When studying the vast world of biology, one concept that stands out as both fascinating and essential is the phylogenetic tree. This branching diagram displays the evolutionary relationships between different species, offering a visual representation of the history of life on Earth. Not only does the phylogenetic tree provide insights into how various organisms are connected, but it also helps scientists uncover crucial information about their shared traits, genetic sequences, and common ancestors.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of phylogenetic trees and uncover 18 fascinating facts about them. From their origins to their significance in understanding biodiversity, these facts will shed light on the importance of phylogenetic trees in the field of biology. So, let’s embark on this captivating journey through the branches of the phylogenetic tree and explore the wondrous discoveries it holds.
Key Takeaways:
- Phylogenetic trees show how all living things are connected, like a big family tree. They help scientists understand the history and relationships between different organisms, from tiny bacteria to giant whales.
- By studying phylogenetic trees, scientists can learn about the spread of diseases, protect endangered species, and uncover the mysteries of evolution. These tree diagrams reveal the beauty and unity of life on Earth.
The Origin of Phylogenetic Tree
The concept of phylogenetic trees dates back to the mid-19th century when Charles Darwin first proposed the idea of common ancestry among species. Through the study of comparative anatomy and genetics, scientists developed the method of representing evolutionary relationships through tree-like diagrams.
What is a Phylogenetic Tree?
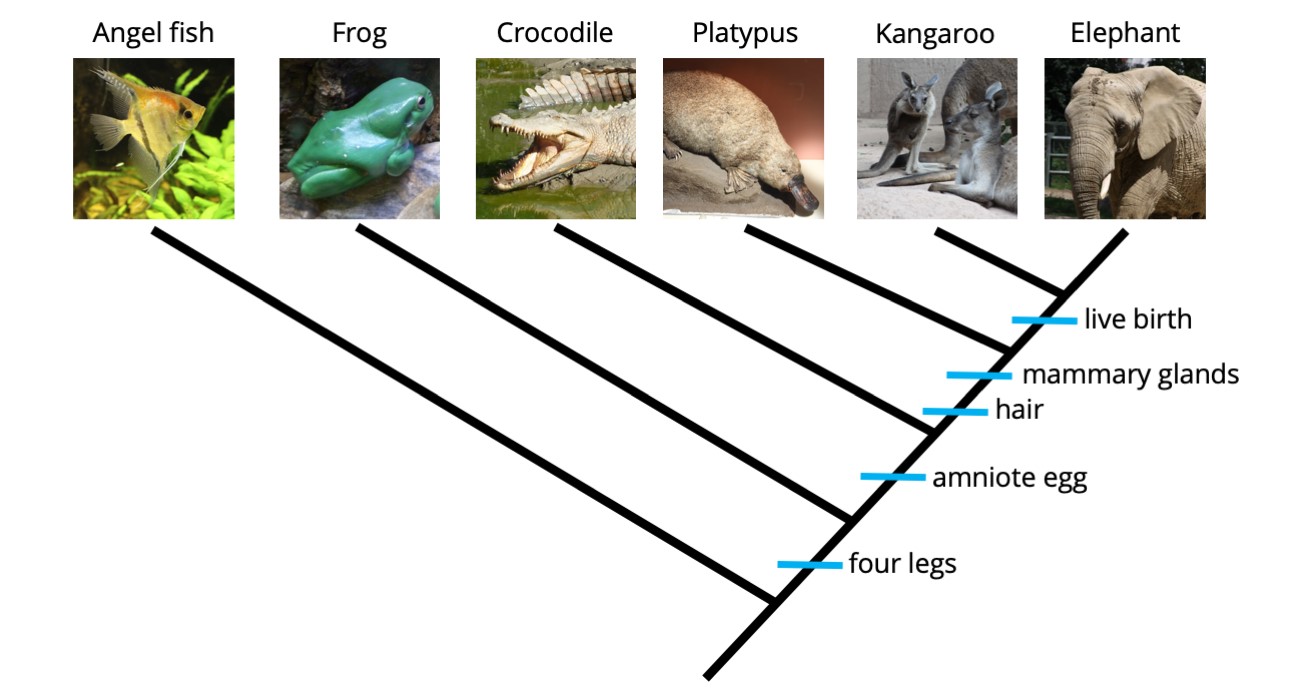
A phylogenetic tree is a visual representation of the evolutionary history and relationships between different organisms. It showcases the branching pattern of descent from a common ancestor, with each branch representing a distinct lineage.
The Tree of Life
The famous “Tree of Life” is a phylogenetic tree that aims to illustrate the evolutionary connections between all living organisms on Earth. It showcases the remarkable diversity of life and provides insights into the origins and relationships between species.
Branches and Nodes
In a phylogenetic tree, branches represent the evolutionary pathways, while nodes indicate common ancestors. The length of the branches often reflects the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred over time.
Cladistics and Phylogenetic Analysis
Phylogenetic trees are constructed using a method called cladistics, which groups species based on shared characteristics. Phylogenetic analysis involves comparing and analyzing specific traits or genetic markers to determine evolutionary relationships.
Fossils and Phylogenetic Trees
Fossils play a crucial role in constructing phylogenetic trees by providing evidence of extinct species and their relationship to living organisms. Fossil records help scientists piece together the puzzle of evolutionary history.
