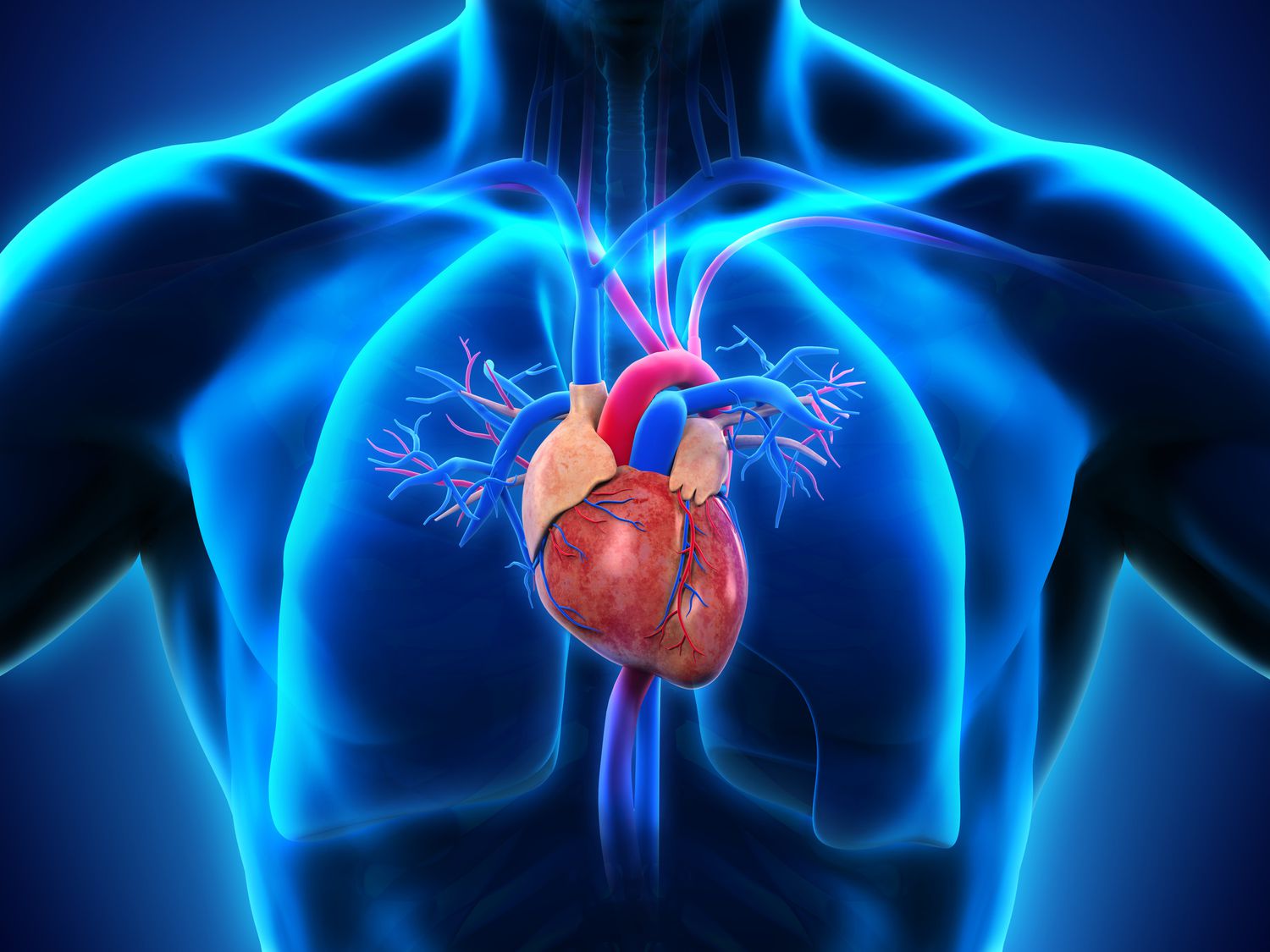
When it comes to human anatomy, there are countless fascinating structures that play important roles in our bodies. One such structure is the atria, which are found on both the left and right sides of the heart. These small chambers are vital components of the cardiovascular system and contribute to the efficient circulation of blood throughout the body.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of the atria, exploring their anatomy, function, and diverse characteristics. From their position within the heart to their role in the cardiac cycle, there is much to discover about these remarkable chambers. So, let’s embark on a journey of exploration as we uncover 11 captivating facts about the atria on both the left and right sides of the heart.
