Ever wondered how your body manages to do everything from blinking to running without you having to think about it? Well, you're in for a treat! Our bodies are like finely tuned machines, with each part playing a crucial role in keeping us alive and kicking. From the heart pumping gallons of blood to the lungs bringing in life-giving oxygen, every system works in perfect harmony. But hey, there's more to it than just the basics. Did you know that the human body holds some mind-boggling secrets that are sure to make your jaw drop? Yes, the body system is a marvel of nature, packed with fascinating facts that are as intriguing as they are enlightening. Ready to have your mind blown by some of the most astonishing facts about the human body? Let's dive right in!
Key Takeaways:
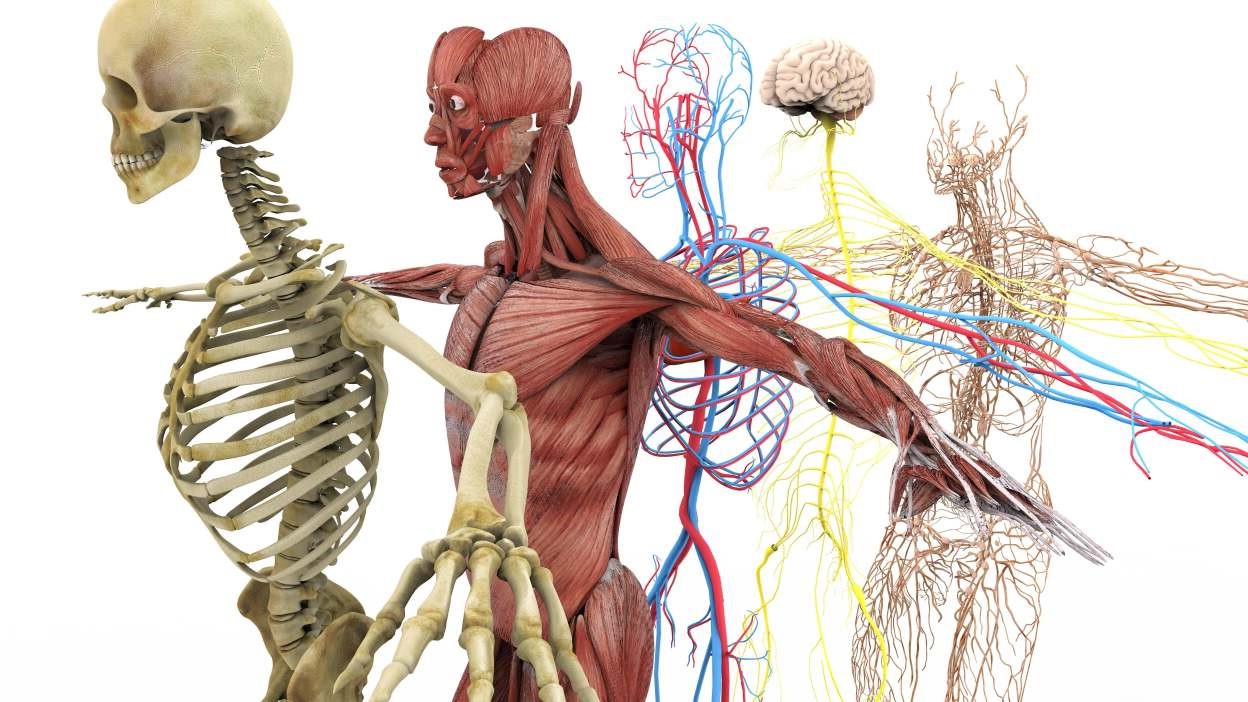
- The human body is a marvel of complexity, with 11 major systems working together to keep us alive and healthy. From the circulatory system's incredible endurance to the skeletal system's strength, our bodies are truly remarkable.
- Our bodies are full of fascinating facts, from the 100 billion neurons in the brain to the 600 muscles enabling movement. With the ability to regenerate cells, detect scents, and even laugh for better health, the human body is truly amazing.
Understanding the Complexity of the Human Body
The human body is an intricate network of systems working together to maintain life. Each system has its unique functions but collaborates closely with others to ensure our survival and well-being.
- Humans have 11 major body systems, including the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, excretory, nervous, endocrine, immune, integumentary, skeletal, muscle, and reproductive systems. Each plays a crucial role in keeping us alive and healthy.
The Marvels of the Circulatory System
Blood circulation is vital for transporting nutrients, oxygen, and waste products throughout the body. This system's efficiency is nothing short of remarkable.
-
The heart beats about 100,000 times a day, pumping approximately 2,000 gallons of blood through the body. This shows the heart's incredible endurance and capacity for work.
-
Blood travels a long journey daily. If you were to lay out all the blood vessels in the human body end to end, they would stretch over 60,000 miles. That's enough to circle the Earth more than twice!
Respiratory System: The Breath of Life
Breathing is an automatic process, yet it's complex and essential for life.
-
On average, an adult breathes around 12 to 20 times per minute. This rate can increase significantly during exercise or decrease in sleep.
-
The lungs are highly efficient at gas exchange. In a single day, they move about 11,000 liters (or roughly 2,900 gallons) of air.