Molecular Clocks
Molecular clocks are used in phylogenetic analysis to estimate the timing of evolutionary events. By comparing DNA sequences or protein structures, scientists can determine the rate of genetic change and infer the divergence time between species.
Phylogenetics and Biogeography
Phylogenetic trees can also shed light on the distribution of species across different geographic regions. By mapping evolutionary relationships onto geographical maps, scientists can uncover patterns of speciation and migration.
Taxonomy and Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees have revolutionized the field of taxonomy by providing a robust framework for classifying and naming organisms. The hierarchical structure of the tree allows for a more systematic and accurate categorization of species.
Phylogenetic Trees in Medicine
Phylogenetic analysis is not limited to studying the evolution of species. It also plays a crucial role in understanding the spread of diseases and designing targeted treatment strategies.
Limitations of Phylogenetic Trees
While phylogenetic trees are powerful tools, they have certain limitations. Factors such as incomplete fossil records, horizontal gene transfer, and convergent evolution can complicate the accurate representation of evolutionary relationships.
Phylogenetic Trees and Conservation
Phylogenetic trees provide valuable insights into the conservation of biodiversity. By identifying species that are evolutionarily distinct or at risk of extinction, conservation efforts can be targeted more effectively.
The Tree-Thinking Concept
The concept of “tree-thinking” refers to the shift in perspective that phylogenetic trees bring to our understanding of evolution. It emphasizes the interconnectedness and shared history of all living organisms.
Phylogenetics and Evolutionary Biology
Phylogenetic trees are central to the field of evolutionary biology. They enable scientists to study patterns of speciation, identify key evolutionary events, and unravel the mysteries of life’s history.
Phylogenetic Inference Methods
There are various methods for inferring phylogenetic trees, including Maximum Likelihood, Bayesian Inference, and Neighbor-Joining. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and researchers choose the most appropriate approach based on their data and research questions.
The Power of DNA Sequencing
The advent of DNA sequencing technology has revolutionized the field of phylogenetics. DNA sequences provide a wealth of information for constructing accurate and detailed phylogenetic trees.
The Complexity of Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees can be incredibly complex, especially when dealing with large-scale studies or diverse groups of organisms. Advanced computational tools and algorithms are used to analyze and interpret these intricate evolutionary relationships.
The Beauty and Wonder of Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees not only provide a scientific understanding of life’s evolutionary history, but they also reflect the beauty and interconnectedness of our natural world. They remind us of the incredible diversity and unity of life on Earth.
Conclusion
The phylogenetic tree is an invaluable tool that helps us understand the evolutionary relationships between different species. It provides a visual representation of how organisms are related to one another, allowing us to trace their ancestry back in time. Through the study of phylogenetic trees, scientists can unravel the complex web of life on Earth and gain insights into evolutionary processes.By analyzing the branches, nodes, and patterns in a phylogenetic tree, researchers can make predictions about common ancestors, identify shared traits, and classify organisms into distinct groups. This information is crucial for fields like evolutionary biology, systematics, and conservation.As we continue to uncover more about our planet’s biodiversity, phylogenetic trees will play a central role in organizing and interpreting this knowledge. With advancements in genetic sequencing and computational methods, our understanding of the Tree of Life will deepen, providing us with a clearer picture of how all life forms are interconnected.In summary, the study of phylogenetic trees not only sheds light on the origins and relationships of different species but also helps us appreciate the vast diversity of life that exists on our planet.
FAQs
Q: What is a phylogenetic tree?
A: A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships between different species or groups of organisms. It shows the common ancestors and the branches that lead to different descendants. Q: How are phylogenetic trees constructed?
A: Phylogenetic trees are constructed using various methods, including genetic data analysis, morphological comparisons, and fossil records. These methods help scientists identify similarities and differences between organisms to determine their evolutionary relatedness. Q: Why are phylogenetic trees important?
A: Phylogenetic trees are crucial for understanding evolutionary history, biodiversity, and the classification of organisms. They provide insights into how species have evolved and how they are connected through common ancestors. Q: Can phylogenetic trees change over time?
A: Yes, phylogenetic trees are not static and can be modified as new evidence and data become available. With advancements in technology and research, our understanding of evolutionary relationships can evolve and lead to updates in the tree’s structure. Q: What is the significance of nodes in a phylogenetic tree?
A: Nodes in a phylogenetic tree represent common ancestors from which different species or groups diverged. The closer the nodes are to each other, the more recent the common ancestor. Q: How can I interpret a phylogenetic tree?
A: To interpret a phylogenetic tree, look for the branching patterns, lengths of branches, and the position of organisms or groups on the tree. These factors indicate relationships, time of divergence, and evolutionary distance.
Phylogenetic trees reveal fascinating evolutionary relationships, but there's more to explore in the captivating world of biology. Dive into the intricacies of systematics, where organisms are classified based on shared characteristics. Uncover the secrets of life at its most fundamental level with molecular biology, from DNA to proteins. Don't forget about the cutting-edge field of bioinformatics, which combines computer science and biology to analyze vast amounts of biological data. Each area offers a unique perspective on the incredible diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
