What is Feline Hyperesthesia Syndrome? Feline Hyperesthesia Syndrome (FHS), also called rolling skin syndrome or twitchy cat disease, is a puzzling condition that makes cats extremely sensitive, especially around their lower back. Imagine your cat suddenly twitching, their skin rippling, or even chasing their tail like it's a game. These behaviors might seem quirky, but they can signal FHS. This syndrome often affects younger cats, particularly breeds like Siamese and Burmese. Symptoms range from skin twitching to obsessive grooming and even self-mutilation. While the exact cause remains a mystery, factors like anxiety, neurological issues, and skin problems are believed to play a role. Understanding FHS can help improve your cat's quality of life.
What is Feline Hyperesthesia Syndrome?
Feline Hyperesthesia Syndrome (FHS) is a mysterious condition affecting cats. It's marked by heightened skin sensitivity, especially on the lower back. Let's dive into some key facts about this intriguing syndrome.
-
Definition: Hyperesthesia means increased sensitivity to touch, a primary feature of FHS.
-
Common Names: Also called rolling skin syndrome, twitchy cat disease, apparent neuritis, and atypical neurodermatitis.
-
Age of Onset: Typically affects younger cats, with the average age of onset around one year old.
-
Breed Predisposition: Breeds like Abyssinian, Persian, Burmese, and Siamese are more prone to FHS.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms can help in early detection and management of FHS. Here are some common signs to look out for.
-
Symptoms: Cats may show rippling or twitching skin, dilated pupils, sudden bursts of activity, excessive meowing, tail-chasing, and biting or licking the lower back, sides, hind paws, rear, or tail.
-
Behavioral Changes: Compulsive behaviors such as excessive grooming, self-mutilation, and anxiety-related actions can occur.
What Causes Feline Hyperesthesia Syndrome?
The exact cause of FHS remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development.
-
Causes: Linked to skin problems, neurological issues, and psychological factors like anxiety and stress.
-
Neurological Factors: Some experts think FHS could be related to seizure disorders or other neurological conditions.
-
Dermatological Factors: Skin conditions like allergies, flea dermatitis, and fungal infections may contribute.
-
Psychological Factors: Anxiety, stress, and obsessive-compulsive behaviors are also potential contributors.
Complications and Related Issues
FHS can lead to several complications, making it essential to manage the condition effectively.
-
Self-Mutilation: In severe cases, cats may engage in self-mutilation, especially targeting the tail.
-
Tail Trauma: Trauma to the tail has been identified as a potential trigger for FHS in some cases.
-
Spinal Disease: Conditions like intervertebral disc disease can also contribute to FHS.
-
Muscle Problems: Muscle issues and pain can lead to spasms and twitching.
Managing Feline Hyperesthesia Syndrome
Managing FHS involves a combination of dietary changes, medications, and behavioral modifications.
-
Food Sensitivity: Food sensitivity might contribute to FHS.
-
Dietary Changes: Introducing a diet free from common allergens may help alleviate symptoms.
-
Nutritional Supplements: Supplements like omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, taurine, and B vitamins can support skin health and reduce inflammation.
-
Medications: Corticosteroids for skin inflammation, gabapentin for nerve pain and seizures, and clomipramine and fluoxetine for compulsive behaviors are commonly used.
-
Behavioral Modification: Techniques like providing interactive toys and safe spaces can help reduce anxiety and compulsive behaviors.
Creating a Supportive Environment
A calm and enriched environment can significantly help in managing FHS.
-
Environmental Enrichment: Strategies like regular play, changing toys regularly, and providing structures to climb on and scratch can reduce stress.
-
Anxiety Reduction: Consistent routines and minimizing stressors such as loud noises and sudden movements are crucial.
-
Pheromone Therapy: Pheromone diffusers and calming supplements like L-theanine or tryptophan can create a soothing environment.
