Anaerobic respiration is a fascinating process observed in various organisms, from microscopic bacteria to complex multicellular organisms. Unlike aerobic respiration, which relies on the presence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. This metabolic pathway offers valuable insights into the adaptability and survival strategies of organisms in oxygen-deprived environments.
In this article, we will explore 16 intriguing facts about anaerobic respiration that will shed light on its significance, mechanisms, and diverse applications. From its role in energy production to its impact on global carbon cycles, anaerobic respiration plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of anaerobic respiration and uncover some captivating facts about this unique metabolic process.
Key Takeaways:
- Anaerobic respiration is a cool process that helps organisms make energy without needing oxygen. It’s like a backup plan for when oxygen is in short supply.
- Anaerobic respiration is super important for making things like beer, wine, and even biogas! It’s been around for a really long time and has helped shape the way living things have evolved.
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
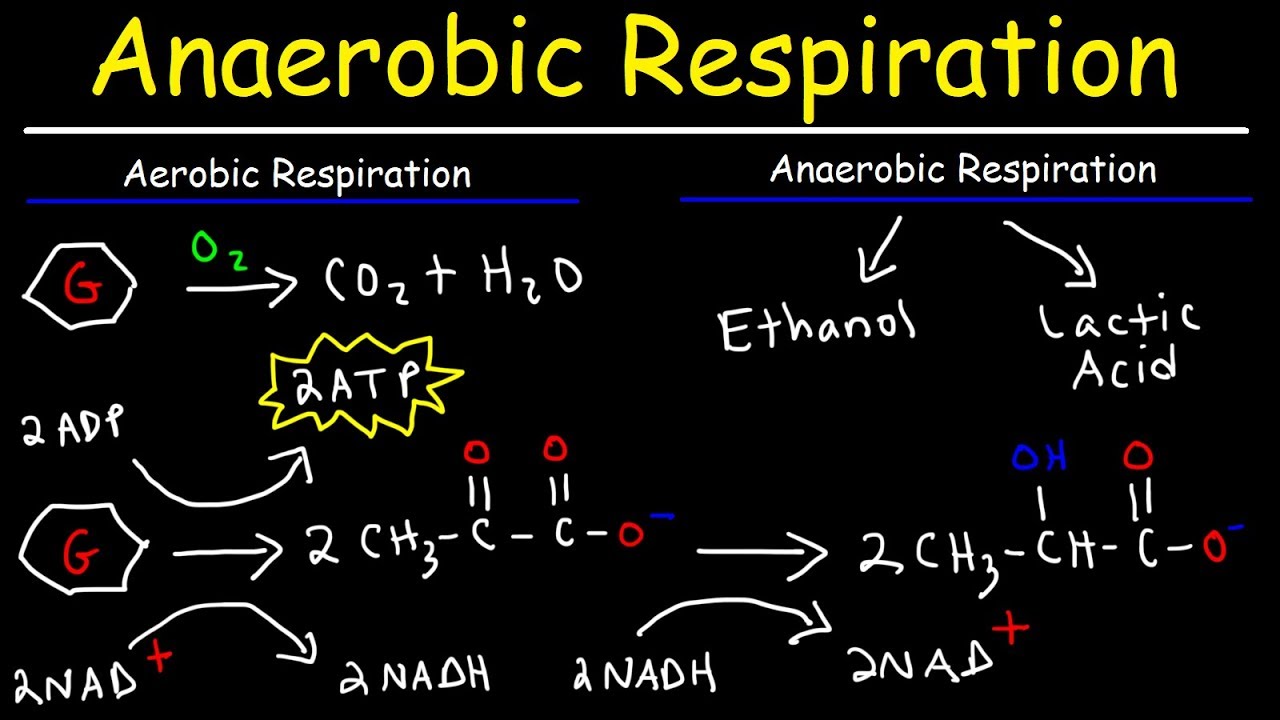
Anaerobic respiration is a cellular process that occurs in the absence of oxygen. It is a vital metabolic pathway that provides energy to organisms in environments with low oxygen levels.
Two Types of Anaerobic Respiration
There are two primary types of anaerobic respiration: alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation. These processes allow cells to generate energy by breaking down glucose without the need for oxygen.
Occurrence in Microorganisms
Anaerobic respiration is commonly observed in microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, and some fungi. These organisms have adapted to survive and thrive in environments where oxygen is limited.
Energy Yield
While aerobic respiration produces more energy overall, anaerobic respiration is still a valuable energy-producing pathway. It can generate approximately 5% to 10% of the energy produced in aerobic respiration.
Importance in Human Physiology
Anaerobic respiration plays a significant role in human physiology during intense physical activities. When the oxygen demand exceeds its supply, the body relies on anaerobic pathways to produce energy, leading to the buildup of lactic acid.
