When we think of plants, we often envision their vibrant colors, lush foliage, and graceful blooms. However, beneath their beautiful exteriors lies a complex world of plant nutrition that is crucial for their growth and survival. Understanding the intricacies of how plants obtain and utilize nutrients is not only fascinating but also key to optimizing their health and productivity.
In this article, we will dive deep into the realm of plant nutrition and explore some intriguing facts about how plants obtain and process nutrients. From their ability to harness energy from the sun to the symbiotic relationships they form with other organisms, plants have incredibly sophisticated strategies for obtaining the essential elements they need to thrive.
So, join us as we unravel the mysteries of plant nutrition and discover 16 fascinating facts that shed light on the incredible world of plant biology.
Key Takeaways:
- Plants make their own food through photosynthesis, using sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- Soil pH, nutrient balance, and root adaptations are vital for plants to grow healthy and strong. Sustainable practices support optimal plant nutrition.
Plants are autotrophs.
Plants have the amazing ability to produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy.
Through the process of photosynthesis, plants harness the power of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth.
Nitrogen plays a crucial role in the formation of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which are essential for plant growth and development.
The pH level of the soil affects nutrient availability.
The pH level of the soil plays a critical role in determining the availability of nutrients for plant uptake. Different plants thrive in different pH levels.
Plants require macronutrients and micronutrients for optimal growth.
Macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are required in large quantities, while micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese are needed in smaller amounts.
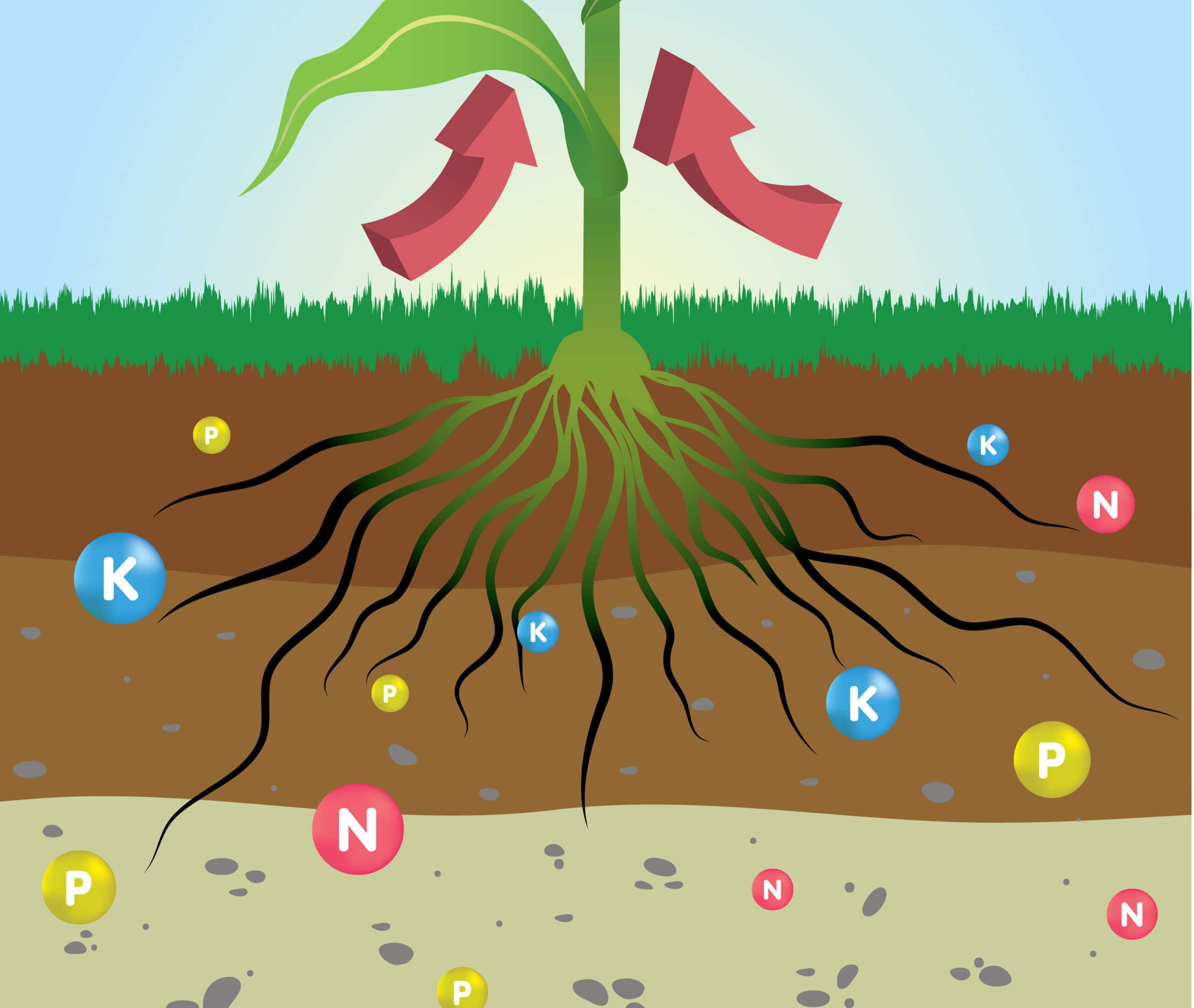
Plant roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
The root system of plants plays a vital role in absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, which are then transported to other parts of the plant for growth and development.
