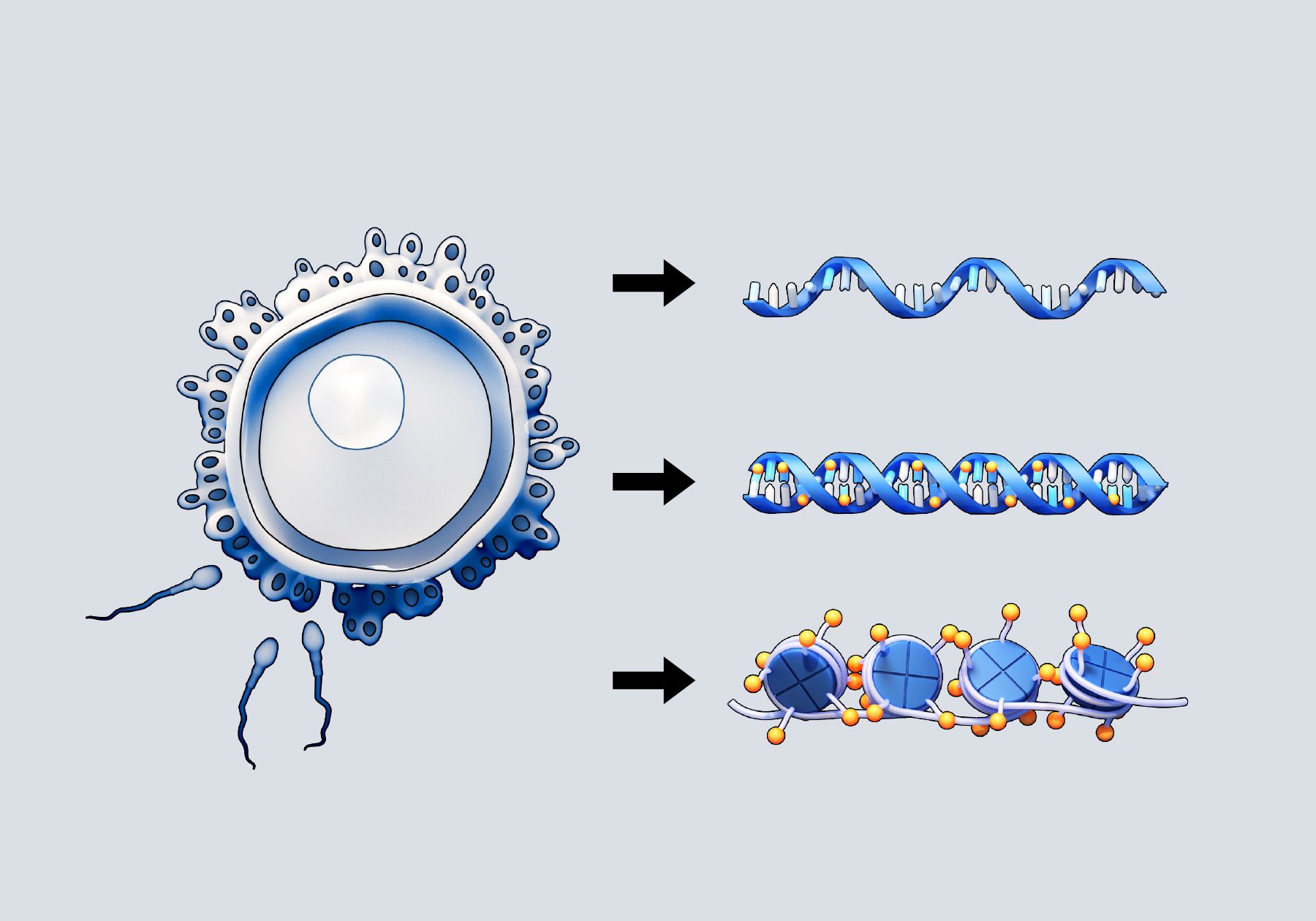
Epigenetic inheritance is a captivating field of study within the realm of biology that has been gaining increasing attention in recent years. While we are familiar with the concept of genetic inheritance, where traits are passed down from one generation to the next through the DNA code, epigenetic inheritance refers to changes in gene expression that can be passed down without altering the DNA sequence itself.
