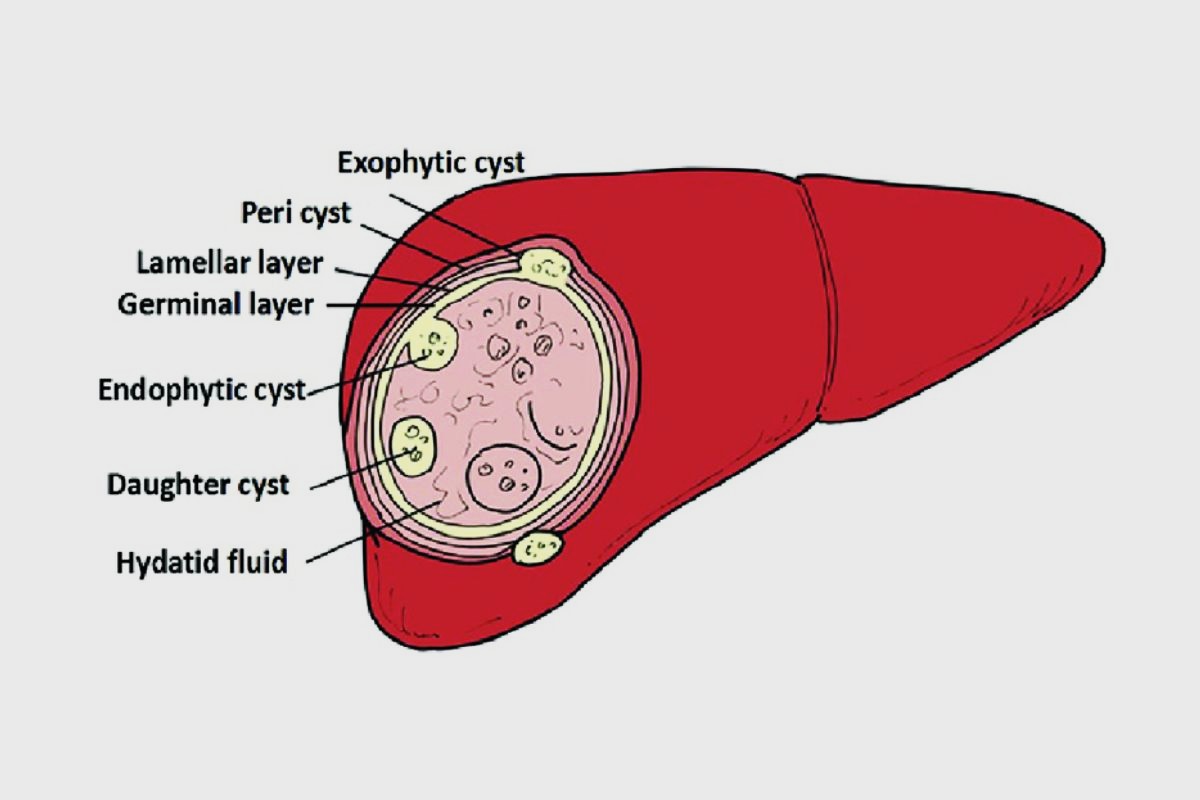
Hydatid disease, also known as echinococcosis, is a parasitic infection caused by the larvae of tapeworms from the genus Echinococcus. This disease primarily affects the liver and lungs but can spread to other organs. Humans become accidental hosts by ingesting eggs from contaminated food, water, or soil, often through contact with infected animals like dogs or livestock. Symptoms can vary widely, from mild discomfort to severe organ dysfunction, depending on the cyst's location and size. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. Let's dive into 36 intriguing facts about hydatid disease that will help you understand this condition better.
What is Hydatid Disease?
Hydatid disease, also known as echinococcosis, is a parasitic infection caused by the Echinococcus tapeworm. This disease primarily affects the liver and lungs but can spread to other parts of the body. Here are some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Hydatid disease is caused by the Echinococcus tapeworm. This tiny parasite can cause large cysts in the organs of its host.
-
Humans are accidental hosts. The primary hosts are usually dogs and other canines, while sheep, cattle, and other herbivores serve as intermediate hosts.
-
The disease is more common in rural areas. Places where livestock farming is prevalent see higher rates of infection.
