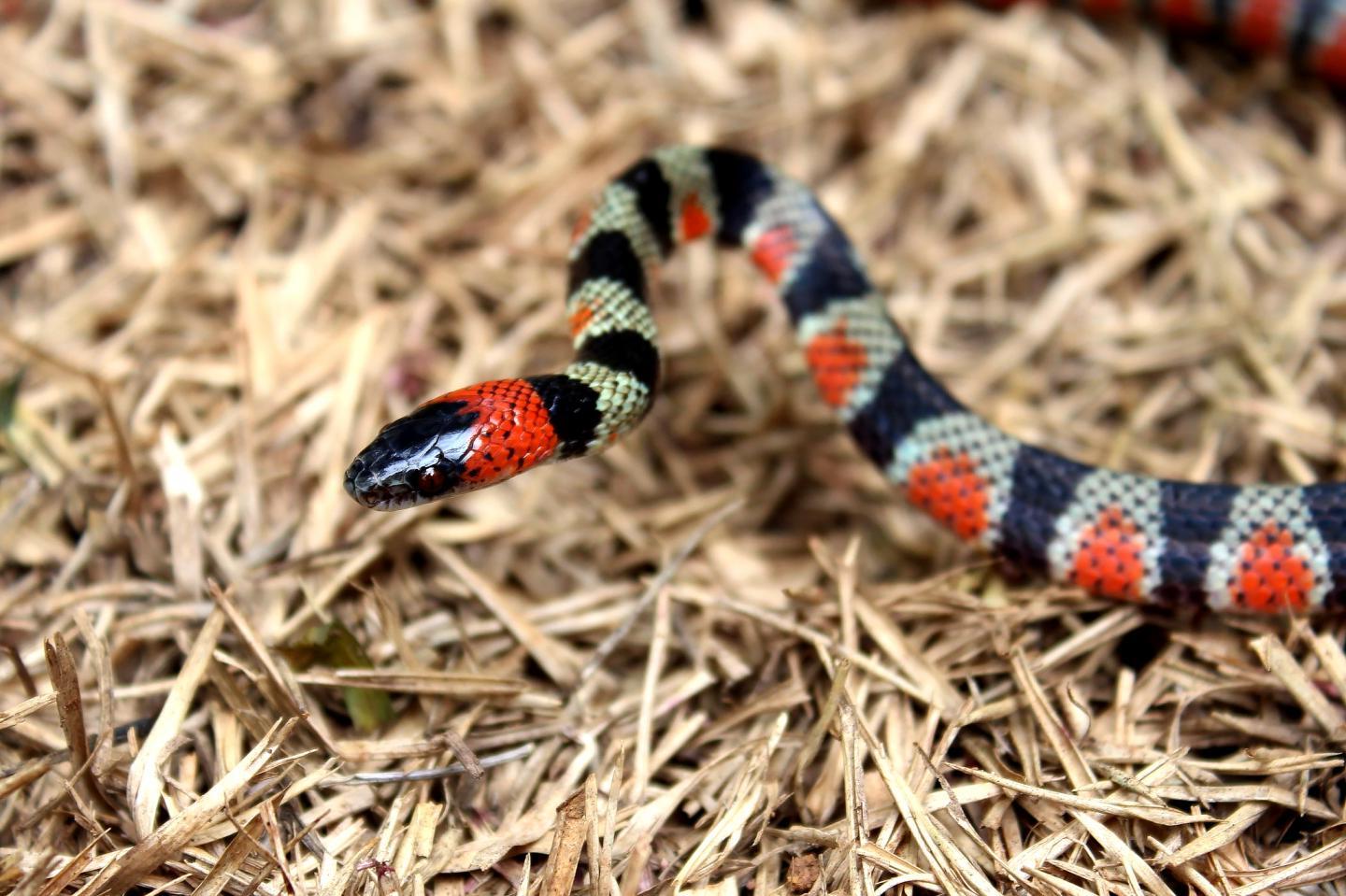
Snakes, often misunderstood creatures, exhibit a wide array of behaviors that are both intriguing and vital for their survival. Understanding snake behavior is key to appreciating these reptiles and debunking common myths surrounding them. From the way they hunt to how they communicate and navigate their environment, each action has a purpose. Snakes use their bodies in remarkable ways to sense heat, smell with their tongues, and even 'hear' through vibrations. Their behavior varies significantly across species, influenced by habitat, diet, and threat levels. This post will shed light on 22 fascinating facts about snake behavior, offering a glimpse into the complex lives of these fascinating reptiles. Whether you're a nature enthusiast or simply curious, these insights will deepen your understanding of snakes and their place in the natural world.