In this article, we will explore 14 intriguing facts about epigenetic inheritance, shedding light on the remarkable ways in which environmental factors can influence gene activity and be inherited by future generations. From the impact of nutrition and stress on gene expression to the long-lasting effects of trauma and exposure to toxins, epigenetic inheritance offers a new perspective on the complex interplay between nature and nurture.
Key Takeaways:
- Environmental factors can influence how our genes are expressed and passed down to future generations through epigenetic inheritance, impacting our health and well-being.
- Epigenetic inheritance challenges the nature versus nurture debate, showing that our lifestyle choices and experiences can leave a lasting mark on our genetic expression, potentially shaping the traits and diseases of future generations.
Epigenetic inheritance refers to the transmission of changes in gene expression from one generation to the next.
Epigenetic inheritance is a fascinating phenomenon that challenges the traditional understanding of genetic inheritance. Unlike classical genetics, which focuses on changes in DNA sequence, epigenetic inheritance involves modifications to the structure of DNA and proteins that can be passed down to future generations.
Epigenetic marks can be influenced by environmental factors.
Diet, stress, exposure to toxins, and other environmental factors can impact the epigenetic marks on our DNA. These modifications can alter gene expression and potentially be inherited by offspring.
Epigenetic changes can occur during early development.
During the early stages of embryonic development, epigenetic modifications play a crucial role in determining cell fate and shaping the overall structure of the organism. These changes can have a lasting impact on an individual’s health and well-being.
Epigenetic inheritance can affect disease susceptibility.
Epigenetic modifications have been linked to various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders. Understanding how these modifications are inherited can provide valuable insights into disease prevention and treatment.
Epigenetic marks can be reversible.
Unlike genetic mutations, which are generally permanent, epigenetic marks are reversible. This means that it is possible to modify gene expression patterns by targeting and altering these marks, offering potential therapeutic opportunities.
Epigenetic inheritance can skip generations.
In some cases, epigenetic changes can be transmitted from one generation to the next, while in others, they may skip a generation entirely. The mechanisms governing this skipping phenomenon are still not fully understood.
Epigenetic inheritance can be sex-specific.
Studies have shown that epigenetic modifications can exhibit sex-specific patterns of inheritance. This suggests that the transmission of epigenetic information can differ between males and females.
Epigenetic inheritance is not exclusive to humans.
Epigenetic inheritance has been observed in a wide range of organisms, including plants and animals. This suggests that the mechanisms underlying epigenetic inheritance are highly conserved throughout evolution.
Epigenetic changes can occur in response to trauma.
Experiencing severe stress or trauma can trigger epigenetic modifications, which can be passed on to offspring. This highlights the potential intergenerational impact of traumatic events.
Epigenetic inheritance can affect behavior.
Epigenetic modifications have been associated with changes in behavior and cognition. These modifications can influence traits such as aggression, anxiety, and memory formation.
Epigenetic marks can be influenced by lifestyle choices.
Your lifestyle choices, such as exercise, sleep patterns, and even social interactions, can impact your epigenetic profile. Making healthy choices can potentially lead to positive epigenetic changes that can be passed on to future generations.
Epigenetic inheritance challenges the nature versus nurture debate.
Epigenetic inheritance blurs the line between nature and nurture, as it suggests that environmental factors can have a lasting impact on gene expression and subsequent generations.
Epigenetic inheritance research is still in its early stages.
Despite significant advancements in understanding epigenetics, there is still much to learn about the mechanisms and implications of epigenetic inheritance. Ongoing research continues to shed light on this complex field.
Epigenetic inheritance has the potential to revolutionize medicine.
Understanding and harnessing the power of epigenetic inheritance can open new doors for personalized medicine, disease prevention, and the development of innovative therapies.
