Alpha diversity is a fascinating concept that plays a crucial role in the field of biology. It refers to the measure of biodiversity within a specific area or habitat. Understanding alpha diversity provides valuable insights into the variety and abundance of species in a given ecosystem, shedding light on its overall health and functioning.
In this article, we will delve into 17 unbelievable facts about alpha diversity that will showcase the incredible diversity of life on our planet. From the vast array of species found in a single drop of water to the surprising factors that influence alpha diversity, these facts will leave you in awe of the intricate web of life that surrounds us.
Key Takeaways:
- Alpha diversity measures the variety of species in an ecosystem, impacting its stability and functioning. It’s influenced by climate, habitat, and human activities, making it crucial for conservation and understanding our natural world.
- The Amazon Rainforest holds the highest alpha diversity, showcasing the incredible richness of life. Understanding and preserving alpha diversity is vital for sustaining the diversity of life on Earth and ensuring the well-being of our planet.
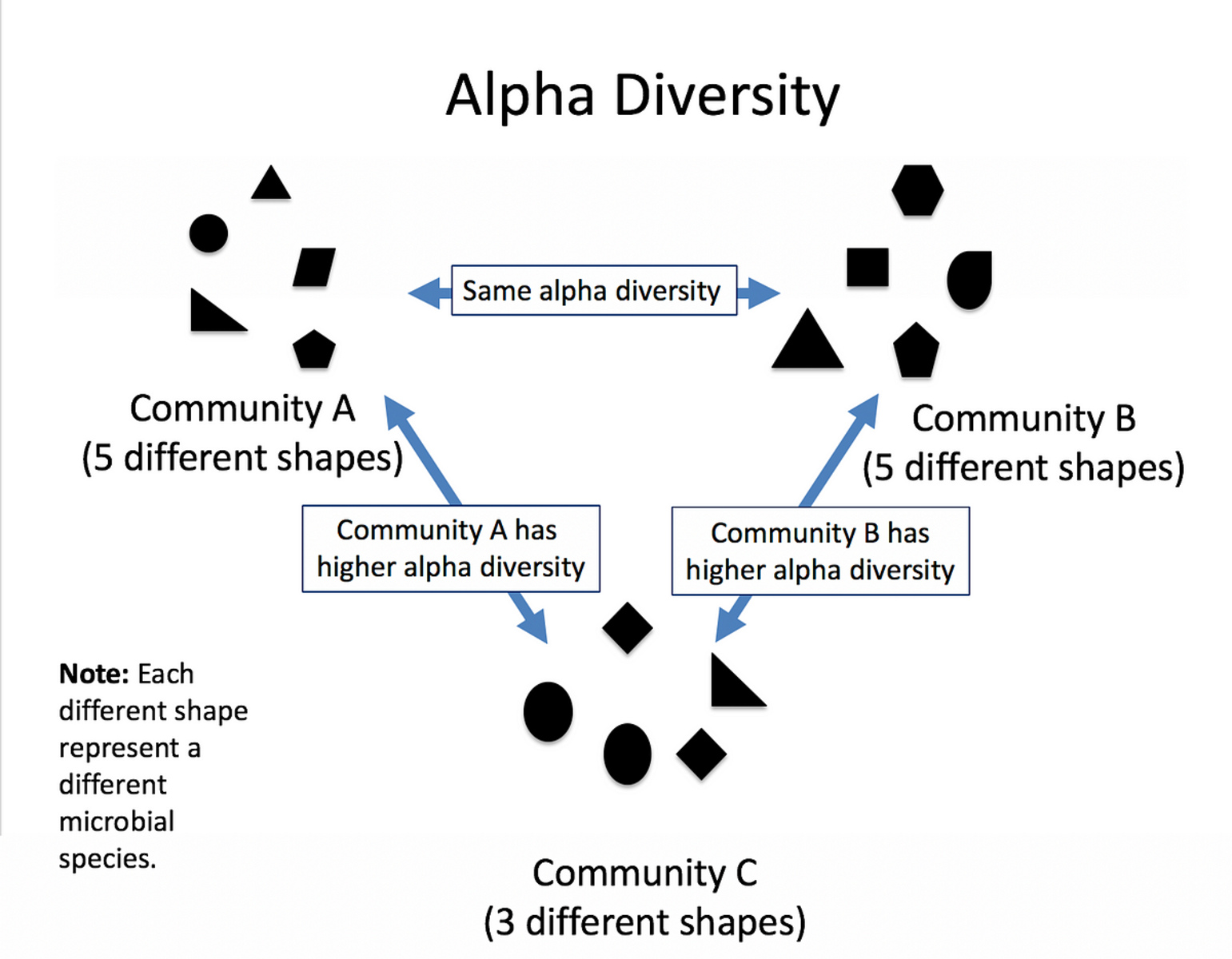
Alpha diversity is a measure of species diversity within a particular habitat or ecosystem.
This metric takes into account the number of different species present and their relative abundance, providing insights into the overall biodiversity of the system.
Alpha diversity can vary significantly across different ecosystems.
A tropical rainforest, for example, may exhibit higher levels of alpha diversity compared to a desert due to its favorable climate and abundance of resources.
