s geological history. By analyzing the composition of rocks and sediments found on these mountains, scientists can unravel past plate tectonic movements and climate changes.
Submarine mountains are potential sources of valuable minerals
Submarine mountains are known to contain deposits of valuable minerals such as iron, manganese, and copper. Exploring and mining these resources in a sustainable manner poses both challenges and opportunities for future generations.
Submarine mountains are research hotspots
Due to their unique characteristics and ecological importance, submarine mountains are a focal point for scientific research and exploration. Scientists use advanced technologies such as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and deep-sea submersibles to study these underwater wonders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, submarine mountains are fascinating geological formations that exist beneath the surface of the ocean. They are often overlooked, but they hold a wealth of information about the Earth’s crust and the processes that shape our planet. From their sheer size and elevation to their unique ecosystems, submarine mountains are truly extraordinary. Exploring these underwater wonders has allowed scientists to discover new species, understand tectonic activity, and uncover ancient geological history. As our knowledge and technology continue to advance, we can expect to unravel even more mysteries and gain a deeper understanding of these magnificent formations. So, the next time you think about mountains, remember that there is a whole world of remarkable structures hidden beneath the waves.
FAQs
1. What exactly are submarine mountains?
Submarine mountains, also known as seamounts, are underwater volcanic mountains that rise from the ocean floor but do not reach the surface. They can vary in size, shape, and composition.
2. How are submarine mountains formed?
Submarine mountains are formed through volcanic activity. As lava erupts from underwater vents, it cools and solidifies, building up layers of rock over time, eventually forming the mountainous structure.
3. How big can submarine mountains get?
Submarine mountains can reach impressive heights, sometimes towering thousands of meters above the surrounding seafloor. Some of the largest seamounts are comparable in size to well-known land-based mountains.
4. Are there any living organisms on submarine mountains?
Yes, submarine mountains are known to host a wide variety of marine life. These underwater ecosystems can be teeming with corals, sponges, fish, and other organisms that thrive in the nutrient-rich waters surrounding these seamounts.
5. Are submarine mountains important for scientific research?
Absolutely! Submarine mountains provide valuable information about geological processes, seafloor mapping, and marine biodiversity. Scientists study these formations to better understand the Earth’s history and the impact of volcanic activity on the oceans.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
