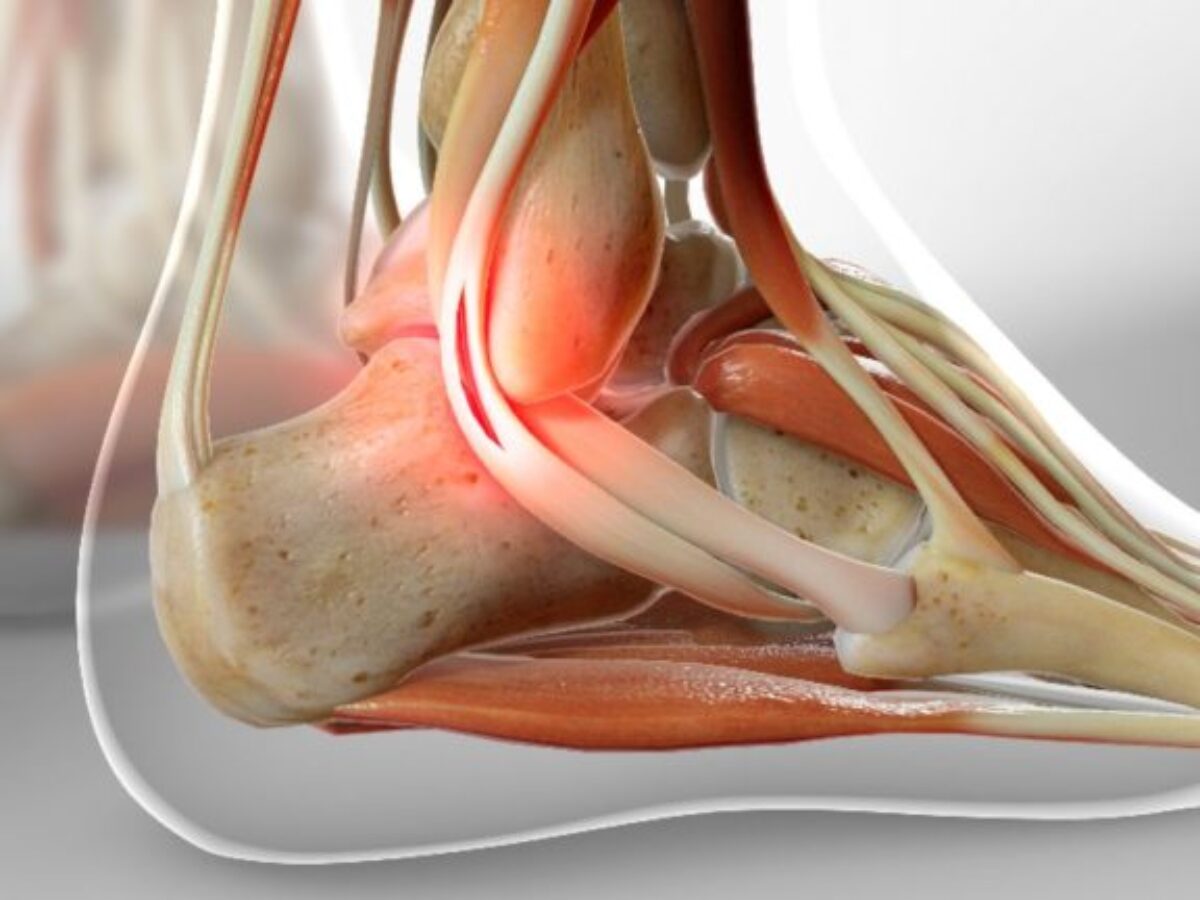
What is the peroneal nerve? The peroneal nerve is a crucial part of the nervous system that helps control movement and sensation in the lower leg and foot. It branches off from the sciatic nerve, running down the leg to the foot. This nerve plays a key role in lifting the foot and toes, making walking and balance possible. Injuries to the peroneal nerve can lead to foot drop, where lifting the front part of the foot becomes difficult. Understanding the peroneal nerve's function and importance can help in recognizing symptoms of nerve damage and seeking timely medical care.
What is the Peroneal Nerve?
The peroneal nerve is a crucial part of the nervous system. It plays a significant role in movement and sensation in the lower leg and foot. Here are some fascinating facts about this important nerve.
- The peroneal nerve is also known as the common fibular nerve.
- It branches off from the sciatic nerve, which is the longest nerve in the body.
- This nerve splits into two main branches: the superficial peroneal nerve and the deep peroneal nerve.
- The superficial peroneal nerve provides sensation to the top of the foot and the lower part of the leg.
- The deep peroneal nerve controls the muscles that lift the foot and toes.
- Damage to the peroneal nerve can cause foot drop, a condition where you can't lift the front part of your foot.
Functions of the Peroneal Nerve
Understanding the functions of the peroneal nerve helps us appreciate its importance in daily activities like walking and running.
- The peroneal nerve helps with dorsiflexion, which is the action of lifting the foot upwards.
- It also assists in eversion, which is turning the sole of the foot outward.
- This nerve is responsible for providing sensation to the skin over the upper third of the lateral part of the leg.
- It plays a role in balance and stability while standing and moving.
- The peroneal nerve helps in the coordination of lower leg muscles.
Common Injuries and Conditions
Injuries to the peroneal nerve can lead to various conditions that affect mobility and sensation.
- Peroneal nerve palsy is a condition where the nerve is compressed or damaged, leading to weakness or paralysis of the muscles it controls.
- Trauma to the knee or leg can injure the peroneal nerve.
- Prolonged pressure on the nerve, such as from crossing legs for long periods, can cause damage.
- Diabetes can lead to peroneal nerve damage due to high blood sugar levels affecting nerve health.
- Surgery around the knee or hip can sometimes inadvertently damage the peroneal nerve.
- Sports injuries, especially those involving twisting motions, can harm the peroneal nerve.
Symptoms of Peroneal Nerve Damage
Recognizing the symptoms of peroneal nerve damage can help in seeking timely medical intervention.
- Numbness or tingling in the top of the foot or outer part of the upper or lower leg.
- Weakness in the ankle or foot.
- Foot drop, where the front part of the foot drags on the ground while walking.
- Pain in the lower leg or foot.
- Difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
- Muscle atrophy in the lower leg or foot due to prolonged nerve damage.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing peroneal nerve issues effectively.
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies are used to diagnose peroneal nerve damage.
- MRI scans can help visualize any structural issues affecting the nerve.
- Physical therapy is often recommended to strengthen muscles and improve mobility.
- Surgery may be necessary in severe cases to relieve pressure on the nerve or repair it.
- Braces or splints can help manage foot drop and improve walking.
- Medications like pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage symptoms.
Prevention and Care
Taking care of the peroneal nerve involves adopting certain habits and precautions.
- Avoid prolonged pressure on the legs by changing positions frequently.
- Exercise regularly to maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
- Wear proper footwear to support the feet and prevent injuries.
Final Thoughts on Peroneal Tendonitis
Peroneal tendonitis can be a real pain, literally. Knowing the symptoms and causes helps catch it early. Rest, ice, and physical therapy are your best friends for recovery. Ignoring it might lead to more serious issues, so don’t push through the pain. Proper footwear and stretching can prevent it from coming back. If you’re an athlete or just love being active, take care of those tendons. Listen to your body and give it the rest it needs. Consulting a doctor or specialist is always a good idea if you’re unsure. Staying informed and proactive can keep you on your feet and doing what you love. Remember, a little care goes a long way in keeping those tendons happy and healthy.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
