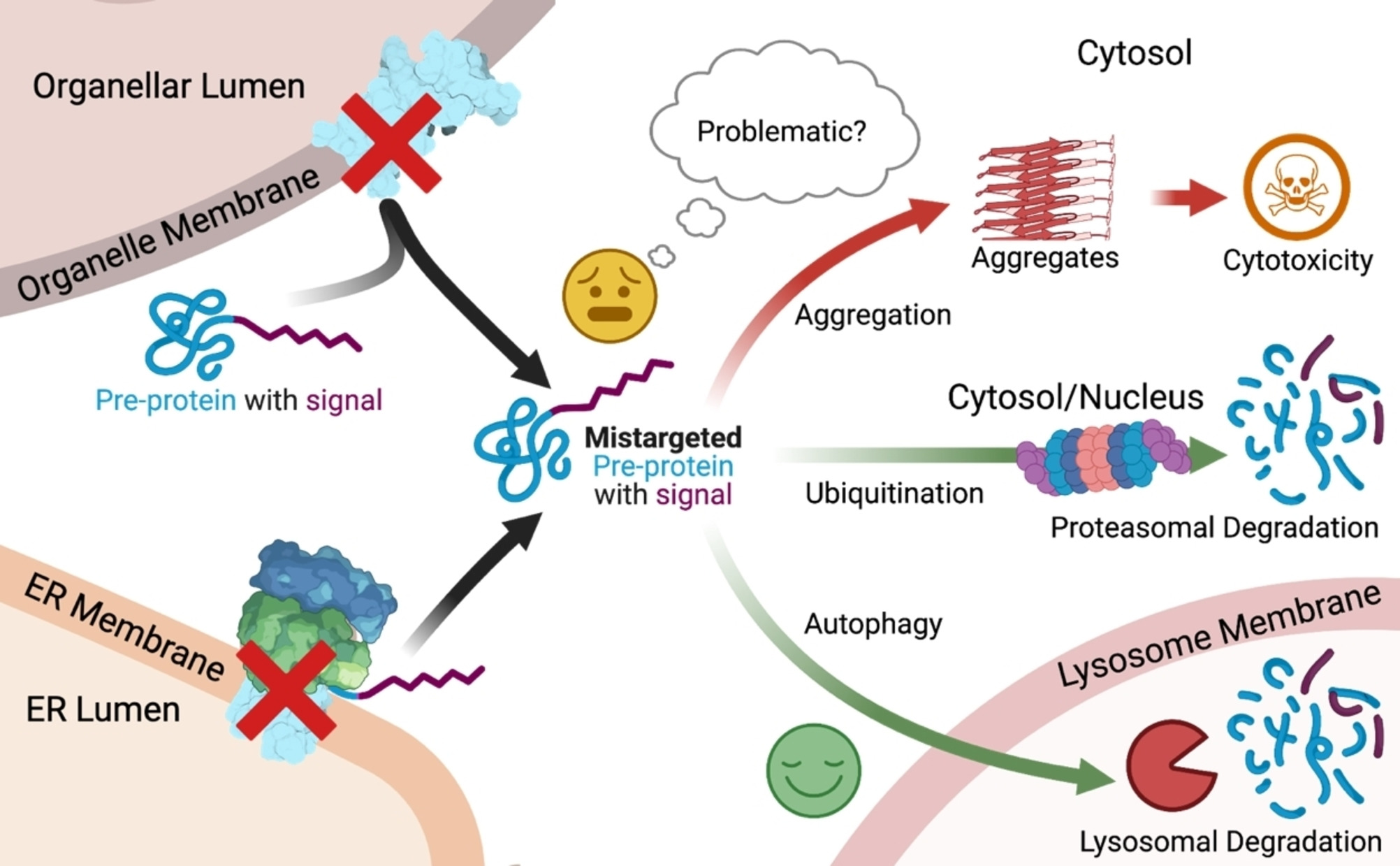
Protein trafficking, also known as intracellular protein transport, is a fascinating process that plays a vital role in maintaining the proper functioning of cells. This intricate system involves the movement of proteins within and between different cellular compartments, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Protein trafficking not only ensures the delivery of proteins to their intended destinations but also regulates various cellular processes, including signal transduction, metabolism, and immune response.
In this article, we will explore 19 captivating facts about protein trafficking that highlight the complexity and importance of this cellular mechanism. From the discovery of protein transport pathways to the role of specific proteins in trafficking, we will delve into the fascinating world of intracellular protein movement. So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on this exciting journey into the realm of protein trafficking!
Key Takeaways:
- Protein trafficking is like a delivery system inside our cells, making sure proteins go where they’re needed. It’s crucial for keeping our cells healthy and working properly.
- Scientists study protein trafficking to understand how cells function and to develop new treatments for diseases like Alzheimer’s and cystic fibrosis. It’s like solving a puzzle to help people stay healthy.
Protein trafficking is essential for cellular organization and function.
Protein trafficking plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by ensuring that proteins are delivered to their intended destinations in the cell.
Proteins are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
The ER acts as the starting point for protein trafficking, where proteins are synthesized and undergo post-translational modifications.
Protein trafficking involves various transport vesicles.
Transport vesicles, small membrane-bound sacs, act as “shuttles” that carry proteins between different cellular compartments.
The Golgi apparatus acts as a central hub for protein trafficking.