The Digestive System's Incredible Journey
From ingestion to excretion, the digestive system performs a critical task of breaking down food to extract energy and nutrients.
-
The entire digestive tract is about 30 feet long in adults. That's as long as a school bus, illustrating the extensive path food travels in the body.
-
Digestion starts in the mouth, not the stomach. Saliva contains enzymes that begin breaking down food the moment it enters your mouth.
The Skeletal System: More Than Just Bones
Our bones do more than just provide structure; they're living tissues that perform several vital functions.
-
The human body has 206 bones. Babies are born with about 270 bones, but some fuse together as they grow.
-
Bones are stronger than steel when compared pound for pound. They can absorb a significant amount of impact without breaking, showcasing their incredible strength and resilience.
Muscular System: The Power of Movement
Muscles allow us to move, speak, and even breathe. They're constantly at work, even when we're at rest.
-
There are over 600 muscles in the human body, working together to enable movement and maintain posture.
-
Muscles can only pull, not push. This is why they usually work in pairs; while one muscle contracts to pull a bone in one direction, another muscle contracts to pull it back.
The Nervous System: A High-Speed Communication Network
The nervous system is the body's control center, sending and receiving messages at incredible speeds.
-
The human brain contains approximately 100 billion neurons. These cells communicate through synapses, with each neuron forming up to 10,000 connections with other neurons.
-
Nerve impulses can travel at speeds of up to 120 meters per second. This rapid communication allows the body to respond quickly to stimuli.
The Immune System: Our Defense Mechanism
Our bodies are constantly under attack from pathogens, but the immune system works tirelessly to protect us.
-
The human body produces about 17 million red blood cells per minute to replace those lost or destroyed, showcasing the body's remarkable ability to regenerate and defend itself.
-
White blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections. Their numbers can significantly increase in response to invaders, from a normal count of around 7,000 to 25,000 per microliter of blood.
The Endocrine System: Regulating Vital Functions
Hormones play a critical role in regulating bodily functions, from growth and metabolism to mood and reproduction.
-
The pituitary gland, often called the "master gland," controls other endocrine glands in the body and regulates growth, metabolism, and reproductive processes.
-
Thyroid hormones influence almost every cell in the body and regulate our metabolic rate, affecting how fast or slow our organs work.
The Excretory System: Eliminating Waste
Proper waste elimination is crucial for maintaining health and preventing disease.
-
The kidneys filter about 120 to 150 quarts of blood to produce 1 to 2 quarts of urine each day, removing waste and extra water from the body.
-
Sweat glands help regulate body temperature and remove waste through perspiration. Humans can produce up to a liter of sweat per day.
The Integumentary System: Our Protective Barrier
Our skin is the largest organ and serves as the first line of defense against external threats.
-
The skin regenerates itself approximately every 27 days, demonstrating the body's incredible capacity for healing and renewal.
-
Humans shed about 600,000 particles of skin every hour. Over a lifetime, this amounts to about 1.5 pounds of skin each year.
The Reproductive System: Ensuring Our Legacy
Reproduction is essential for the survival of the species, and the human reproductive system is designed for this purpose.
-
Sperm cells are the smallest cells in the human body, while egg cells are the largest. This size difference is one of nature's many fascinating contrasts.
-
The average lifespan of a sperm cell in the female reproductive tract is about 5 days, providing a brief window for fertilization to occur.
-
Human pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks, a time during which the fetus grows and develops inside the uterus until birth.
The Marvel of Human Life
-
Every second, the human body produces 25 million new cells. This cell production is essential for growth, healing, and replacing cells that die daily.
-
The human eye can distinguish approximately 10 million different colors, showcasing the incredible sensitivity and complexity of our visual system.
-
Our ears can detect a wide range of sounds, from the softest whisper to the loudest roar. This sensitivity allows us to communicate effectively and enjoy the world's sonic diversity.
-
The sense of touch is distributed unevenly across the body. Fingertips have the highest concentration of touch receptors, making them highly sensitive to changes in texture, pressure, and temperature.
-
Taste buds regenerate every 10 to 14 days, ensuring our sense of taste remains sharp and able to discern different flavors and substances.
-
The human nose can remember 50,000 different scents. This remarkable memory aids in recognizing familiar smells and detecting potential dangers.
-
Each person's tongue print is as unique as their fingerprints, adding another layer to the complexity of human identity.
-
The liver has the incredible ability to regenerate itself. Even if as much as 75% of the liver is removed, it can regrow to its full size.
-
Finally, laughter is not only a universal form of communication but also beneficial for the immune system. It can reduce stress and increase the production of antibodies, highlighting the interconnectedness of emotional well-being and physical health.
A Final Look at Our Body's Marvels
Our bodies are incredible machines, finely tuned and capable of amazing feats. From the power of the brain to the resilience of the immune system, every part works in harmony to keep us going. We've uncovered just a few of the countless wonders hidden within us, each fact a testament to the complexity and brilliance of human biology. Remember, these insights are just the tip of the iceberg. There's so much more to learn and appreciate about what makes us tick. So, next time you're pushing through a tough workout or marveling at your ability to learn something new, give a nod to the intricate systems at play. Here's to the remarkable, ever-surprising human body – a subject we'll never tire of exploring.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