Production of Ethanol
Alcoholic fermentation, a type of anaerobic respiration, is used in the production of alcoholic beverages such as beer and wine. Yeast cells convert sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide, giving these beverages their characteristic flavors.
Industrial Applications
Anaerobic respiration has several industrial applications. It is utilized in the production of biofuels, wastewater treatment, and the fermentation of certain food products like soy sauce and sauerkraut.
Anaerobic Respiration in Environmental Conservation
The process of anaerobic respiration plays a crucial role in the decomposition of organic matter in oxygen-deprived environments, such as wetlands and marine sediments. By breaking down organic material, it helps recycle nutrients and maintain ecological balance.
Anaerobic Bacteria in the Gut
The human digestive system harbors numerous anaerobic bacteria that aid in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates. These bacteria play a critical role in the fermentation process within the gut, contributing to overall digestive health.
Methanogenesis
One of the fascinating outcomes of anaerobic respiration is methanogenesis, a pathway in which certain archaea produce methane gas. This process occurs in anaerobic environments such as swamps, marshes, and the intestines of ruminant animals.
Anaerobic Respiration in Extremophiles
Extremophiles, organisms that thrive in extreme environments, often utilize anaerobic respiration as an adaptation to their surroundings. These organisms can be found in habitats such as deep-sea hydrothermal vents, hot springs, and frozen environments.
Anaerobic Respiration in the Carbon Cycle
Anaerobic respiration is involved in the carbon cycle, where organic matter is broken down and converted into carbon dioxide and methane. These gases are important contributors to greenhouse effects and climate change.
Anaerobic Respiration in Medical Diagnostics
Anaerobic bacteria can cause infections in wounds, abscesses, and deep tissue injuries. Recognizing these infections is crucial for effective treatment, and laboratory tests often involve culturing samples under anaerobic conditions.
Oxygen Deprivation and Anaerobic Respiration
Cells switch to anaerobic respiration in situations where oxygen supply is reduced, such as high altitudes or in certain medical conditions. This adaptation allows cells to continue generating limited energy in the absence of sufficient oxygen.
Biogas Production
The decomposition of organic waste material in anaerobic environments can produce biogas, which is primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide. This biogas can be harnessed and used as an alternative energy source.
The Evolutionary Significance of Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is believed to be an ancient metabolic pathway that preceded the development of oxygen-dependent aerobic respiration. It played a crucial role in sustaining life before oxygen levels rose on Earth, shaping the evolution of early organisms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, anaerobic respiration is a fascinating biological process that allows organisms to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. Through anaerobic respiration, cells are able to convert organic molecules into usable energy sources like ATP.During anaerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor is something other than oxygen, such as nitrate, sulfate, or even carbon dioxide. This process occurs in various organisms, including bacteria, archaea, and certain types of fungi.Anaerobic respiration also plays a crucial role in our daily lives. For example, it is used in the fermentation of foods and beverages, such as bread, beer, wine, and yogurt. Additionally, anaerobic bacteria are important in the decomposition of organic matter in environments with low oxygen levels.Understanding the intricacies of anaerobic respiration provides valuable insights into the diverse ways in which organisms adapt and survive in different environments. Further research in this field can unlock new possibilities in areas ranging from medicine to biofuels.
FAQs
1. What is anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is a biological process that allows organisms to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. It involves the conversion of organic molecules into usable energy sources.
2. How does anaerobic respiration differ from aerobic respiration?
The main difference is that anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen as the final electron acceptor, while aerobic respiration does. Additionally, anaerobic respiration produces less energy compared to aerobic respiration.
3. Which organisms use anaerobic respiration?
Various organisms use anaerobic respiration, including bacteria, archaea, and some types of fungi. It is also observed in certain animal tissues during periods of low oxygen availability.
4. What is the role of anaerobic respiration in fermentation?
Anaerobic respiration is an essential step in the process of fermentation. It allows the conversion of sugars into alcohol or acids, which is utilized in the production of foods and beverages like bread, beer, wine, and yogurt.
5. How does anaerobic respiration impact the environment?
Anaerobic respiration plays a crucial role in the decomposition of organic matter in environments with low oxygen levels. It helps in breaking down complex organic compounds and recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Anaerobic respiration plays a vital role in energy production for many organisms, but there's still more to explore! Dive deeper into the world of cellular respiration by learning about lactic acid fermentation and its extraordinary facts. Uncover the fascinating processes that keep life thriving in diverse environments, from the depths of the ocean to the inner workings of our own bodies. Stay curious and keep expanding your knowledge of the incredible ways organisms generate energy!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
