Taxonomy, the science of classifying and naming living organisms, may not be the most talked-about topic at dinner parties, but it is undoubtedly a fascinating field. From the discovery of new species to the organization of life into a hierarchical system, taxonomy plays a crucial role in our understanding of the natural world. In this article, we will delve into some intriguing facts about taxonomy that will surely pique your interest. Get ready to embark on a journey through the intricate web of scientific classification, the intricacies of binomial nomenclature, and the exciting realm of evolutionary relationships. Whether you’re a lover of biology or simply curious about the diversity of life on Earth, these 15 fascinating facts about taxonomy will leave you with a newfound appreciation for the complex world of scientific naming and categorization.
Key Takeaways:
- Taxonomy, led by the famous Carl Linnaeus, helps scientists organize and understand the diverse world of living organisms through classification and naming.
- By using traits and DNA, taxonomy not only aids in species conservation but also reveals evolutionary relationships and helps predict how species respond to environmental changes.
Taxonomy is the science of classification.
Taxonomy is the branch of biology that deals with the identification, classification, and naming of organisms based on their characteristics and relationships. It provides a system for organizing and categorizing living organisms into hierarchical groups.
The father of modern taxonomy is Carl Linnaeus.
Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is widely regarded as the pioneer of modern taxonomy. His influential work in the 18th century laid the foundation for the binomial nomenclature system still used today to name species.
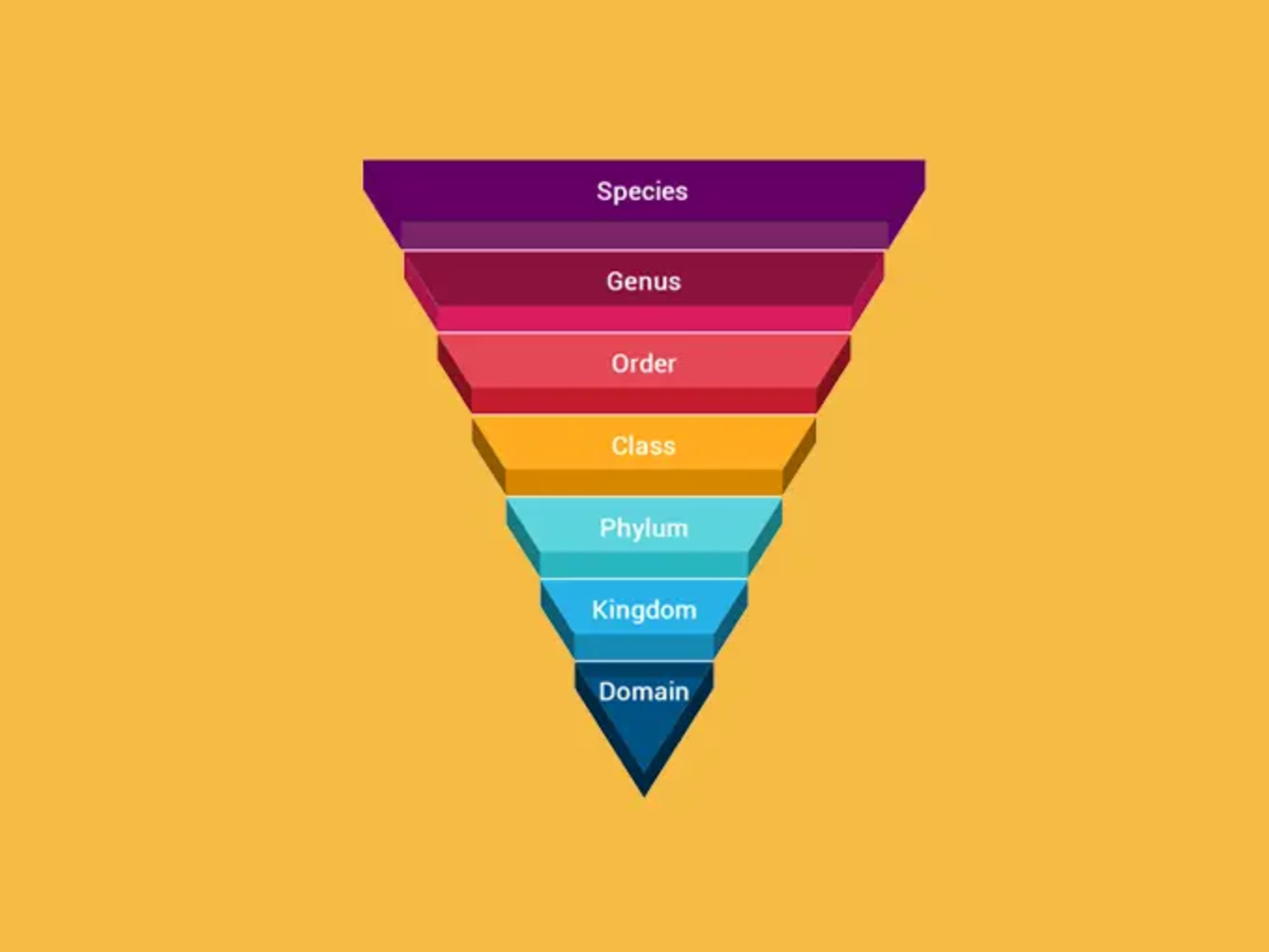
The Linnaean system categorizes organisms into seven hierarchical levels.