Mycorrhizal fungi help plants in nutrient absorption.
Mycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic associations with plant roots, aiding in the absorption of nutrients, particularly phosphorus, from the soil.
Plants can adjust their root systems to optimize nutrient uptake.
Plants have the ability to alter their root architecture in response to nutrient availability, ensuring efficient uptake and utilization of essential nutrients.
Legumes have a unique ability to fix nitrogen.
Legume plants have specialized root nodules that house nitrogen-fixing bacteria, enabling them to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for plant growth.
Nutrient deficiencies can impact plant health and productivity.
A lack of essential nutrients can lead to stunted growth, nutrient deficiencies, and decreased plant productivity. It is crucial to provide plants with a balanced nutrient supply.
Organic matter improves soil fertility and nutrient availability.
Adding organic matter to the soil enhances its fertility, improves nutrient retention, and promotes beneficial microbial activity, ultimately benefiting plant nutrition.
Plants can communicate and respond to nutrient stress.
Plants have sophisticated signaling mechanisms that allow them to detect nutrient deficiencies and respond by altering their root architecture or releasing specific signaling molecules.
Over-fertilization can have negative environmental impacts.
Excessive use of fertilizers can lead to nutrient runoff, polluting water bodies, and causing harmful algal blooms. It is essential to practice responsible fertilizer application.
The health of the soil microbiome influences plant nutrition.
The diversity and activity of soil microorganisms play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and availability, impacting plant nutrient uptake and overall health.
Biofortification enhances the nutritional value of crops.
Through selective breeding or genetic modification, crops can be fortified with essential nutrients to address specific nutrient deficiencies in human diets.
Sustainable agricultural practices promote optimal plant nutrition.
Implementing sustainable practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated nutrient management systems help maintain soil fertility, minimize nutrient loss, and support healthy plant nutrition.
The “16 Intriguing Facts About Plant Nutrition” provide a fascinating insight into the complex world of plant nutrition. Understanding these facts is crucial for optimizing crop production, reducing environmental impacts, and ensuring sustainable food systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding plant nutrition is essential for the thriving growth and development of plants. Plants are not only dependent on sunlight and water, but also on essential nutrients that they obtain from the soil. These nutrients play a crucial role in various physiological processes, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and the production of new cells.
By harnessing the power of soil nutrients, plants are able to convert sunlight into energy and synthesize the organic molecules necessary for their survival. From the fascinating process of nitrogen fixation to the symbiotic relationships between plants and microorganisms, plant nutrition is a complex and dynamic field of study.
As we continue to explore and understand the intricate mechanisms of plant nutrition, we can unlock the potential to improve crop yields, enhance agricultural practices, and contribute to sustainable food production.
FAQs
1. What are the essential nutrients that plants need?
Plants require a range of essential nutrients, including macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc.
2. How do plants obtain nutrients from the soil?
Plants have specialized root structures that allow them to absorb nutrients from the soil. They take up water and dissolved nutrients through their roots and transport them to different parts of the plant.
3. What is nitrogen fixation?
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which certain bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use. This nitrogen is essential for the synthesis of proteins and other vital molecules in plants.
4. Can plants grow without soil?
Yes, plants can grow without soil. Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, without the need for traditional soil. This allows for controlled and efficient plant growth.
5. How do plants interact with microorganisms in the soil?
Plants form mutualistic relationships with certain beneficial microorganisms in the soil, such as mycorrhizal fungi. These microorganisms help plants access nutrients and improve their overall health and resilience.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