-
Echinococcus granulosus is the most common species. This species is responsible for cystic echinococcosis, the most widespread form of the disease.
-
Echinococcus multilocularis causes alveolar echinococcosis. This form is more severe and can be fatal if untreated.
-
Humans get infected by ingesting tapeworm eggs. These eggs are usually found in contaminated food, water, or soil.
-
Dogs play a crucial role in the transmission. They can carry the adult tapeworm in their intestines and shed eggs in their feces.
-
The disease can remain asymptomatic for years. Cysts grow slowly, and symptoms often appear only when they become large enough to cause problems.
-
Liver is the most commonly affected organ. About 70% of hydatid cysts are found in the liver.
-
Lung involvement is also common. Around 20% of cases have cysts in the lungs.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how hydatid disease is diagnosed can help in early detection and treatment.
-
Symptoms depend on the cyst's location. Liver cysts can cause abdominal pain, while lung cysts might lead to coughing and chest pain.
-
Jaundice can occur if the bile ducts are obstructed. This happens when liver cysts grow large enough to block bile flow.
-
Ruptured cysts can cause severe allergic reactions. This can lead to anaphylactic shock, which is life-threatening.
-
Ultrasound is the primary diagnostic tool. It helps in visualizing the cysts in the organs.
-
CT scans and MRIs provide detailed images. These imaging techniques are used to assess the extent of the disease.
-
Serological tests detect antibodies. These blood tests help confirm the diagnosis by identifying the body's immune response to the parasite.
-
Biopsy is rarely needed. It is usually avoided due to the risk of cyst rupture and spreading the infection.
-
Early diagnosis improves treatment outcomes. Timely detection allows for better management and reduces complications.
Treatment Options
Treating hydatid disease involves a combination of medication and surgical intervention.
-
Albendazole is the most commonly used drug. This antiparasitic medication helps shrink the cysts and kill the larvae.
-
Mebendazole is another effective drug. It works similarly to albendazole but is used less frequently.
-
Surgery is often required for large cysts. Removing the cysts can prevent complications and improve symptoms.
-
PAIR technique is a minimally invasive option. PAIR stands for Puncture, Aspiration, Injection, and Re-aspiration, and it is used to drain the cysts.
-
Laparoscopic surgery is less invasive. This technique uses small incisions and a camera to remove the cysts.
-
Post-surgery medication is crucial. Continuing antiparasitic drugs after surgery helps prevent recurrence.
-
Regular follow-up is necessary. Monitoring for any new cysts or complications ensures long-term health.
Prevention and Control
Preventing hydatid disease involves breaking the transmission cycle between animals and humans.
-
Deworming dogs regularly is essential. This reduces the number of adult tapeworms in the primary hosts.
-
Proper disposal of animal carcasses is crucial. This prevents dogs from eating infected organs and spreading the disease.
-
Good hygiene practices can prevent infection. Washing hands thoroughly after handling animals or soil reduces the risk.
-
Avoiding raw or undercooked meat is important. Cooking meat properly kills any tapeworm eggs present.
-
Public health education raises awareness. Informing communities about the disease helps in adopting preventive measures.
-
Vaccinating livestock can reduce transmission. Vaccines for sheep and other intermediate hosts are being developed.
-
Regular veterinary checks for pets help. Ensuring pets are healthy and free from parasites protects human health.
-
Controlling stray dog populations is necessary. Stray dogs are more likely to carry the tapeworm and spread the disease.
-
Safe water and sanitation are vital. Access to clean water and proper sanitation facilities reduces contamination.
-
Government policies support control efforts. Implementing and enforcing regulations helps in managing the disease.
-
International cooperation is needed. Working together across borders can effectively control and eventually eradicate hydatid disease.
Final Thoughts on Hydatidiform Mole
Hydatidiform mole, though rare, is a serious condition requiring prompt medical attention. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can make a significant difference in outcomes. Early detection through regular prenatal care is key. If diagnosed, treatment options like dilation and curettage (D&C) or medication can effectively manage the condition. Follow-up care is crucial to monitor for any complications or recurrence. Emotional support and counseling can also help those affected cope with the stress and uncertainty. Staying informed and vigilant can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to dealing with complex medical conditions like hydatidiform mole. Stay educated, seek medical advice when needed, and prioritize your well-being.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
