The concept of trophic levels is a fundamental principle in ecological studies, providing insights into the intricate dynamics of food chains and energy transfer within ecosystems. Understanding trophic levels is key to comprehending the complex interactions between organisms and the flow of nutrients through different levels of a food web. It helps scientists assess the stability and sustainability of ecosystems and predict the potential impacts of disturbances or environmental changes.
In this article, we will dive into the enigmatic world of trophic levels and explore eight fascinating facts that shed light on their significance in the intricate web of life. From the concept’s origins to its implications for biodiversity and ecological balance, we will uncover the mysteries behind trophic levels and how they shape the dynamics of ecosystems.
Key Takeaways:
- Trophic levels show how energy moves through an ecosystem, from plants to animals. Only 10% of energy is passed on, and decomposers play a vital role in recycling nutrients.
- Human actions can disrupt trophic levels, affecting the whole ecosystem. Understanding these interactions is crucial for protecting nature’s balance.
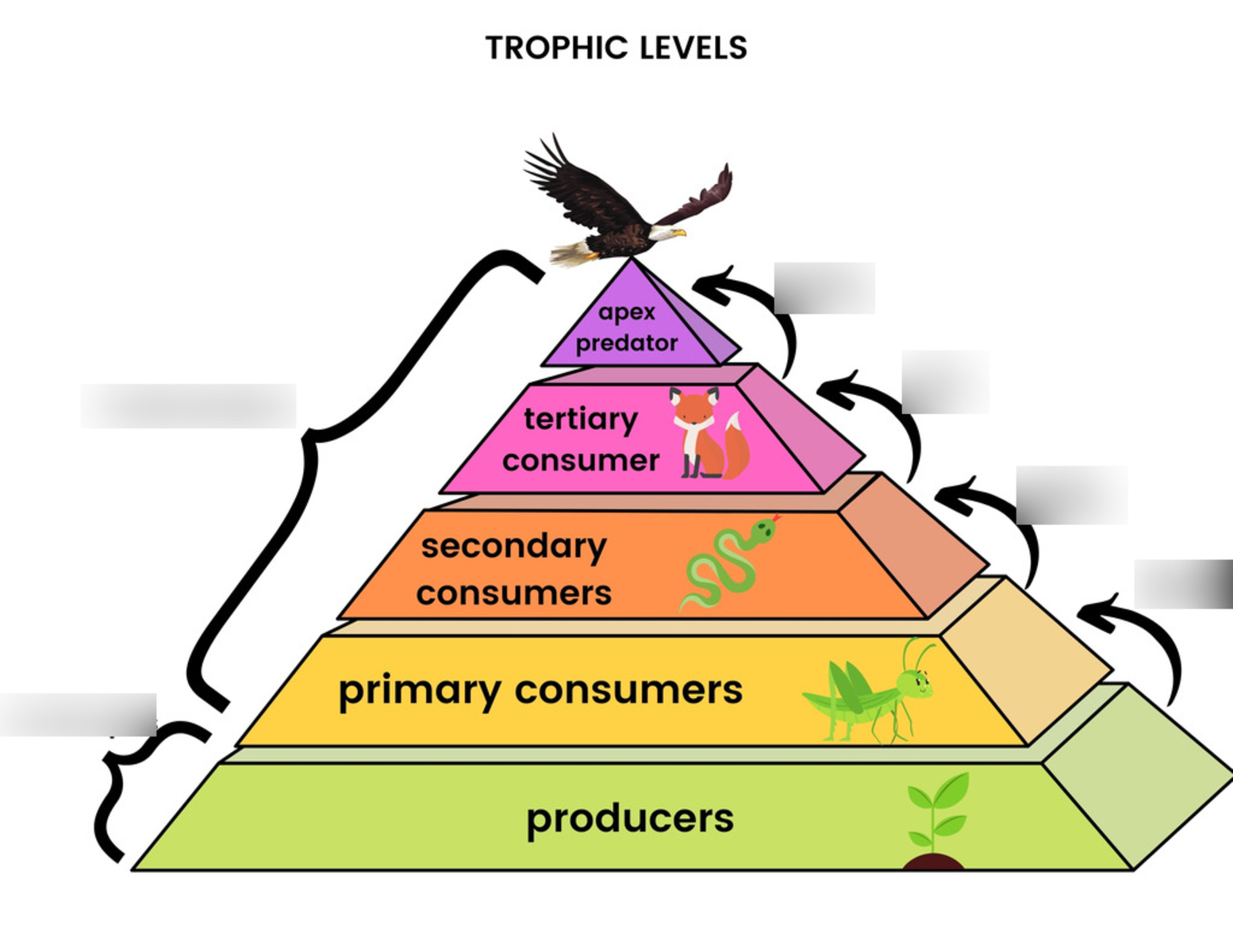
What is a Trophic Level?
