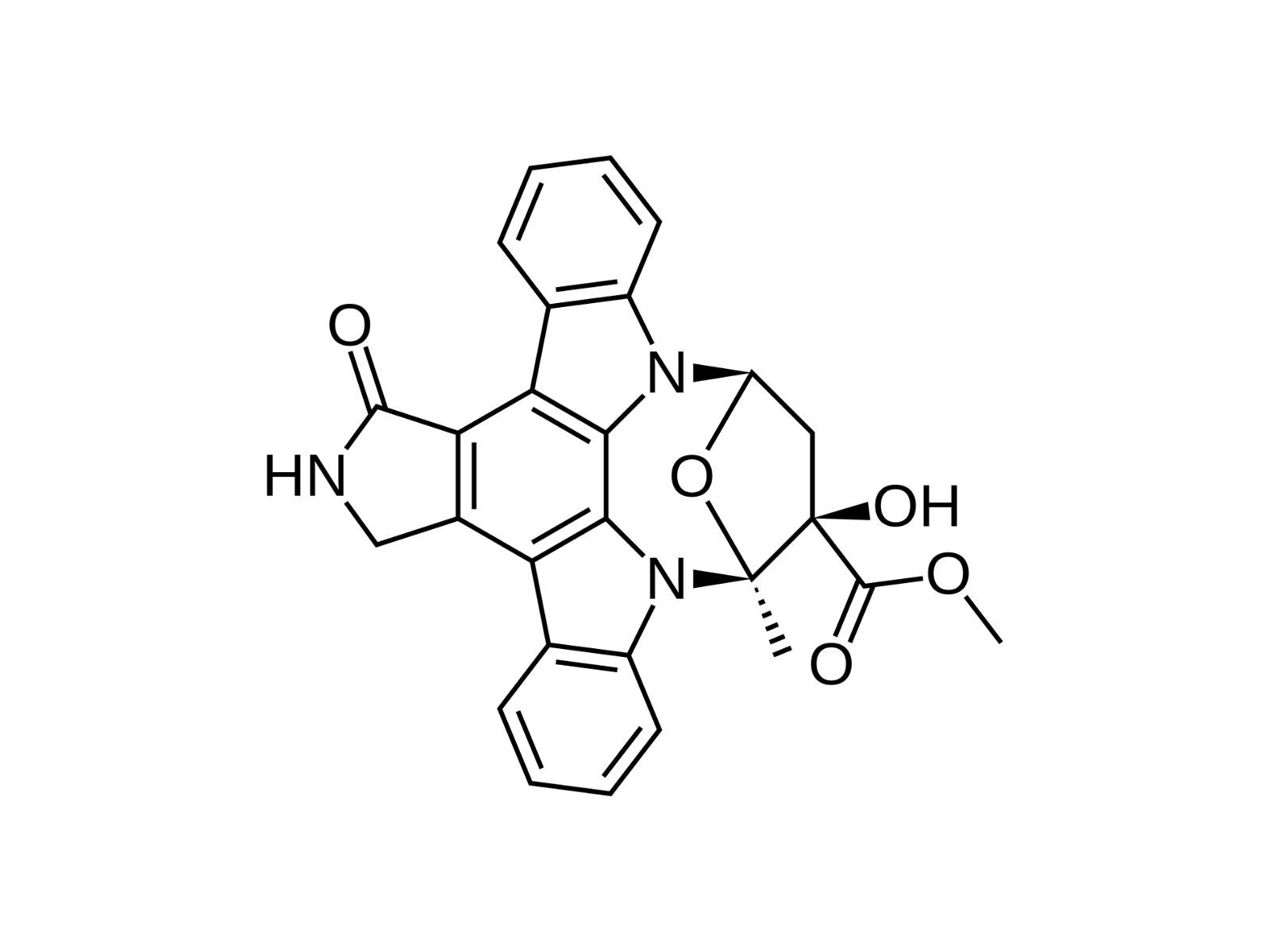
K252A is a fascinating compound with a range of applications in scientific research. What exactly is K252A? K252A is a potent, naturally occurring alkaloid that inhibits protein kinases, enzymes crucial for many cellular processes. This compound, originally isolated from the bacterium Nocardiopsis sp., has been a valuable tool in studying cell signaling pathways. Researchers have found it particularly useful in neuroscience, cancer research, and developmental biology. Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier makes it a unique candidate for neurological studies. Despite its benefits, handling K252A requires caution due to its high potency. Ready to dive into more intriguing facts about K252A? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- K252A is a powerful compound derived from bacteria, with potential applications in neuroscience, cancer research, and drug development. Its unique properties make it a valuable tool for studying and treating various diseases.
