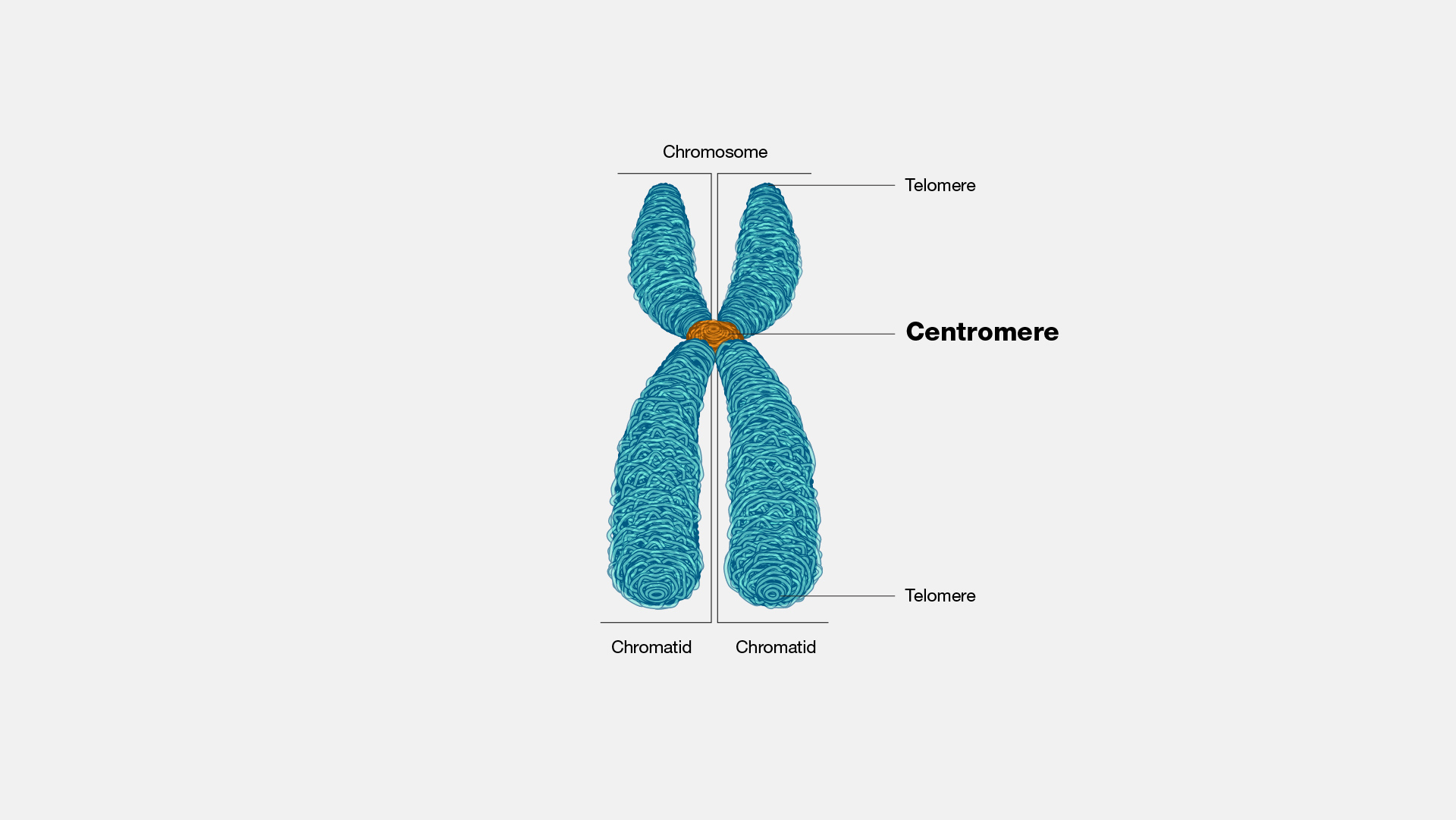
Centromeres are fascinating structures found in the chromosomes of eukaryotic organisms. They play a crucial role in the faithful transmission of genetic information during cell division. While they may seem like small and insignificant parts of the chromosome, centromeres are actually complex and dynamic regions that have been the subject of intense scientific research. In this article, we will explore 15 captivating facts about centromeres, shedding light on their structure, function, and importance in the study of genetics and cell biology. From their role in establishing the attachment of chromosomes to the spindle apparatus to their involvement in genetic disorders, centromeres are key players in ensuring the stability and integrity of our genomes. So, let’s embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries surrounding these fascinating chromosomal elements.
Key Takeaways:
- Centromeres are like traffic controllers for chromosomes, making sure they’re divided properly during cell division to keep our bodies healthy and functioning.
- Scientists are still uncovering the mysteries of centromeres, which play a crucial role in genetics and cell biology, influencing everything from genetic diversity to cell fate.
Centromeres are essential for cell division.
Centromeres play a crucial role in cell division, ensuring the accurate distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells during mitosis and meiosis. Without centromeres, proper cell division would not be possible.
Centromeres are specialized regions of the chromosome.
Located near the center of the chromosome, centromeres are distinct regions characterized by specific DNA sequences and unique protein structures. These features allow centromeres to bind and organize the spindle fibers that help segregate chromosomes during cell division.
Centromeres ensure equal distribution of genetic material.
During cell division, centromeres guide the separation of sister chromatids, the exact copies of each chromosome. This ensures that each daughter cell receives an equal share of the genetic material from the parent cell.
Centromeres are involved in chromosome stability.
Centromeres play a critical role in maintaining the stability of chromosomes. They help prevent rearrangements, fusions, and other abnormalities that could lead to genetic disorders and diseases.
