What is Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA)?
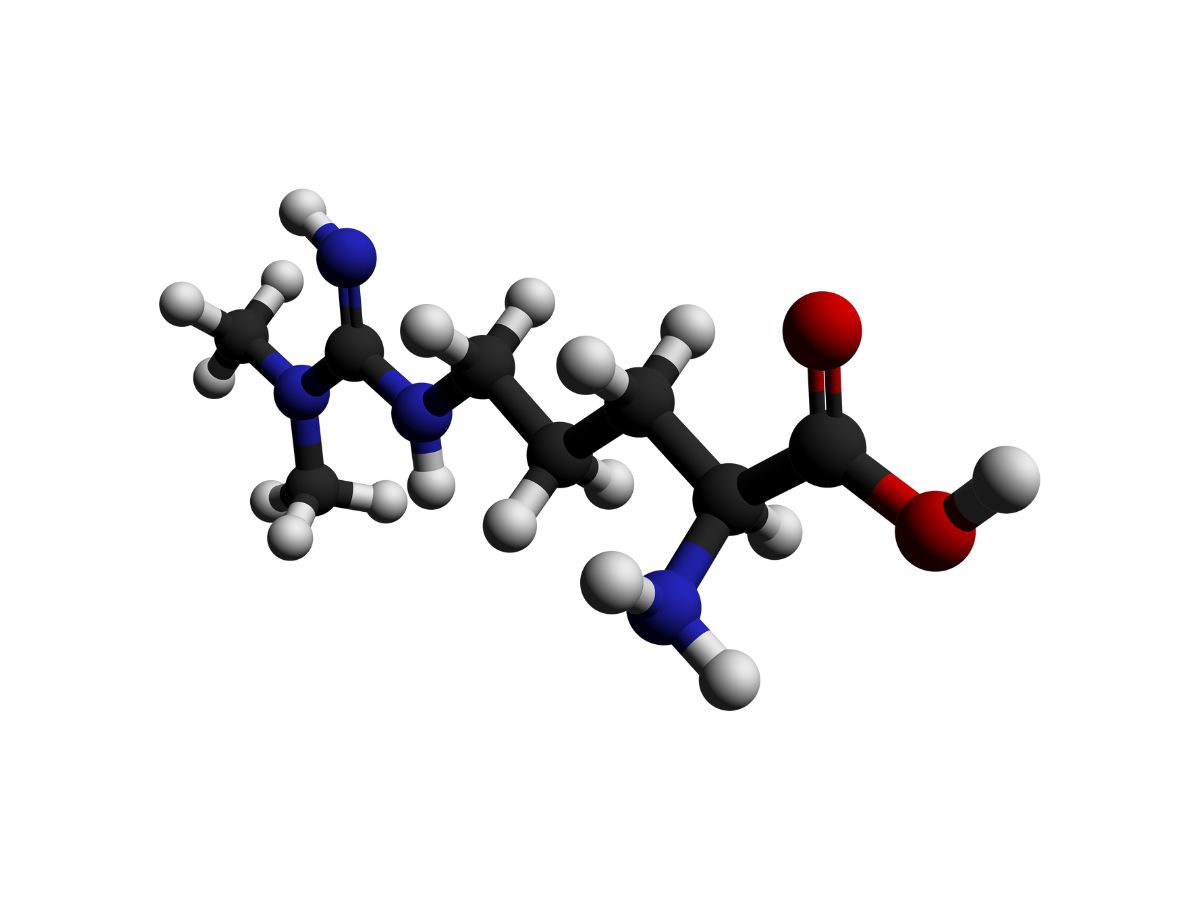
Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) is a naturally occurring chemical in the body that can affect blood vessel function. It’s a byproduct of protein metabolism and can interfere with nitric oxide production, which is crucial for blood flow regulation. Elevated levels of ADMA are linked to cardiovascular diseases, kidney problems, and other health issues. Understanding ADMA’s role can help in diagnosing and treating these conditions. This molecule is gaining attention in medical research due to its potential as a biomarker for various diseases. Let’s dive into 20 intriguing facts about ADMA that you might not know!
What is Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA)?
Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) is a naturally occurring chemical found in blood plasma. It plays a crucial role in regulating nitric oxide production, which is essential for blood vessel health. Here are some fascinating facts about ADMA.
-
ADMA is an amino acid derivative: It is formed from the breakdown of proteins in the body, specifically from the amino acid arginine.
-
Inhibits nitric oxide synthesis: ADMA competes with arginine to inhibit nitric oxide production, which can affect blood flow and pressure.
-
Linked to cardiovascular diseases: Elevated ADMA levels are associated with an increased risk of heart diseases, including hypertension and atherosclerosis.
-
Measured in blood tests: Doctors can measure ADMA levels through blood tests to assess cardiovascular health.
How ADMA Affects the Body
ADMA's influence extends beyond just the cardiovascular system. It impacts various bodily functions and processes. Here are some key effects of ADMA on the body.
-
Affects kidney function: High ADMA levels can impair kidney function, leading to chronic kidney disease.
-
Influences insulin resistance: Elevated ADMA is linked to insulin resistance, which can contribute to type 2 diabetes.
-
Impacts endothelial function: ADMA affects the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, which can lead to vascular diseases.
-
Role in aging: Increased ADMA levels are observed in aging individuals, potentially contributing to age-related diseases.
ADMA in Medical Research
ADMA is a significant focus in medical research due to its implications for various health conditions. Here are some insights from recent studies.
-
Biomarker for cardiovascular risk: ADMA is considered a biomarker for assessing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
-
Potential therapeutic target: Researchers are exploring ways to lower ADMA levels as a potential treatment for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
-
Genetic factors: Genetic variations can influence ADMA levels, affecting an individual's susceptibility to certain diseases.
-
ADMA and pregnancy: Elevated ADMA levels during pregnancy are linked to complications such as preeclampsia.
Reducing ADMA Levels
Managing ADMA levels can have significant health benefits. Here are some strategies to reduce ADMA levels.
-
Healthy diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower ADMA levels.
-
Regular exercise: Physical activity improves nitric oxide production, which can counteract the effects of ADMA.
-
Medications: Certain medications, such as statins and ACE inhibitors, can reduce ADMA levels.
-
Supplements: Supplements like L-arginine and L-citrulline may help lower ADMA by increasing nitric oxide production.
Interesting Facts About ADMA
Beyond its medical significance, ADMA has some intriguing aspects worth noting.
-
Discovered in the 1990s: ADMA was first identified in the early 1990s, making it a relatively recent discovery in medical science.
-
Present in all humans: Every person has ADMA in their bloodstream, but levels vary based on health and lifestyle factors.
-
Environmental factors: Pollution and exposure to certain chemicals can increase ADMA levels.
-
Potential for new treatments: Ongoing research into ADMA could lead to new treatments for a variety of diseases, improving overall health outcomes.
The Final Word on Asymmetric Dimethylarginine
Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) plays a crucial role in our bodies, acting as a natural inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis. Elevated ADMA levels can indicate cardiovascular issues, making it a valuable biomarker for heart health. Understanding ADMA's function helps in early detection and prevention of heart diseases.
Research continues to uncover more about ADMA's impact on health, offering potential new treatments and diagnostic tools. Keeping an eye on ADMA levels could become a routine part of health check-ups in the future.
Incorporating this knowledge into daily life can lead to better health outcomes. Stay informed and proactive about heart health by understanding the significance of ADMA.
That’s the scoop on ADMA. Keep this info in mind, and you’ll be better equipped to manage your heart health.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.