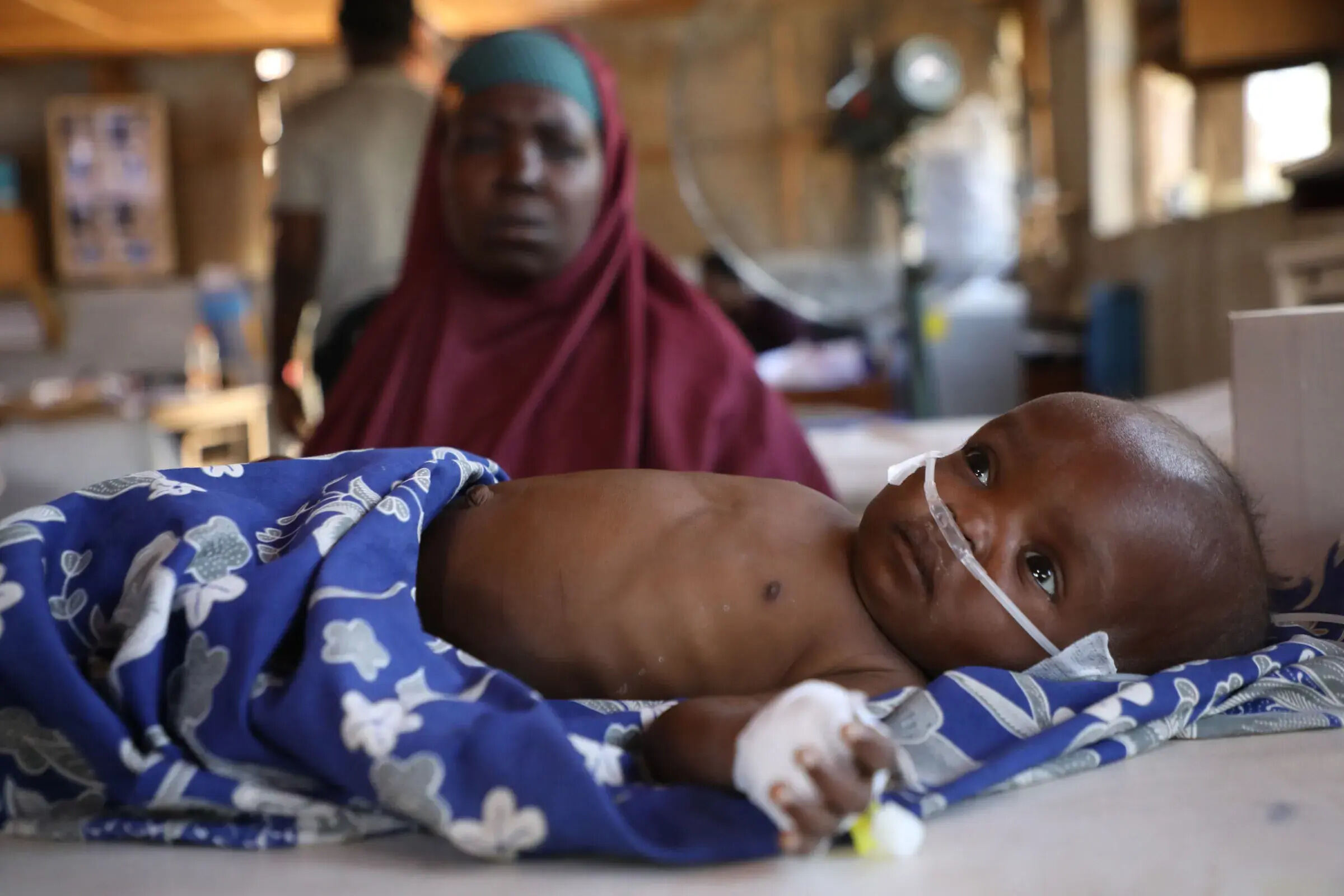
Lead poisoning is a serious health issue that affects millions worldwide, especially children. But what exactly is lead poisoning? It's a condition caused by the accumulation of lead in the body, often from sources like old paint, contaminated water, and certain toys. Even small amounts can cause severe health problems. Symptoms range from developmental delays in kids to high blood pressure in adults. Why should you care? Because lead poisoning is preventable. Knowing the facts can help you protect yourself and your loved ones. This article will provide 50 essential facts about lead poisoning, from its sources to its effects and prevention methods.
Key Takeaways:
- Lead poisoning can harm almost every part of your body, especially for kids. It can cause learning problems, anemia, and even affect unborn babies. Prevention and early treatment are crucial.
- Lead exposure can come from old paint, contaminated soil, and even water. It's important to test your home for lead and take steps to prevent exposure, like cleaning and using cold water for drinking.
What is Lead Poisoning?
Lead poisoning occurs when lead builds up in the body, often over months or years. Even small amounts can cause serious health problems. Here are some important facts about lead poisoning.