Proteins arriving from the ER are processed and sorted in the Golgi apparatus before being directed to their final destinations.
Protein trafficking occurs through different pathways.
There are two main pathways of protein trafficking: the constitutive secretory pathway and the regulated secretory pathway.
Protein trafficking is highly regulated.
Cells employ elaborate mechanisms to ensure that proteins are directed to the right place at the right time, preventing errors and maintaining cellular integrity.
Protein trafficking is involved in signal transduction.
Proteins involved in signaling pathways are transported to the cell membrane or specific organelles, allowing for efficient communication within the cell.
Protein trafficking is crucial for immune system function.
The proper trafficking of immune-related proteins is vital for immune cell development, antigen presentation, and immune response regulation.
Viruses can hijack protein trafficking machinery.
Some viruses exploit protein trafficking pathways to facilitate their replication and evasion of the immune system.
Protein trafficking abnormalities are linked to various diseases.
Disruptions in protein trafficking have been associated with neurodegenerative disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancer.
Protein trafficking occurs in all eukaryotic cells.
From simple yeast to complex human cells, protein trafficking is a universal process essential for cell survival.
Protein trafficking can be spatially and temporally regulated.
Certain signals and cellular cues can modulate protein trafficking, allowing for dynamic control over protein localization.
Protein trafficking defects can lead to protein accumulation.
Impaired trafficking can result in the buildup of misfolded or damaged proteins, leading to cellular dysfunction and diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Protein trafficking can be influenced by environmental factors.
Changes in temperature, pH levels, and stress conditions can impact the efficiency of protein trafficking, affecting cell survival.
Protein trafficking is involved in synaptic plasticity.
During synaptic plasticity, the process by which neural connections are strengthened or weakened, protein trafficking is crucial for the delivery of receptors and signaling molecules to synapses.
Protein trafficking plays a role in embryonic development.
Proper protein trafficking is vital for embryogenesis, ensuring the right proteins are delivered to the right locations during critical stages of development.
Protein trafficking is a dynamic process.
Proteins can be continuously shuttled between different compartments in response to cellular needs and environmental changes.
Protein trafficking can be modulated by post-translational modifications.
Modifications such as phosphorylation and ubiquitination can regulate protein trafficking, influencing protein stability and localization.
Protein trafficking research has led to therapeutic advancements.
Understanding protein trafficking mechanisms has paved the way for the development of targeted therapies for various diseases, including cystic fibrosis and lysosomal storage disorders.
Protein trafficking is a fascinating field of study that continues to unravel the intricacies of cellular biology. From its essential role in maintaining cellular function to its implications in disease, the study of protein trafficking opens doors to new therapeutic strategies and a deeper understanding of the building blocks of life.
Conclusion
The process of protein trafficking is a fascinating and complex mechanism that plays a crucial role in maintaining the proper functioning of cells. Through intricate pathways and signaling mechanisms, proteins are directed to their intended destinations within the cell, enabling them to perform their specific functions.The study of protein trafficking has provided valuable insights into various biological processes, including development, signal transduction, and disease progression. Understanding the intricacies of protein trafficking not only helps advance our knowledge of fundamental cellular processes but also opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions.Continued research in this field promises to unveil even more captivating insights into the dynamic world of protein trafficking, shedding light on the inner workings of cells and driving advancements in numerous scientific disciplines.
FAQs
1. What is protein trafficking?
Protein trafficking is the process by which proteins are transported to their specific destinations within a cell. It involves various mechanisms, including vesicular transport, protein sorting, and signal recognition.
2. Why is protein trafficking important?
Protein trafficking is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and proper functioning. It ensures that proteins are delivered to their intended locations, allowing them to carry out their specific functions in different cellular compartments.
3. How are proteins targeted for trafficking?
Proteins are targeted for trafficking through the presence of specific targeting signals or motifs within their amino acid sequences. These signals can be recognized by various trafficking machinery and direct the proteins to their designated compartments.
4. What are the different pathways involved in protein trafficking?
There are several pathways involved in protein trafficking, including the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to Golgi apparatus pathway, endocytic pathway, secretory pathway, and retrograde pathway. Each pathway serves a specific purpose in delivering proteins to their appropriate destinations.
5. Can protein trafficking be disrupted?
Yes, disruptions in protein trafficking can lead to various diseases and disorders. Inefficient or incorrect trafficking of proteins can result in cellular dysfunction, impaired signal transduction, and the development of pathological conditions.
6. What techniques are used to study protein trafficking?
Researchers use various techniques to study protein trafficking, including fluorescence microscopy, live-cell imaging, molecular biology approaches, and biochemical assays. These tools enable scientists to visualize and track the movement of proteins within cells.
7. Are there any therapeutic implications of studying protein trafficking?
Yes, studying protein trafficking has significant therapeutic implications. Understanding how proteins are trafficked within cells can help in developing targeted therapies for diseases associated with trafficking defects, such as certain types of cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Protein trafficking's captivating facts reveal its crucial role in cellular organization, disease development, and therapeutic advancements. From synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum to transport via vesicles and the Golgi apparatus, protein trafficking is a highly regulated, dynamic process essential for immune function, signal transduction, and embryonic development. Environmental factors and post-translational modifications can influence this intricate process, while abnormalities may lead to protein accumulation and various diseases. Exploring the complexities of protein trafficking and sorting further illuminates its significance in biological processes and potential for groundbreaking discoveries.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