Conclusion
Epigenetic inheritance is a captivating area of study that holds immense potential for unraveling the complexities of genetics and heredity. The interplay between genetics and the environment is intricately woven through epigenetic modifications, offering a new perspective on how traits and diseases can be influenced across generations. Continued research in this field will undoubtedly uncover even more intriguing facts about epigenetic inheritance and its impact on human health and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, epigenetic inheritance is a fascinating and complex field of biology that has transformed our understanding of how traits can be passed down from one generation to the next. Through epigenetic modifications, certain genes can be turned on or off, leading to changes in gene expression and ultimately influencing phenotypic traits. This phenomenon has significant implications for evolution, development, and even disease.The 14 intriguing facts about epigenetic inheritance highlighted in this article provide a glimpse into the diverse mechanisms and surprising effects of this phenomenon. From transgenerational epigenetic inheritance to the impact of environmental factors, each fact reveals a unique aspect of how epigenetics shapes our lives and the world around us.As our knowledge in the field continues to expand, it is clear that epigenetic inheritance plays a crucial role in shaping biological diversity and adaptability. Understanding the intricacies of epigenetic processes enhances our understanding of genetics as a whole and opens up new avenues of research and potential applications in various fields.
FAQs
Q: What is epigenetic inheritance?
A: Epigenetic inheritance refers to the transmission of traits from one generation to the next through modifications in gene expression that do not involve changes in the DNA sequence itself.
Q: How is epigenetic inheritance different from genetic inheritance?
A: Genetic inheritance is based on the transmission of genetic material (DNA) from parents to offspring, while epigenetic inheritance involves the transmission of changes in gene expression patterns that can be influenced by environmental factors.
Q: Can epigenetic modifications be reversed?
A: Yes, epigenetic modifications can be reversible and are influenced by various factors such as diet, exercise, and exposure to certain substances or environments.
Q: Do epigenetic modifications only occur in humans?
A: No, epigenetic modifications occur in various organisms, including plants and animals. These modifications play crucial roles in development, adaptation, and disease susceptibility across different species.
Q: Can epigenetic changes be inherited across multiple generations?
A: Yes, some epigenetic changes can be inherited across multiple generations, a phenomenon known as transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. This means that environmental factors experienced by previous generations can influence the traits of future generations.
Q: How do epigenetic modifications affect disease susceptibility?
A: Epigenetic modifications can influence the expression of genes associated with various diseases. Certain modifications can increase or decrease the risk of developing certain conditions, including cancer, mental disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
Q: Are all epigenetic modifications heritable?
A: Not all epigenetic modifications are heritable. Some modifications are reversible and do not get passed down to future generations, while others can be stably maintained and passed on to offspring.
Q: Can epigenetic changes occur during adulthood or only during early development?
A: Epigenetic changes can occur throughout life, including during adulthood. The environment and lifestyle factors can continue to influence epigenetic modifications and gene expression patterns, leading to changes in health and disease risk.
Q: How do scientists study epigenetic inheritance?
A: Scientists study epigenetic inheritance through various techniques, including DNA methylation analysis, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and sequencing methods. They explore how specific environmental exposures or genetic mutations affect epigenetic patterns.
Q: Can epigenetic modifications be passed on to future generations without genetic changes?
A: Yes, epigenetic modifications can be passed on to future generations without changes in the DNA sequence. These modifications can have long-lasting effects on gene expression and phenotype, influencing the traits of subsequent generations.
Q: How do environmental factors influence epigenetic inheritance?
A: Environmental factors, such as diet, stress, toxins, and maternal exposures, can influence epigenetic patterns and subsequently affect gene expression, potentially leading to transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.
Q: Can epigenetic modifications be used in medical treatments?
A: Epigenetic modifications hold promise as potential targets for medical treatments. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, scientists can develop therapies to modulate gene expression and potentially treat diseases that have an epigenetic component.
Q: Can epigenetic changes be passed down through sperm and eggs?
A: Yes, epigenetic changes can be passed down through sperm and eggs, allowing these modifications to be inherited by future generations.
Q: How does epigenetic inheritance impact evolution?
A: Epigenetic inheritance can have profound effects on evolution by allowing rapid adaptations to changing environments. This mechanism provides a way for organisms to pass on acquired traits and respond to environmental pressures in a quicker timeframe than genetic changes alone.
Epigenetic inheritance is a fascinating field, but it's just one piece of the epigenetics puzzle. Dive deeper into epigenetics and its impact on gene expression, development, and disease. Explore how gene regulation works and the intricate mechanisms that control which genes are turned on or off. Don't forget about DNA methylation, a crucial epigenetic process that plays a significant role in gene expression and cellular function. Keep learning and discovering more about the captivating world of epigenetics and its far-reaching implications in biology and medicine.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