The Amazon Rainforest boasts the highest alpha diversity on the planet.
With an estimated 40,000 plant species and countless animal species, this megadiverse ecosystem is unparalleled in terms of its richness and variety of life.
Alpha diversity is influenced by various factors such as climate, habitat complexity, and geographic location.
Warmer climates and diverse topography often contribute to higher alpha diversity by providing a wide range of niches for species to occupy.
Alpha diversity plays a vital role in ecosystem functioning and stability.
A diverse community of species ensures essential ecosystem processes such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control.
Alpha diversity can be measured using various indices, including the Simpson’s Diversity Index and the Shannon-Wiener Diversity Index.
These indices take into account both the number of species present and their evenness in the community.
Alpha diversity provides valuable information for conservation efforts.
By understanding the distribution and abundance of species within an ecosystem, conservationists can develop strategies to protect endangered species and preserve biodiversity hotspots.
Species richness is an essential component of alpha diversity.
It refers to the total number of different species present in a habitat and is a fundamental measure of biodiversity.
Alpha diversity can be studied at different scales, from small plots of land to entire continents.
Scientists can analyze the patterns of species diversity and identify ecological patterns and processes operating within and across ecosystems.
Human activities, such as habitat destruction and pollution, can significantly impact alpha diversity.
As we continue to encroach on natural habitats and disrupt ecosystems, we disrupt the delicate balance of species interactions and reduce biodiversity.
Alpha diversity can contribute to the discovery of new species.
Exploring areas with high alpha diversity often leads to the identification of previously unknown species, highlighting the importance of preserving diverse habitats.
Alpha diversity can be enhanced by ecosystem restoration efforts.
By restoring degraded habitats and reintroducing native species, we can promote the recovery of alpha diversity and increase overall ecosystem resilience.
The loss of alpha diversity can have cascading effects on ecosystem functioning.
When keystone species or crucial ecological interactions are lost, it can disrupt the balance of the entire ecosystem and lead to the decline of other species.
Alpha diversity can have economic benefits.
Healthy ecosystems with high alpha diversity can support industries such as ecotourism and provide valuable ecosystem services.
Alpha diversity is not limited to terrestrial ecosystems.
Oceans and freshwater systems also exhibit high levels of alpha diversity, with coral reefs and tropical rainforests being particularly rich in species.
Alpha diversity has a positive correlation with ecosystem productivity.
More diverse ecosystems tend to be more productive in terms of biomass production and carbon sequestration.
Alpha diversity is constantly evolving.
Natural processes such as speciation, adaptation, and extinction contribute to the dynamic nature of alpha diversity over both short and long timescales.
These 17 unbelievable facts about alpha diversity showcase the incredible complexity and importance of biodiversity in shaping our natural world. From the dense rainforests of the Amazon to the vast oceans, understanding and preserving alpha diversity is essential for the well-being of our planet and future generations.
So, next time you explore a natural habitat or learn about different species, remember the wonders of alpha diversity and its role in sustaining the diversity of life on Earth.
Conclusion
Alpha diversity is a fascinating aspect of biology that provides invaluable insights into the variety and abundance of species within a specific ecosystem. In this article, we have uncovered 17 unbelievable facts about alpha diversity.
We have learned that alpha diversity is often measured using indices such as the Shannon index and Simpson’s index, which take into account both species richness and evenness. These indices allow scientists to compare the diversity of different habitats or track changes in diversity over time.
We have also discovered that alpha diversity can vary greatly across different ecosystems, with some habitats harboring a rich array of species while others may be relatively low in diversity. Factors such as climate, habitat complexity, and human activities can influence alpha diversity.
Furthermore, alpha diversity plays a crucial role in ecosystem stability and functioning. High alpha diversity is often associated with increased ecosystem resilience, as diverse communities are better able to adapt to environmental changes and maintain essential ecological processes.
Overall, studying alpha diversity allows us to better understand the intricate web of life on our planet and underscores the need for conservation efforts to protect and preserve Earth’s incredible biodiversity.
FAQs
Q: What is alpha diversity?
A: Alpha diversity refers to the diversity of species within a particular habitat or ecosystem. It takes into account both the number of different species present (species richness) and the relative abundance of each species (species evenness).
Q: How is alpha diversity measured?
A: Alpha diversity is typically measured using various indices, such as the Shannon index and Simpson’s index. These indices provide a quantitative measure of diversity by incorporating both species richness and evenness into their calculations.
Q: What factors can influence alpha diversity?
A: Alpha diversity can be influenced by a range of factors, including climate, habitat complexity, and human activities. Different ecosystems may have varying levels of alpha diversity due to differences in these factors.
Q: Why is alpha diversity important?
A: Alpha diversity is important because it plays a key role in ecosystem stability and functioning. High alpha diversity is often associated with increased ecosystem resilience, as diverse communities are better able to withstand disturbances and maintain essential ecological processes.
Q: How can alpha diversity be conserved?
A: Conserving alpha diversity involves preserving and protecting the habitats that support diverse species communities. It requires implementing sustainable practices, reducing habitat destruction, and limiting the introduction of invasive species.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