A trophic level refers to the position of an organism in a food chain or web. It represents the feeding relationship and energy transfer between different organisms within an ecosystem. These levels can be categorized into primary producers, herbivores, primary carnivores, secondary carnivores, and so on.
The Flow of Energy
One of the key aspects of trophic levels is the flow of energy. Energy enters an ecosystem through the primary producers, such as plants or algae, who convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred from one trophic level to the next as organisms consume and are consumed by others.
The 10% Rule
The 10% rule is a fundamental concept in trophic levels. It states that only about 10% of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. This is due to energy losses through metabolic processes and heat. As a result, the higher the trophic level, the less energy is available.
The Role of Decomposers
Decomposers play a crucial role in trophic levels by breaking down organic matter and returning nutrients back into the ecosystem. They feed on dead plants and animals, effectively recycling the nutrients and allowing them to be reused by primary producers.
Trophic Cascade Effects
Trophic cascades occur when there is a disruption or change in one trophic level that impacts the entire ecosystem. For example, the removal of top predators can lead to an increase in herbivore populations, which in turn can negatively affect primary producers and alter the structure of the ecosystem.
Human Impact on Trophic Levels
Human activities, such as overfishing and habitat destruction, can have significant effects on trophic levels. By removing certain species or disrupting the balance, it can lead to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. Understanding these impacts is crucial for conservation and sustainable management of natural resources.
Trophic Efficiency
Trophic efficiency measures the amount of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next. It is typically low, averaging around 10%. This inefficiency is due to energy loss through respiration, excretion, and incomplete digestion. It highlights the challenges organisms face in acquiring sufficient energy to survive and reproduce.
The Complexity of Trophic Interactions
Trophic interactions within an ecosystem are highly complex. They involve not only direct feeding relationships but also indirect interactions and feedback loops. Changes in one trophic level can have ripple effects throughout the food web, shaping the dynamics and stability of the entire system.
Overall, the 8 enigmatic facts about trophic levels highlight the intricate web of energy flow and interactions within ecosystems. Understanding these concepts is essential for studying and protecting the balance of nature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, trophic levels play a crucial role in understanding the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem. They provide insight into the complex interactions between different organisms and their reliance on one another for survival. The eight enigmatic facts about trophic levels presented in this article shed light on the fascinating intricacies of the food chain and highlight the interconnectedness of all living organisms.From the fascinating phenomenon of biomagnification, where toxins become more concentrated as they move up the trophic levels, to the intriguing concept of keystone species that have disproportionate effects on the entire ecosystem, these facts remind us of the delicate balance that exists in nature. Understanding and studying trophic levels not only deepens our knowledge of the natural world but also helps us make informed decisions about conservation and preserving biodiversity.By exploring these enigmatic facts, we can appreciate the intricate web of life that exists within our planet and recognize the importance of maintaining the delicate equilibrium of trophic levels for the well-being of all organisms.
FAQs
1. What are trophic levels?
Trophic levels refer to the different positions in a food chain or food web where organisms obtain their energy. They represent the transfer of energy and nutrients from one organism to another.
2. How many trophic levels are there?
The number of trophic levels can vary depending on the complexity of the ecosystem. Generally, there are four to five trophic levels, including producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and sometimes quaternary consumers.
3. What is the significance of trophic levels?
Trophic levels help us understand the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem. They provide insight into the interactions between organisms and their reliance on one another for survival. Studying trophic levels is crucial for understanding the stability and functioning of ecosystems.
4. What is biomagnification?
Biomagnification refers to the process where certain pollutants or toxins become more concentrated as they move up the food chain. Organisms at higher trophic levels end up with higher levels of these substances, posing a risk to their health and the health of the entire ecosystem.
5. What are keystone species?
Keystone species are organisms that have a disproportionately large impact on the structure and function of an ecosystem. Their removal can lead to significant changes in the ecosystem’s dynamics, highlighting their crucial role in maintaining biodiversity.
6. How do trophic levels impact biodiversity?
Trophic levels are essential for maintaining biodiversity. Each trophic level relies on the one below it for energy and nutrients, creating a balance in the ecosystem. Disruptions in trophic levels can lead to cascading effects and affect the overall diversity of the ecosystem.
7. Are trophic levels the same in every ecosystem?
No, trophic levels can vary in different ecosystems. Factors such as the availability of resources, predation patterns, and the presence of keystone species can influence the number and complexity of trophic levels within an ecosystem.
8. How can studying trophic levels benefit conservation efforts?
Understanding trophic levels helps identify key species and their importance in maintaining ecosystem stability. This knowledge is crucial for making informed decisions about conservation strategies and preserving biodiversity.
Trophic levels play a crucial role in understanding ecosystems, but there's still much to learn. Delving deeper into the complexities of trophic levels reveals even more intriguing facts waiting to be explored. Food webs showcase intricate relationships between organisms, while energy flow through ecosystems follows fascinating patterns. Unraveling these ecological concepts provides valuable insights into the delicate balance of our natural world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