The Linnaean system organizes living organisms into a hierarchical classification that includes kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. This system provides a standardized framework for identifying and classifying all known species.
Taxonomists use morphological, genetic, and ecological data.
Taxonomists analyze various characteristics of organisms, including their physical appearance, genetic makeup, and ecological relationships, to determine their classification. Advances in molecular biology have significantly contributed to the understanding and refinement of taxonomic relationships.
Taxonomy helps scientists understand biodiversity.
By classifying and organizing organisms, taxonomy provides valuable insights into biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life on Earth. It helps scientists study the evolutionary relationships between species and identify patterns of species distribution across different habitats.
The study of taxonomy has practical applications.
Taxonomy plays a crucial role in fields such as agriculture, medicine, conservation, and evolutionary biology. It helps in identifying and understanding the characteristics of economically important plants and animals, developing effective conservation strategies, and studying the evolutionary history of species.
There are estimated to be millions of undiscovered species.
Despite significant advancements in taxonomy, much of the Earth’s biodiversity remains undiscovered. It is believed that millions of species, particularly microorganisms and insects, are yet to be identified and classified.
Taxonomy aids in species conservation efforts.
Efforts to conserve endangered species heavily rely on accurate taxonomic information. Proper identification and classification of species are essential for implementing conservation measures and protecting vulnerable ecosystems.
Some species have undergone reclassification over time.
As our understanding of taxonomy evolves, certain species may be reclassified based on new scientific evidence. This can lead to changes in their placement within the classification hierarchy.
Taxonomy can reveal evolutionary relationships.
Through taxonomy, scientists can discern the evolutionary relationships between different species. By studying shared traits and genetic similarities, they can reconstruct the evolutionary history of organisms and trace their common ancestors.
The exploration of new habitats often leads to taxonomic discoveries.
Expeditions to previously unexplored regions, such as deep-sea environments or remote rainforests, frequently result in the discovery of new species. Taxonomy plays a crucial role in identifying and classifying these newfound organisms.
Taxonomy has undergone advancements through the use of DNA sequencing.
Recent advancements in DNA sequencing technologies have revolutionized taxonomy. DNA analysis provides a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of genetic relationships between organisms, leading to more precise classifications.
Taxonomy helps in the identification of disease-causing organisms.
Taxonomy is vital in the identification and classification of pathogens responsible for diseases. Accurate species identification enables researchers to develop targeted treatments and preventive measures.
Taxonomy can aid in predicting species responses to environmental changes.
By understanding the taxonomic relationships and ecological requirements of different species, scientists can make predictions about their responses to environmental changes such as climate change or habitat destruction.
Taxonomy provides a standardized language for communication.
The hierarchical classification system of taxonomy allows scientists from different countries and disciplines to communicate using a standardized language. It facilitates the sharing of knowledge and promotes collaboration among researchers worldwide.
Conclusion
Taxonomy is a captivating field that allows us to understand and organize the incredible diversity of life on our planet. Through the classification and naming of species, taxonomy provides a framework for scientists to study and communicate about the living world. From the groundbreaking work of Carl Linnaeus to the modern advancements in molecular techniques, taxonomy continues to evolve, providing us with valuable insights into the relationships between species.
By exploring the 15 fascinating facts about taxonomy, we have gained a deeper appreciation for this scientific discipline. From the discovery of new species to the development of innovative classification systems, taxonomy reveals the intricacies and wonders of the natural world. So, the next time you encounter a plant or animal, take a moment to appreciate the fascinating world of taxonomy that underlies its identity and place in the broader web of life.
FAQs
1. What is taxonomy?
Taxonomy is the science of classification, involving the identification, naming, and categorization of organisms based on their characteristic features.
2. Why is taxonomy important?
Taxonomy is important because it helps scientists understand the relationships between species and allows for efficient communication within the scientific community.
3. How do taxonomists name new species?
Taxonomists follow a system of binomial nomenclature, assigning a unique scientific name to each species using a combination of genus and species names.
4. How many species have been identified so far?
While it is difficult to determine the exact number, scientists estimate that approximately 1.7 million species have been identified and named.
5. Can species be reclassified?
Yes, as our understanding of species improves and new information emerges, species can be reclassified to reflect their true evolutionary relationships.
6. Are all organisms classified using the same system?
No, different groups of organisms have their own specialized classification systems. For example, plants are classified using a system called taxonomy, while viruses have their own classification system.
7. How does taxonomy help conservation efforts?
Taxonomy plays a crucial role in conservation by identifying and monitoring endangered species, helping to inform conservation strategies and prioritize conservation efforts.
8. What are some challenges in taxonomy?
Some challenges in taxonomy include identifying and classifying cryptic species, resolving complex evolutionary relationships, and dealing with specimens that are difficult to access or preserve.
Taxonomy's fascinating world extends far beyond these captivating facts. Delving deeper into viral taxonomy uncovers astonishing revelations about nature's tiniest organisms. Molecular taxonomy harnesses cutting-edge techniques, offering unprecedented insights into life's building blocks. Invertebrate taxonomy, with its enigmatic creatures, holds secrets waiting to be unveiled. Each branch of taxonomy promises a thrilling journey of discovery, revealing the intricate tapestry of life on Earth. Explore these captivating realms and expand your understanding of the incredible diversity that surrounds us.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
