Eosinophilia might sound like a complicated medical term, but it's simply a condition where your body has too many eosinophils, a type of white blood cell. These cells help fight off infections and play a role in your immune response. However, having too many can signal issues like allergies, infections, or even more serious conditions. What causes eosinophilia? It can be triggered by various factors including parasitic infections, allergic reactions, certain medications, and autoimmune diseases. Symptoms can range from mild, like a rash, to severe, such as organ damage. Understanding eosinophilia can help you recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment. Let's dive into 36 intriguing facts about this condition to better understand its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
What is Eosinophilia?
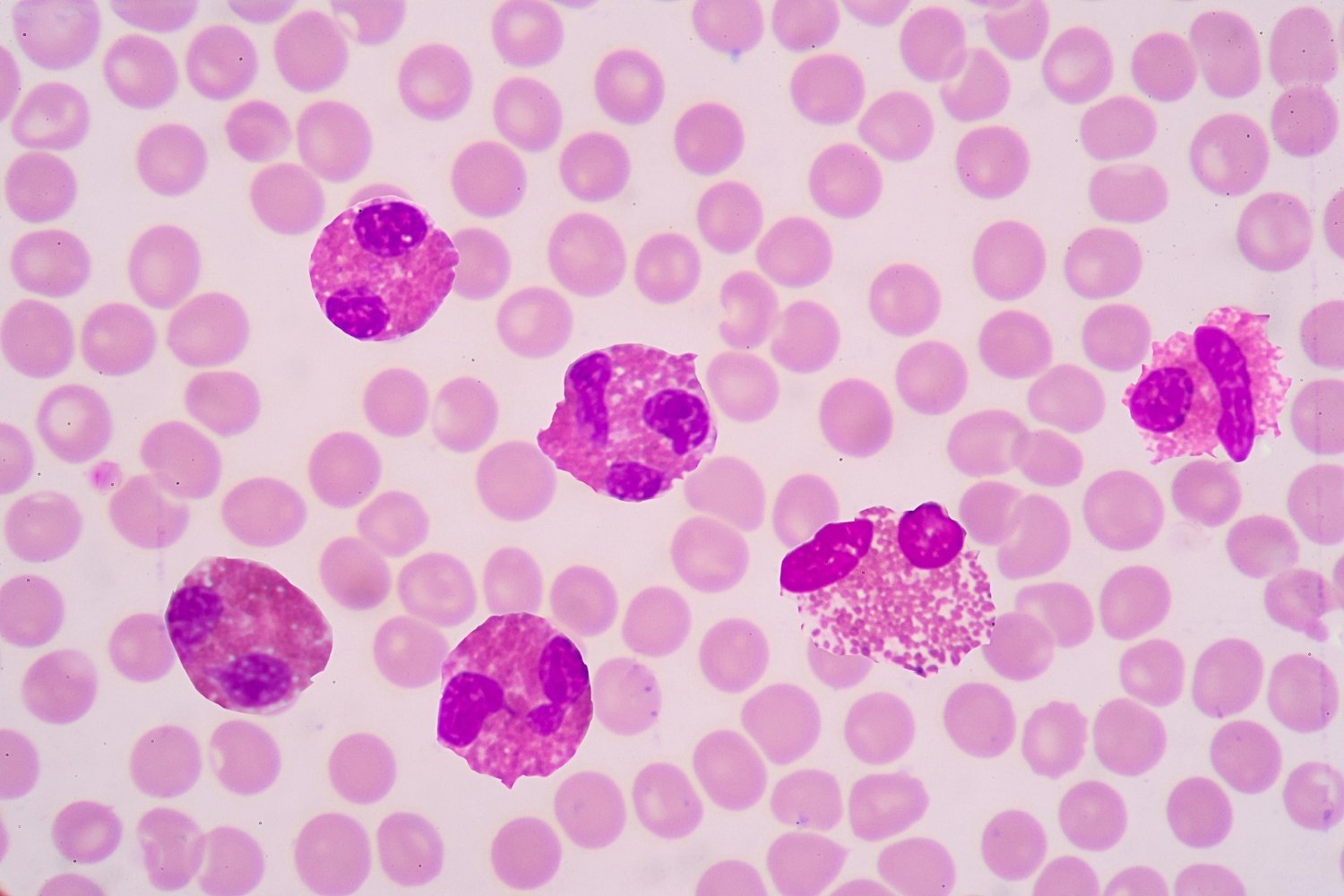
Eosinophilia is a condition where the body has an unusually high number of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell. These cells play a crucial role in the immune system, especially in fighting off parasites and responding to allergies.
- Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that makes up about 1-4% of the total white blood cell count in a healthy person.
- The normal range of eosinophils in the blood is between 100 and 500 cells per microliter.
- Eosinophilia is diagnosed when the eosinophil count exceeds 500 cells per microliter.
- There are two types of eosinophilia: primary and secondary. Primary is due to disorders in the bone marrow, while secondary is caused by other conditions like infections or allergies.
Causes of Eosinophilia
Eosinophilia can be triggered by various factors. Understanding these causes can help in diagnosing and treating the condition effectively.
- Parasitic infections are one of the most common causes of eosinophilia, especially in tropical regions.
- Allergic reactions, including asthma and hay fever, can lead to elevated eosinophil levels.
- Certain medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, can cause eosinophilia as a side effect.
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can also result in high eosinophil counts.
- Some cancers, particularly those affecting the blood and bone marrow, can lead to eosinophilia.
- Skin conditions like eczema and dermatitis are often associated with increased eosinophil levels.
Symptoms of Eosinophilia
Symptoms of eosinophilia vary depending on the underlying cause. Some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
- Common symptoms include fatigue, fever, and cough.
- Skin rashes and itching are frequent in cases related to allergies or skin conditions.
- Respiratory symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath are common in eosinophilia caused by asthma.
- Gastrointestinal issues such as abdominal pain and diarrhea can occur if the condition is related to parasitic infections.
- Muscle pain and joint swelling may be present in eosinophilia linked to autoimmune diseases.
Diagnosing Eosinophilia
Diagnosing eosinophilia involves a series of tests to determine the eosinophil count and identify the underlying cause.
- A complete blood count (CBC) is the primary test used to measure eosinophil levels.
- Blood smears can help visualize eosinophils and other blood cells under a microscope.
- Bone marrow biopsy may be necessary if a bone marrow disorder is suspected.
- Stool tests can detect parasitic infections that might be causing eosinophilia.
- Allergy tests, including skin prick tests, can identify allergens triggering the condition.
- Imaging tests like X-rays and CT scans can help detect organ involvement or tumors.
Treatment Options for Eosinophilia
Treatment for eosinophilia focuses on addressing the underlying cause. The approach varies depending on the specific condition leading to elevated eosinophil levels.
- Antiparasitic medications are effective in treating eosinophilia caused by parasitic infections.
- Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and lower eosinophil counts in cases related to allergies and autoimmune diseases.
- Discontinuing or switching medications can resolve drug-induced eosinophilia.
- Immunosuppressive drugs may be prescribed for severe autoimmune conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are options for treating eosinophilia caused by cancer.
- Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding known allergens, can help manage symptoms.
Complications of Eosinophilia
If left untreated, eosinophilia can lead to serious complications. Awareness of these potential issues is crucial for timely intervention.
- Chronic eosinophilia can cause damage to organs like the heart, lungs, and liver.
- Eosinophilic myocarditis is a rare but severe condition where eosinophils infiltrate the heart muscle.
- Eosinophilic pneumonia occurs when eosinophils accumulate in the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Gastrointestinal complications include eosinophilic esophagitis, which causes inflammation of the esophagus.
- Neurological issues like peripheral neuropathy can arise if eosinophils affect the nervous system.
- Blood clotting disorders may develop due to high eosinophil levels affecting blood vessels.
Preventing Eosinophilia
While not all cases of eosinophilia can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing this condition.
- Practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, can prevent parasitic infections.
- Avoiding known allergens and irritants can help manage allergy-related eosinophilia.
- Regular medical check-ups can detect early signs of eosinophilia and its underlying causes.
Final Thoughts on Eosinophilia
Eosinophilia, a condition marked by high levels of eosinophils in the blood, can signal various health issues. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Common triggers include allergies, infections, and certain medications. Symptoms might range from mild, like fatigue, to severe, such as organ damage.
Diagnosis often involves blood tests and sometimes bone marrow exams. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause, which might involve medications like corticosteroids or antihistamines. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding allergens and maintaining a healthy diet, can also help manage symptoms.
Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers ensures better management of eosinophilia. Knowledge empowers patients to take proactive steps in their health journey. Always consult a medical professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