-
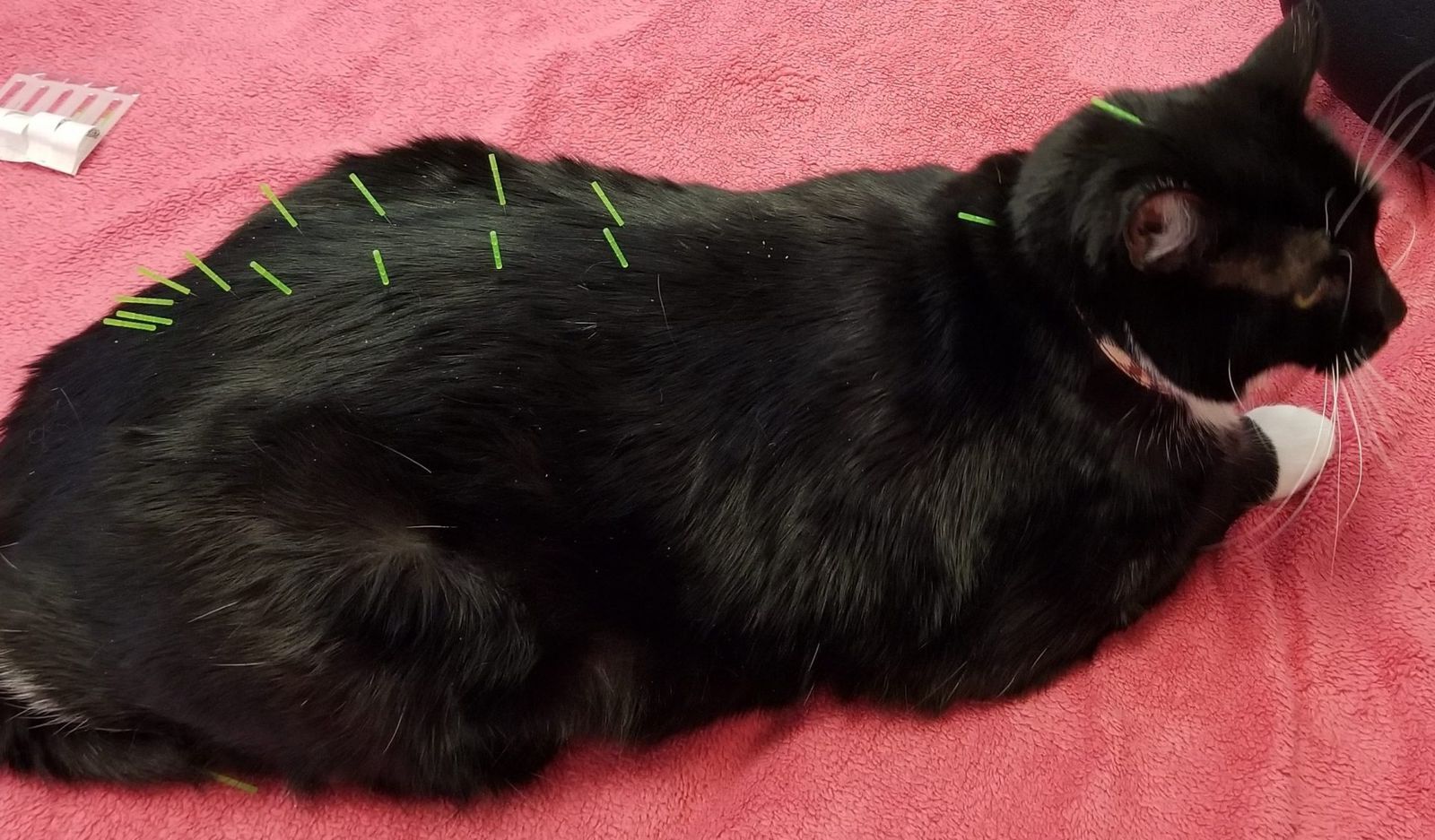
Acupuncture and Massage: Alternative therapies like acupuncture and massage may alleviate pain and reduce stress.
Diagnostic Challenges and Veterinary Care
Accurate diagnosis and ongoing veterinary care are essential for managing FHS effectively.
-
Diagnostic Challenges: Accurate diagnosis requires ruling out other possible causes of the observed behaviors.
-
Veterinary Care: Regular check-ups, monitoring of symptoms, and adjusting treatment plans as needed are crucial.
Home Environment and Preventive Measures
Creating a safe and comfortable home environment and taking preventive measures can help manage FHS.
-
Home Environment: Providing a calm and stable environment with minimal stressors, safe spaces, and regular play is crucial.
-
Preventive Measures: Keeping the cat indoors to reduce the risk of flea infestation and using year-round parasite preventives can help.
-
Stress Management: Managing stress through gradual changes in the home environment and using short-term anxiety medications if necessary can help.
Integrated Approach and Quality of Life
An integrated approach involving various specialists can help improve the quality of life for cats with FHS.
-
Integrated Approach: Involves veterinarians, behaviorists, and other specialists as needed.
-
Quality of Life: With appropriate treatment and care, most cats can lead happy and active lives despite FHS.
Understanding and Managing Feline Hyperesthesia Syndrome
Feline hyperesthesia syndrome is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach. Recognizing symptoms like skin rippling, muscle spasms, and behavioral changes is crucial for early intervention. While the exact cause remains elusive, factors like neurological issues, skin problems, and psychological stress play significant roles. Effective management often involves a combination of medications, dietary changes, and environmental enrichment. Regular veterinary care ensures that your cat receives the best possible treatment. By creating a calm, stress-free environment and providing appropriate medical and behavioral interventions, you can significantly improve your cat's quality of life. Remember, each cat is unique, so what works for one may not work for another. Stay observant, consult your vet regularly, and adjust treatments as needed to keep your feline friend happy and healthy.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


