Dyspepsia, often called indigestion, is a common issue that affects many people worldwide. But what exactly is it? Dyspepsia refers to a group of symptoms that cause discomfort in the upper abdomen. These symptoms can include bloating, nausea, and burping. Many factors can trigger dyspepsia, such as overeating, spicy foods, or stress. Sometimes, it can be a sign of an underlying condition like GERD or ulcers. Understanding the causes and symptoms of dyspepsia can help manage and prevent it. Let's dive into 36 interesting facts about dyspepsia that will help you better understand this common digestive problem.
What is Dyspepsia?
Dyspepsia, commonly known as indigestion, is a term used to describe discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen. It is a common issue that many people experience at some point in their lives. Here are some intriguing facts about dyspepsia.
-
Dyspepsia affects about 20-30% of the population globally. This means millions of people experience this discomfort regularly.
-
Symptoms of dyspepsia include bloating, nausea, burping, and a feeling of fullness after eating. These symptoms can vary in intensity from person to person.
-
Dyspepsia is not a disease but a symptom of other conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastritis. It often signals an underlying issue.
-
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate dyspepsia symptoms. Mental health plays a significant role in digestive health.
-
Eating too quickly or overeating can trigger dyspepsia. Taking time to eat slowly and mindfully can help prevent symptoms.
Causes of Dyspepsia
Understanding what causes dyspepsia can help in managing and preventing it. Here are some key causes.
-
Certain foods and drinks, like spicy foods, fatty foods, chocolate, and caffeine, can trigger dyspepsia. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can reduce symptoms.
-
Smoking and alcohol consumption are known to worsen dyspepsia. Both can irritate the stomach lining and increase acid production.
-
Medications such as NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can cause dyspepsia. Always consult a doctor before taking new medications.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection, a common bacterial infection in the stomach, can lead to dyspepsia. This infection is treatable with antibiotics.
-
Peptic ulcers, which are sores on the lining of the stomach or small intestine, can cause dyspepsia. These ulcers require medical treatment.
Diagnosing Dyspepsia
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some facts about diagnosing dyspepsia.
-
Doctors often start with a detailed medical history and physical examination. This helps identify potential causes and rule out serious conditions.
-
Blood tests can help detect infections or other issues that might be causing dyspepsia. These tests provide valuable information about overall health.
-
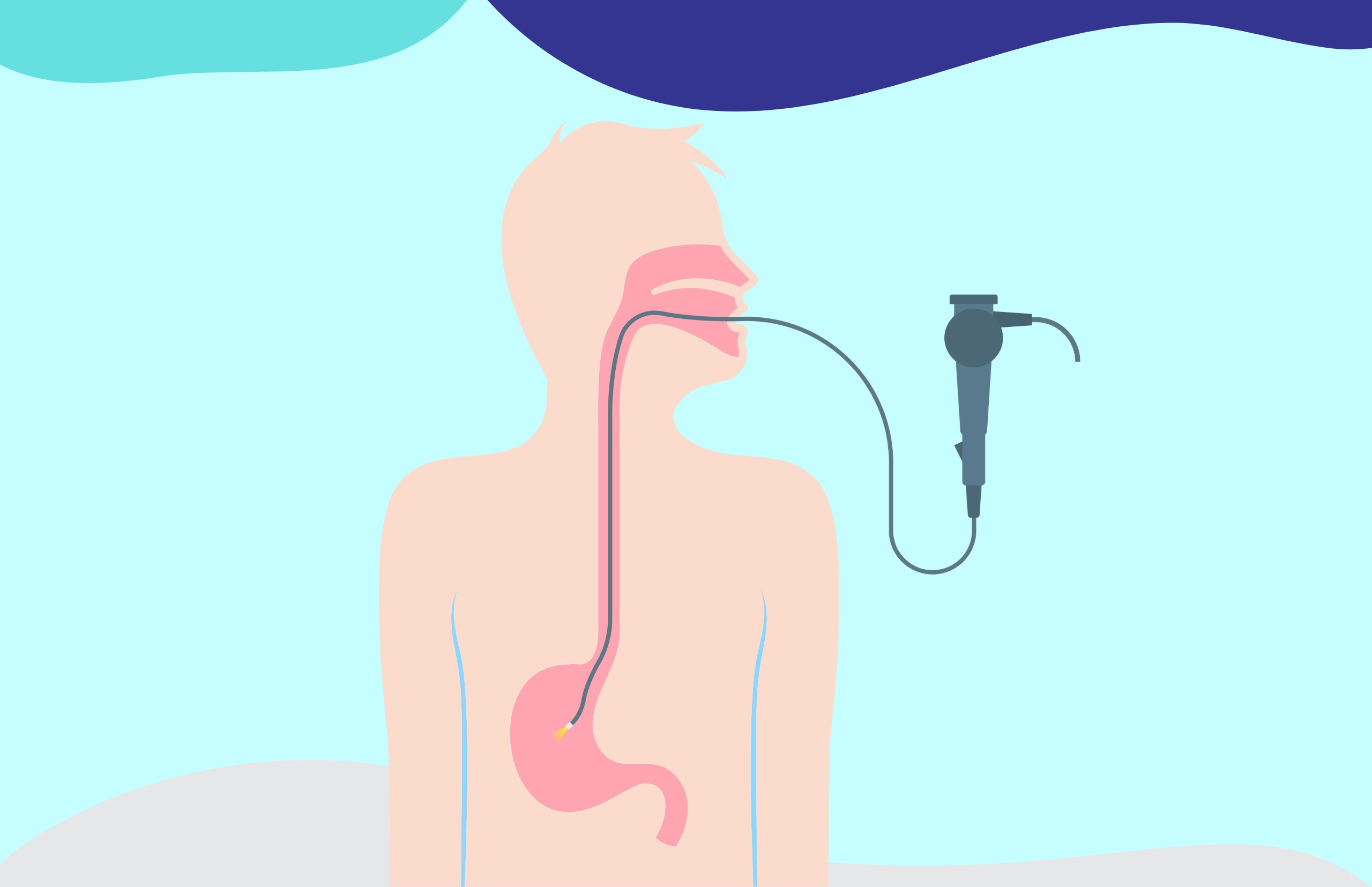
Endoscopy is a procedure where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the stomach. It allows doctors to see the stomach lining and identify any abnormalities.