- Despite its challenges, K252A continues to intrigue researchers with its diverse biological activities and potential therapeutic applications. Future studies aim to overcome its limitations and harness its benefits for the benefit of human health.
What is K252A?
K252A is a fascinating compound with a range of biological activities. It has been widely studied for its potential applications in various fields, including neuroscience and cancer research. Here are some intriguing facts about K252A that highlight its significance.
- K252A is a natural product derived from the bacterium Nocardiopsis sp..
- It belongs to the class of compounds known as indolocarbazoles.
- K252A is known for its potent protein kinase inhibition properties.
- It was first isolated in the 1980s.
- K252A has a complex molecular structure, making it a subject of interest for chemists.
K252A in Neuroscience
K252A has shown promise in the field of neuroscience, particularly in the study of nerve growth and neuroprotection.
- K252A inhibits Trk receptors, which are crucial for nerve growth factor signaling.
- It has been used to study the mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases.
- K252A can cross the blood-brain barrier, making it useful for brain research.
- It has been shown to protect neurons from apoptosis (programmed cell death).
- K252A has potential therapeutic applications for Alzheimer's disease.
K252A in Cancer Research
Researchers have also explored the potential of K252A in cancer treatment due to its ability to inhibit certain cellular pathways.
- K252A inhibits protein kinase C (PKC), which is involved in cell proliferation.
- It has shown anti-tumor activity in various cancer cell lines.
- K252A can induce cell cycle arrest in cancer cells.
- It has been studied for its effects on glioblastoma, a type of brain cancer.
- K252A may enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy drugs.
Chemical Properties of K252A
Understanding the chemical properties of K252A helps in its application and synthesis.
- K252A has a molecular formula of C31H25N3O4.
- It has a molecular weight of 503.55 g/mol.
- K252A is relatively insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
- It has a melting point of approximately 250°C.
- K252A exhibits fluorescence, which is useful for certain types of imaging studies.
K252A in Drug Development
The unique properties of K252A make it a candidate for drug development in various therapeutic areas.
- K252A has been used as a lead compound for developing new kinase inhibitors.
- It has inspired the synthesis of analogues with improved properties.
- K252A derivatives are being explored for their selectivity and potency.
- It serves as a tool compound in pharmacological research.
- K252A has potential applications in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its potential, there are challenges associated with the use of K252A in research and therapy.
- K252A has limited bioavailability in vivo.
- Its toxicity at high concentrations poses a challenge for therapeutic use.
- K252A's complex synthesis makes it difficult to produce in large quantities.
- Researchers are working on modifying K252A to reduce its toxicity.
- Future studies aim to improve the delivery methods for K252A.
Interesting Tidbits
Here are some lesser-known facts about K252A that highlight its versatility and intrigue.
- K252A has been used in studies involving plant biology.
- It has applications in marine biology for studying marine organisms.
- K252A has been featured in biochemical assays for kinase activity.
- It has been used to study the mechanisms of cell differentiation.
- K252A continues to be a subject of intense research due to its diverse biological activities.
Final Thoughts on K252A
K252A is a fascinating compound with a wide range of applications in scientific research. Its ability to inhibit protein kinases makes it a valuable tool for studying cell signaling pathways. Researchers have used it to explore neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and other conditions. Despite its potential, handling K252A requires caution due to its potency and toxicity. Proper lab protocols and safety measures are essential when working with this compound. As science advances, K252A will likely continue to play a crucial role in uncovering new insights into cellular processes. Whether you're a seasoned researcher or just curious about biochemistry, understanding K252A's significance can deepen your appreciation for the complexities of life at the molecular level. Keep an eye on future studies involving this compound; they might just lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
