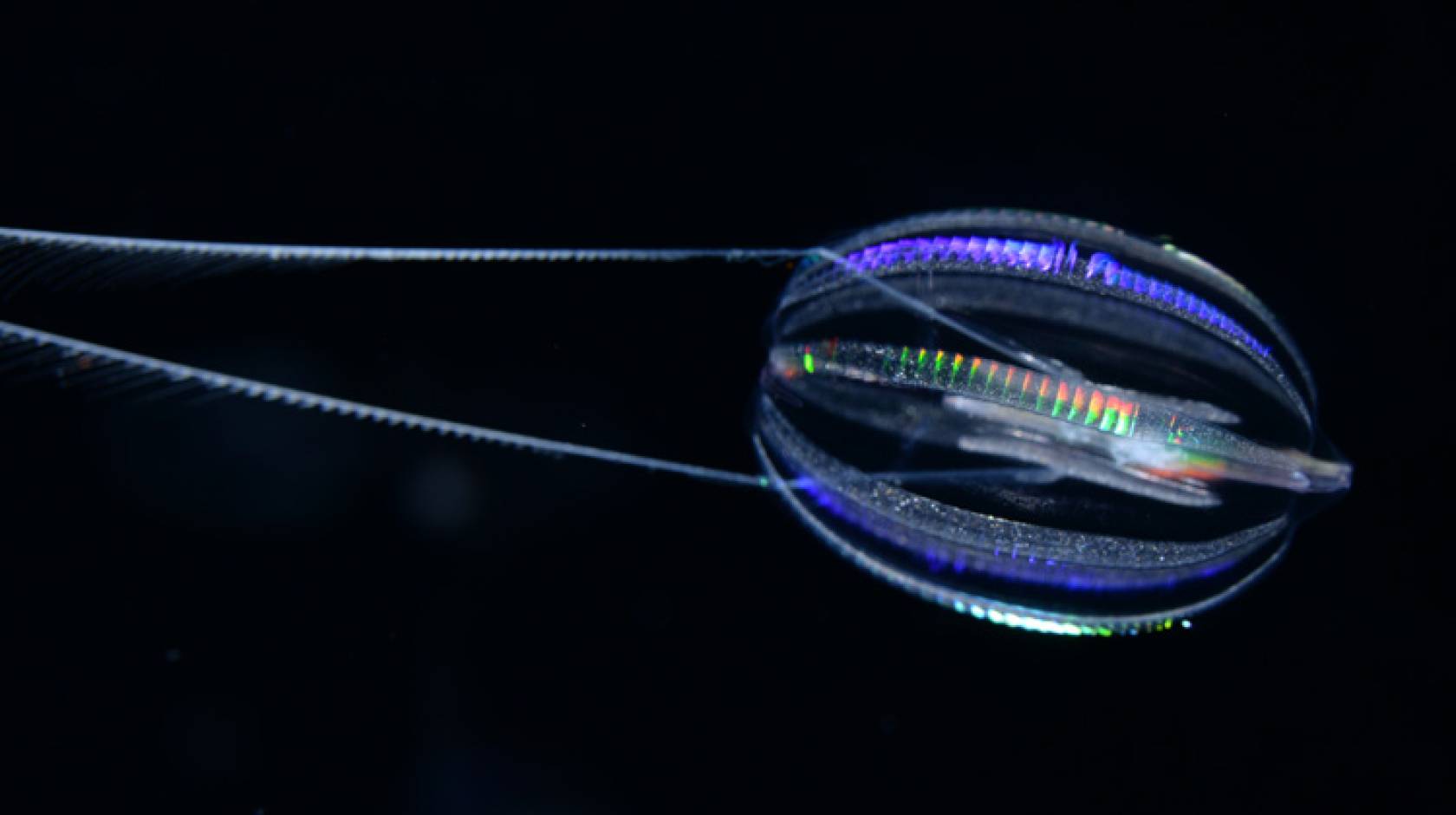
Comb jellies, also known as ctenophores, are fascinating creatures that inhabit the world’s oceans. These gelatinous organisms may resemble jellyfish, but they are actually quite different. Comb jellies belong to a distinct phylum known as Ctenophora and are considered one of the oldest multicellular animals on Earth.
With their unique anatomy and captivating bioluminescence, comb jellies have captured the attention of both scientists and nature enthusiasts. In this article, we will explore 19 intriguing facts about comb jellies, shedding light on their diverse species, remarkable adaptations, and mesmerizing behavior.
So, let’s dive into the realm of comb jellies and unravel the mysteries surrounding these enchanting creatures.
Key Takeaways:
- Comb jellies, also known as ctenophores, are mesmerizing creatures that propel themselves through water using rows of cilia, creating a shimmering effect. They come in vibrant colors and play a vital role in marine ecosystems.