-
Imaging tests like X-rays or ultrasounds can also be used to diagnose dyspepsia. These tests provide a clear picture of the digestive organs.
-
Sometimes, a breath test is used to detect Helicobacter pylori infection. This non-invasive test is simple and effective.
Treatment Options for Dyspepsia
There are various ways to manage and treat dyspepsia. Here are some common treatment options.
-
Lifestyle changes, such as eating smaller meals and avoiding trigger foods, can significantly reduce symptoms. These changes are often the first step in treatment.
-
Over-the-counter antacids can provide quick relief from dyspepsia. They neutralize stomach acid and ease discomfort.
-
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are medications that reduce stomach acid production. They are often prescribed for chronic dyspepsia.
-
H2-receptor antagonists are another type of medication that reduces stomach acid. They are available both over-the-counter and by prescription.
-
Antibiotics are used to treat Helicobacter pylori infection. Eradicating this infection can alleviate dyspepsia symptoms.
Preventing Dyspepsia
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips to prevent dyspepsia.
-
Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help prevent dyspepsia. A healthy diet supports overall digestive health.
-
Avoiding large meals and eating smaller, more frequent meals can reduce the risk of dyspepsia. This helps the stomach digest food more easily.
-
Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is essential. Water aids digestion and prevents stomach irritation.
-
Regular exercise can improve digestion and reduce stress. Both factors play a role in preventing dyspepsia.
-
Avoiding lying down immediately after eating can prevent dyspepsia. It’s best to wait at least two hours before lying down.
Interesting Facts About Dyspepsia
Here are some lesser-known facts about dyspepsia that might surprise you.
-
Dyspepsia can sometimes mimic the symptoms of a heart attack. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience severe chest pain.
-
Some people are more prone to dyspepsia due to genetic factors. Family history can play a role in digestive health.
-
Dyspepsia is more common in women than men. Hormonal differences might contribute to this disparity.
-
Children can also experience dyspepsia. It’s important to monitor their symptoms and seek medical advice if needed.
-
Dyspepsia can affect sleep quality. Discomfort and pain can make it difficult to get a good night’s sleep.
Myths About Dyspepsia
There are many myths surrounding dyspepsia. Here are some common ones debunked.
-
Myth: Dyspepsia is always caused by spicy food. Fact: While spicy food can trigger symptoms, it’s not the only cause.
-
Myth: Only older adults get dyspepsia. Fact: Dyspepsia can affect people of all ages, including children.
-
Myth: Drinking milk can cure dyspepsia. Fact: Milk might provide temporary relief, but it can also increase stomach acid production later.
-
Myth: Dyspepsia is always a sign of a serious condition. Fact: While it can indicate an underlying issue, it’s often caused by less serious factors like diet or stress.
-
Myth: You should avoid all fat if you have dyspepsia. Fact: Healthy fats, like those found in avocados and nuts, can be part of a balanced diet.
-
Myth: Dyspepsia will go away on its own. Fact: While mild cases might resolve without treatment, persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a doctor.
Final Thoughts on Dyspepsia
Dyspepsia, often called indigestion, affects many people worldwide. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help manage this common condition. Key symptoms include bloating, nausea, and stomach pain. Causes range from overeating to stress and certain medications. Simple lifestyle changes like eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, and managing stress can make a big difference. Over-the-counter medications and natural remedies like ginger or peppermint tea also provide relief. If symptoms persist, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Knowledge is power, and being informed about dyspepsia can lead to better health and well-being. Stay proactive, listen to your body, and don't hesitate to seek medical advice when needed.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