Key Takeaways:
- The atria, or the left and right chambers of the heart, play a crucial role in regulating blood flow and heart function, ensuring a steady and efficient heartbeat.
- Atrial fibrillation, a common disorder affecting the atria, can lead to irregular heartbeats and increase the risk of blood clots and other heart-related complications.
The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood.
The left atrium is responsible for receiving oxygenated blood from the lungs. This blood is then pumped into the left ventricle, which further distributes it to the rest of the body.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body’s tissues via the superior and inferior vena cava. This blood is then sent to the right ventricle to be pumped to the lungs for oxygenation.
The atria have thinner walls compared to the ventricles.
Unlike the muscular ventricles, the walls of the atria are relatively thinner. This difference in thickness allows for efficient contraction and relaxation of these chambers, facilitating blood flow.
The atria function as priming pumps.
By filling with blood during diastole, the atria act as priming pumps, preparing the ventricles for efficient contraction and ejection of blood during systole.
The atria help regulate heart rate.
The atria contribute to regulating heart rate by producing electrical signals that coordinate the contraction of the heart muscles. This ensures a steady and efficient heartbeat.
Atrial fibrillation is a common disorder.
Atrial fibrillation, a condition characterized by irregular and rapid heartbeat originating in the atria, affects millions of people worldwide. It can increase the risk of blood clots and other heart-related complications.
Both atria contract simultaneously.
During normal heart rhythm, both atria contract simultaneously, pushing blood into the ventricles. This coordinated contraction ensures an effective flow of blood through the heart.
Atria play a vital role in ventricular filling.
The atria play a crucial role in ventricular filling. As they contract, blood is propelled into the ventricles, helping to optimize cardiac output.
Atrial septal defects can occur at birth.
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect where there is a hole in the atrial wall. This condition can lead to abnormal blood flow and may require intervention or surgery.
The smooth walls of the atria prevent blood clot formation.
The atria have smooth walls without muscular ridges called trabeculae carneae, which reduces the risk of blood clot formation and helps maintain smooth blood flow.
Atrial enlargement can be a sign of heart disease.
Enlargement of the atria may occur in certain heart conditions such as atrial fibrillation or congestive heart failure. It is an indication that the heart is working harder and may require medical attention.
These are just a few captivating facts about atria (left and right). Understanding the importance of these chambers and their role in maintaining a healthy heart can help us appreciate the complexity and beauty of the human cardiovascular system.
Conclusion
The left and right atria are vital structures in the human heart. Understanding their functions and characteristics can help us appreciate the complexity and efficiency of our circulatory system.
The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it into the left ventricle, which then distributes it to the rest of the body. On the other hand, the right atrium receives oxygen-depleted blood from the body and sends it to the right ventricle to be pumped back to the lungs for oxygenation.
With their unique features and role in maintaining circulation, the atria play a crucial part in our overall health and well-being. Continual research and advancements in medical technology allow us to deepen our understanding of these captivating structures and improve treatments for various cardiovascular conditions.
FAQs
Q: What is the main function of the left atrium?
A: The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it into the left ventricle to be distributed throughout the body.
Q: What happens in the right atrium?
A: The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and sends it to the right ventricle for pumping it back to the lungs for oxygenation.
Q: Are the left and right atria the same size?
A: No, the left atrium is slightly smaller compared to the right atrium.
Q: Can problems occur in the atria?
A: Yes, various conditions can affect the atria, including arrhythmias, atrial fibrillation, and atrial septal defects.
Q: How are issues with the atria diagnosed?
A: Doctors often use diagnostic tools such as electrocardiograms (ECGs), echocardiograms, and cardiac catheterization to evaluate the health of the atria.
Q: Can lifestyle changes help maintain healthy atria?
A: Yes, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can contribute to maintaining the health of the atria.
Q: Can atrial fibrillation be cured?
A: While there is no permanent cure for atrial fibrillation, various treatment options are available to manage and control the condition.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