Understanding Snake Behavior
Snakes, often misunderstood creatures, exhibit fascinating behaviors that reflect their survival strategies and environmental adaptations. Their behavior varies widely among species, but some common patterns can be observed.
-
Snakes are primarily solitary animals, coming together only for mating or occasionally basking in the sun. This solitary nature helps reduce competition for food and increases survival chances by making them less noticeable to predators.
-
They use their tongues to smell. By flicking their tongues in the air, snakes pick up scent particles and transfer them to the Jacobson's organ in the mouth, providing crucial information about their surroundings, prey, and other snakes.
-
Many snakes are known for their ability to mimic the appearance or behavior of more dangerous species. This mimicry serves as a defense mechanism, deterring potential predators.
How Snakes Hunt and Feed
Snakes have developed various hunting techniques that showcase their adaptability and efficiency as predators.
-
Constriction is a common method among many species, where the snake coils around its prey and tightens its grip every time the prey exhales, eventually leading to suffocation.
-
Venomous snakes inject toxins through their fangs to immobilize or kill their prey. The composition of venom varies, with some targeting the nervous system and others causing tissue damage.
-
Some species have evolved to eat specific prey, such as eggs, which they swallow whole. Specialized adaptations, like the ability to unhinge their jaws, allow them to consume prey much larger than their heads.
Snake Communication
Despite their silent reputation, snakes communicate through a variety of subtle means.
-
Body language plays a significant role in snake communication. Postures such as coiling, flattening the body, or raising the head can indicate readiness to strike or a desire to avoid conflict.
-
Pheromones are chemical signals used extensively in mating rituals. Male snakes can follow a female's scent trail for miles to find a mate.
-
Some species vibrate their tails when threatened, which, in leaf litter or against hard surfaces, can mimic the sound of a rattlesnake as a warning to potential predators.
Navigating Their Environment
Snakes have adapted to a wide range of habitats, from deserts to rainforests, showcasing their incredible versatility.
-
Many snakes are excellent swimmers, with some species, like the sea snake, spending almost their entire lives in the ocean.
-
Arboreal snakes have developed prehensile tails and other adaptations for climbing trees, allowing them to hunt in the canopy and escape ground-based threats.
-
Desert-dwelling snakes have evolved ways to minimize contact with hot surfaces, such as sidewinding, a movement pattern that reduces their body's exposure to the scorching ground.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Snake reproduction varies widely among species, with some fascinating differences observed.
-
Some snakes lay eggs, while others give birth to live young. This trait can even vary within the same genus, depending on environmental conditions and evolutionary pressures.
-
Female snakes can store sperm for months after mating, choosing the optimal time to fertilize their eggs. This ability ensures that they give birth or lay eggs when conditions are most favorable for their offspring's survival.
-
In some species, the young are entirely independent from birth, receiving no care from their parents. This independence immediately subjects them to the same survival challenges as adult snakes.
Survival Strategies
Snakes employ various strategies to avoid predators and survive in the wild.
-
Camouflage is a common tactic, with many snakes having patterns that blend into their natural habitat, making them nearly invisible to both prey and predators.
-
When threatened, some snakes play dead, hoping to discourage predators looking for a fresh meal.
-
The notorious "hood" of a cobra is not just for show. By spreading their neck ribs, cobras appear larger and more intimidating to potential threats.
-
Hibernation or brumation (a form of hibernation for cold-blooded animals) allows snakes to survive cold temperatures by entering a state of dormancy, significantly reducing their metabolic rate.
Threats to Snakes
Despite their adaptability, snakes face significant threats from both natural and human sources.
-
Habitat destruction due to urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation is a major threat, leading to declining populations in many species.
-
Snakes are often killed on sight due to fear and misunderstanding, despite most species being harmless and beneficial by controlling rodent populations.
-
Climate change poses a significant threat, altering the habitats and ecosystems that snakes depend on for survival, potentially leading to a mismatch between snakes and their prey or breeding seasons.
Piecing Together the Serpentine Puzzle
We've journeyed through the fascinating world of snakes, uncovering behaviors that intrigue and educate. From their unique hunting techniques to the intricate ways they communicate, these creatures continue to captivate our curiosity. Understanding snake behavior is more than just an academic pursuit; it's a window into the resilience and adaptability of nature. By appreciating the complexity of these reptiles, we foster a greater respect for their role in our ecosystems. Whether it's their method of slithering silently or the way they sense their surroundings, each fact about snakes adds a piece to the puzzle of their mysterious lives. Let's keep our minds open and our fears at bay as we continue to learn about these remarkable animals. Their survival strategies and behaviors are not just fascinating—they're vital to the balance of the habitats they occupy.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.