- Despite their delicate appearance, comb jellies are ancient and resilient creatures that have been around for over 500 million years. They have unique bioluminescent abilities and can regenerate lost body parts, adding to their mysterious beauty.
Comb jellies are not actually jellyfish.
Contrary to popular belief, comb jellies are not jellyfish. They belong to a separate phylum called Ctenophora.
They are the largest animals that swim solely by using cilia.
Comb jellies propel themselves through water using rows of cilia that create a mesmerizing shimmering effect.
Comb jellies come in a variety of vibrant colors.
From translucent to iridescent hues, comb jellies can exhibit a wide range of stunning colors, making them a visual delight.
They have a unique bioluminescent ability.
Comb jellies can produce and emit light through specialized cells called photocytes, creating a captivating light show.
Some comb jellies have two long tentacles used for capturing prey.
These tentacles are armed with tiny sticky cells called colloblasts, which immobilize small organisms for the comb jelly to feed on.
Comb jellies have a gelatinous body composition.
Their body is made up of 95% water, giving them a delicate and jelly-like appearance.
They have a unique digestive system.
Comb jellies possess a complete digestive system, with both a mouth and an anus.
Comb jellies reproduce through a process called hermaphroditism.
Most comb jellies have both male and female reproductive organs and can produce both eggs and sperm.
They are found in marine environments worldwide.
Comb jellies can be found in oceans and seas around the globe, from the Arctic to tropical waters.
Comb jellies have been around for over 500 million years.
These ancient creatures have been roaming the seas long before the dinosaurs even existed.
They have a delicate and fragile body structure.
Comb jellies lack a hard skeleton and rely on the buoyancy of water to maintain their shape.
Some comb jellies have a transparent body.
Transparency allows them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them difficult to spot.
Comb jellies can regenerate lost body parts.
If a comb jelly is injured or loses a part of its body, it has the remarkable ability to regenerate and repair itself.
They are not harmful to humans.
Unlike some jellyfish species, comb jellies do not possess stinging cells and are harmless to humans.
Comb jellies have a unique mode of predation.
Rather than actively seeking out prey, comb jellies passively drift in the water and capture food that comes in contact with their tentacles.
Their scientific name, ctenophora, means “comb-bearing.”
This name refers to their characteristic rows of cilia, which resemble the teeth of a comb.
Comb jellies have a short lifespan.
Most comb jellies live for only a few months, although some species can survive for up to a year.
They play a vital role in marine ecosystems.
Comb jellies act as both predators and prey, helping to maintain the delicate balance of the marine food chain.
Scientists are still discovering new species of comb jellies.
With their elusive nature, new species of comb jellies continue to be discovered, adding to the fascination and wonder surrounding these captivating creatures.
So next time you find yourself gazing out into the sea, remember the 19 intriguing comb jelly facts that showcase the mysterious beauty of these mesmerizing organisms. Explore the depths and unravel the secrets of the ocean’s enigmatic comb jellies!
Conclusion
Comb jellies, also known as ctenophores, are captivating creatures that inhabit our oceans. Through the 19 facts provided, we have delved into the extraordinary world of comb jellies and uncovered some fascinating aspects of their biology, behavior, and ecological significance.
We have learned that comb jellies have a unique body structure, with intricately arranged ciliary combs that enable them to propel through the water with grace and elegance. Their ethereal beauty, evident in their bioluminescent displays, has captivated scientists and ocean enthusiasts alike.
Furthermore, comb jellies play important roles in marine ecosystems as both predators and prey. They consume small invertebrates and plankton, contributing to the balance of the food chain. Additionally, they serve as a vital food source for many marine organisms.
As we continue to explore the depth of our oceans, it’s important to appreciate and protect these magnificent creatures. By understanding more about comb jellies, we can work towards conserving their habitats and ensuring their survival for generations to come.
FAQs
Q: What are comb jellies?
A: Comb jellies, or ctenophores, are gelatinous marine creatures characterized by their transparent bodies and rows of ciliary combs that they use for movement.
Q: Where can comb jellies be found?
A: Comb jellies are found in oceans worldwide, from the surface to the depths of the abyss. They are most abundant in warmer tropical and subtropical waters.
Q: Are comb jellies dangerous to humans?
A: No, comb jellies are harmless to humans. They do not possess stinging cells like jellyfish and are not known to cause any significant harm.
Q: What do comb jellies eat?
A: Comb jellies primarily feed on small invertebrates, such as larval fish, crustaceans, and other gelatinous organisms. They are also filter feeders and consume plankton.
Q: Can comb jellies bioluminesce?
A: Yes, many comb jellies are bioluminescent. They produce light through chemical reactions within their bodies, creating beautiful displays of colors in the ocean.
Q: How do comb jellies reproduce?
A: Comb jellies have complex life cycles involving both sexual and asexual reproduction. They can reproduce by releasing eggs and sperm into the water, or through budding and regeneration.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