Centromeres are dynamic structures.
Centromeres undergo changes in their structure and composition throughout the cell cycle. These dynamic changes are essential for proper chromosome attachment and segregation during cell division.
Centromeres have epigenetic marks.
Epigenetic marks, such as specific modifications to the DNA and associated proteins, help maintain the identity of centromeres. These marks ensure that the centromere is recognized and bound by the necessary proteins during cell division.
Centromeres are involved in genetic recombination.
Centromeres play a role in genetic recombination, the process by which genetic material is exchanged between homologous chromosomes. This helps generate genetic diversity and contributes to the evolution of species.
Centromeres vary in size and DNA sequence.
Centromeres can vary significantly in terms of their size and DNA sequence between different organisms. This diversity highlights the complexity and adaptability of centromeres across the biological world.
Centromeres can be the site of chromosomal abnormalities.
Mutations or alterations in centromere structure or function can lead to chromosomal abnormalities, such as the loss or gain of whole chromosomes. These abnormalities are associated with various genetic disorders and diseases.
Centromeres have a centromere protein complex.
The centromere protein complex, known as the kinetochore, assembles on the centromere and plays a crucial role in chromosome attachment to the spindle fibers. It ensures proper chromosome alignment and segregation during cell division.
Centromeres can exhibit neocentromere formation.
Neocentromeres are new centromere structures that can form at atypical locations on chromosomes. This phenomenon provides insights into the flexibility and adaptability of centromeres in maintaining the integrity of the genome.
Centromeres play a role in determining cell fate.
Centromeres have been shown to influence cell fate decisions, such as cell differentiation and development. Changes in centromere function can impact gene expression and cellular processes, leading to altered cell behavior.
Centromeres can be visualized using specific techniques.
Scientists use specialized techniques, such as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and immunostaining, to visualize and study centromeres in cells. These techniques provide valuable insights into centromere structure, function, and dynamics.
Centromeres are a subject of intense research.
Due to their essential role in cell division and chromosome stability, centromeres are a subject of extensive research in the field of genetics and cell biology. Scientists continue to unravel the intricacies of centromere biology and its implications.
Centromeres are fascinating and mysterious.
Despite significant progress in the understanding of centromeres, many questions and mysteries still surround these vital structures. Their complex nature continues to capture the curiosity of scientists seeking to unravel their many secrets.
These 15 captivating facts about centromeres highlight their significance in cell division, chromosome stability, and genetics. From their role in ensuring accurate chromosome segregation to their dynamic nature and influence on cell fate decisions, centromeres remain a captivating subject of scientific exploration.
Conclusion
Centromeres are fascinating structures that play a crucial role in the organization and stability of chromosomes. Through their association with kinetochores, they ensure accurate segregation of genetic material during cell division. Their unique composition and dynamic behavior have captivated researchers for decades.
From their discovery in the early 20th century to the recent advancements in understanding their molecular mechanisms, centromeres continue to intrigue biologists around the world. These 15 captivating facts about centromeres provide a glimpse into the complexity and importance of these remarkable chromosomal regions.
As our knowledge of centromeres continues to expand, they will undoubtedly remain a focal point of research, shedding light on fundamental biological processes and contributing to advancements in fields such as genetics, cell biology, and cancer research.
FAQs
Q: What are centromeres?
A: Centromeres are specialized regions of chromosomes that play a critical role in the faithful segregation of genetic material during cell division.
Q: How many types of centromeres are there?
A: There are three main types of centromeres found in eukaryotic organisms: point centromeres, regional centromeres, and holocentromeres.
Q: What is the function of centromeres?
A: Centromeres serve as attachment sites for spindle fibers and kinetochores, which are essential for proper chromosome alignment and separation during cell division.
Q: Do centromeres have a specific DNA sequence?
A: While centromeres do not have a specific DNA sequence, they contain repetitive DNA elements that play a role in centromere formation and function.
Q: Can centromeres change their position on a chromosome?
A: Yes, centromeres can change their position through evolutionary processes such as centromere repositioning or chromosomal rearrangements.
Q: What happens if centromeres are not properly functioning?
A: Dysfunctional centromeres can lead to chromosome missegregation, aneuploidy (abnormal chromosome number), and genomic instability.
Q: Are centromeres conserved across different species?
A: While the DNA sequences of centromeres vary across different species, the underlying principles of centromere function remain conserved.
Q: Can centromeres be targeted for therapeutic interventions?
A: Targeting centromeres and their associated proteins holds potential for therapeutic strategies, particularly in the treatment of cancer where abnormal centromere function is often observed.
Q: Are centromeres involved in genetic diseases?
A: Yes, defects or mutations in centromere-related genes can contribute to various genetic diseases, including chromosomal instability syndromes.
Q: How are centromeres studied?
A: Centromeres are studied using a combination of molecular biology techniques, microscopy, genome sequencing, and advanced imaging technologies.
Q: Can centromeres be artificially engineered?
A: Researchers are exploring the possibility of engineering artificial centromeres with the goal of understanding their function and potentially modifying them for various applications.
Q: Can centromeres be passed on through generations?
A: Centromeres can be inherited, as they are an integral part of chromosomes that are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction.
Q: What is the relationship between epigenetics and centromeres?
A: Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, play a role in centromere function and stability.
Q: Are centromeres involved in meiosis?
A: Yes, centromeres are involved in meiosis, ensuring proper chromosome segregation during the formation of gametes.
Q: Can centromeres be used for evolutionary studies?
A: The study of centromere evolution has provided insights into species divergence, genome organization, and the mechanisms driving chromosomal rearrangements.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