- Lead poisoning can affect almost every organ and system in your body.
- Children under the age of six are especially vulnerable to lead poisoning.
- Lead exposure can cause developmental delays in children.
- High levels of lead can cause seizures, coma, and even death.
- Lead poisoning is often caused by exposure to lead-based paint and lead-contaminated dust in older buildings.
Sources of Lead Exposure
Understanding where lead exposure comes from can help in preventing it. Here are some common sources.
- Lead-based paint in homes built before 1978 is a major source of lead exposure.
- Contaminated soil can also be a source of lead, especially near highways and industrial areas.
- Drinking water can become contaminated with lead from old pipes and plumbing fixtures.
- Some toys and jewelry may contain lead, posing a risk to children.
- Certain occupations, like construction and battery manufacturing, can expose workers to lead.
Symptoms of Lead Poisoning
Recognizing the symptoms of lead poisoning is crucial for early intervention. Here are some signs to watch for.
- Symptoms in children can include irritability, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Adults may experience high blood pressure, joint and muscle pain, and memory problems.
- Lead poisoning can cause abdominal pain and constipation.
- In severe cases, lead poisoning can lead to neurological damage.
- Symptoms often develop slowly, making it hard to diagnose early.
Health Effects of Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning can have long-lasting effects on health. Here are some of the potential impacts.
- Lead can damage the brain and nervous system.
- It can cause learning and behavior problems in children.
- Lead exposure can result in reduced IQ and attention span.
- It can also cause anemia by affecting red blood cell production.
- Pregnant women exposed to lead can pass it to their unborn babies, causing developmental issues.
Diagnosing Lead Poisoning
Early diagnosis is key to managing lead poisoning. Here’s how it’s done.
- Blood tests are the most common way to diagnose lead poisoning.
- Doctors may also ask about potential sources of lead exposure.
- X-rays can sometimes show lead particles in the body.
- In some cases, bone scans may be used to detect lead.
- Regular screening is recommended for children at risk.
Treating Lead Poisoning
Treatment can help reduce lead levels in the body. Here are some common methods.
- Removing the source of lead exposure is the first step in treatment.
- Chelation therapy uses medication to bind lead so it can be excreted from the body.
- EDTA therapy is another treatment option for severe cases.
- Nutritional changes, like increasing calcium and iron intake, can help reduce lead absorption.
- Ongoing medical monitoring is often necessary to ensure lead levels remain low.
Preventing Lead Poisoning
Prevention is the best way to protect against lead poisoning. Here are some strategies.
- Regularly clean floors, windowsills, and other surfaces to reduce lead dust.
- Wash children’s hands and toys frequently to prevent ingestion of lead particles.
- Use cold water for drinking and cooking, as hot water is more likely to contain lead.
- Test your home for lead if it was built before 1978.
- Ensure that renovations in older homes are done safely to avoid spreading lead dust.
Lead Poisoning in History
Lead poisoning has been a problem for centuries. Here are some historical facts.
- Ancient Romans used lead pipes for plumbing, leading to widespread lead exposure.
- Lead-based cosmetics were popular in the 18th and 19th centuries.
- The use of leaded gasoline contributed to environmental lead contamination until it was phased out in the 1980s.
- Lead poisoning was first recognized as a medical condition in the early 20th century.
- Public health campaigns in the 1970s and 1980s led to significant reductions in lead exposure.
Global Impact of Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning is a worldwide issue. Here are some global facts.
- An estimated 1 million people die each year from lead poisoning.
- Developing countries often have higher rates of lead exposure due to less stringent regulations.
- International efforts are underway to eliminate lead in paint and gasoline.
- The World Health Organization considers lead poisoning one of the top environmental health threats.
- Lead poisoning disproportionately affects low-income communities.
Interesting Facts About Lead
Lead has some unique properties and uses. Here are a few interesting tidbits.
- Lead is a heavy metal that is soft and malleable.
- It has been used in batteries, radiation shielding, and even stained glass windows.
- Lead’s symbol on the periodic table is Pb, from the Latin word "plumbum."
- Despite its dangers, lead is still used in some industrial applications.
- Lead poisoning awareness has led to significant public health improvements over the past few decades.
Final Thoughts on Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning remains a serious health issue. Understanding its sources, symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial for safeguarding health. Exposure often comes from old paint, contaminated soil, and certain household items. Symptoms can range from headaches and stomach pain to more severe neurological effects. Children are especially vulnerable, making it vital to keep homes lead-free.
Preventive measures include regular home inspections, proper cleaning, and avoiding products known to contain lead. If exposure is suspected, seeking medical advice promptly can prevent long-term damage. Awareness and proactive steps can significantly reduce risks.
By staying informed and vigilant, we can protect ourselves and our loved ones from the dangers of lead poisoning. Knowledge truly is power in this fight. Stay safe, stay healthy, and keep learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
