Orofaciodigital Syndrome 1 (OFD1) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the mouth, face, fingers, and toes. Caused by mutations in the OFD1 gene, this condition primarily impacts females, as males with the mutation often do not survive. Symptoms can vary widely but typically include abnormalities in the oral cavity, such as cleft palate or tongue lobulation, facial asymmetry, and digital malformations like extra fingers or toes. Understanding OFD1 is crucial for early diagnosis and management, which can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. This article delves into 28 intriguing facts about OFD1, shedding light on its complexities and the challenges faced by individuals living with this condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Orofaciodigital Syndrome 1 (OFD1) is a rare genetic disorder primarily affecting females, causing facial, oral, and digit abnormalities. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for improving quality of life.
- Families affected by OFD1 can benefit from genetic counseling and reproductive options to make informed decisions about family planning. Ongoing research offers hope for future treatments and support resources are available to help cope with the challenges.
What is Orofaciodigital Syndrome 1?
Orofaciodigital Syndrome 1 (OFD1) is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body, including the face, oral cavity, and digits. This condition is primarily seen in females and can lead to a variety of physical abnormalities and developmental issues.
- 01
OFD1 is a genetic disorder: It is caused by mutations in the OFD1 gene, which is located on the X chromosome.
- 02
Primarily affects females: Since the disorder is X-linked dominant, it is more common in females. Males with the mutation often do not survive to birth.
- 03
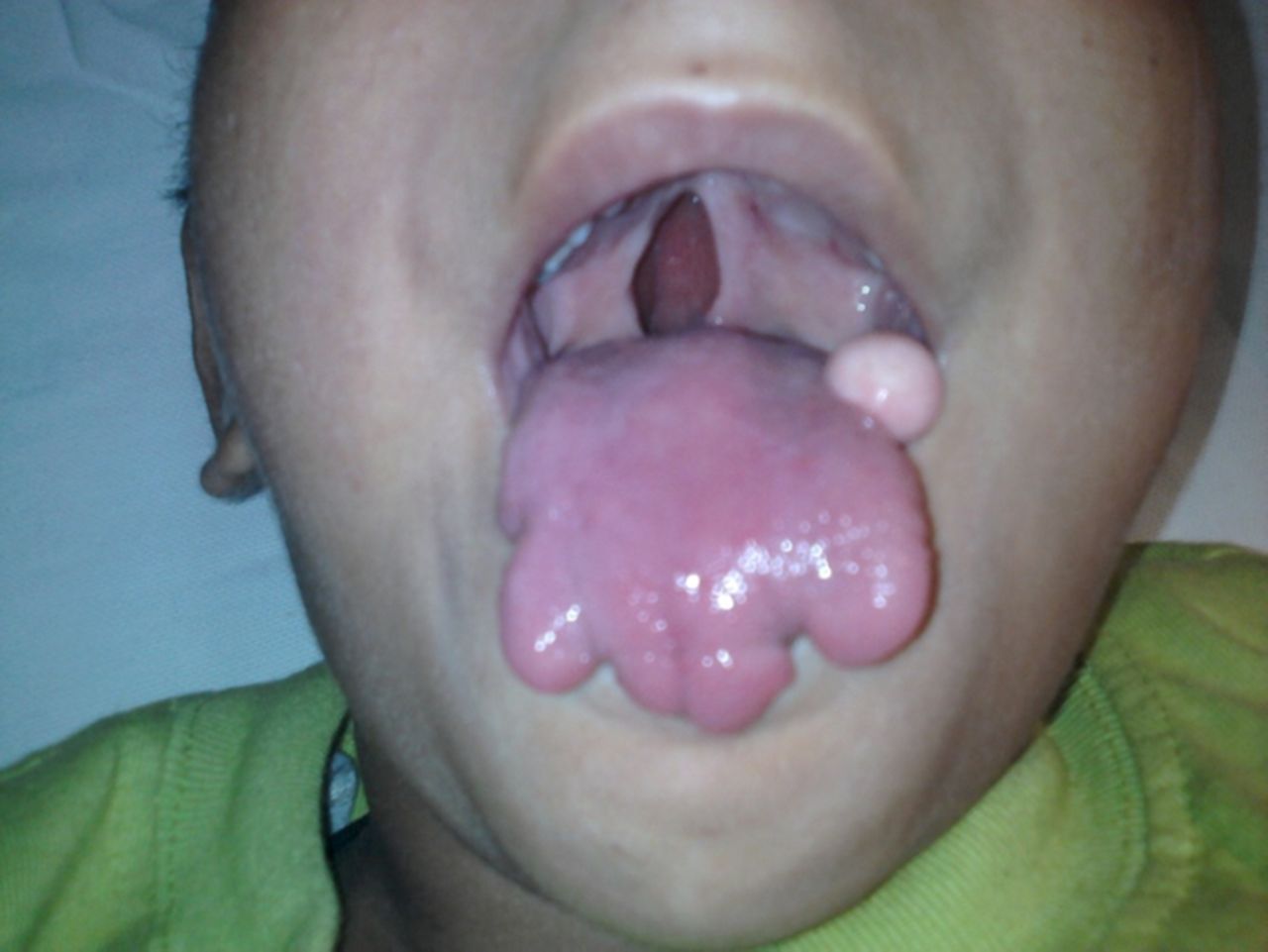
Facial abnormalities: Individuals with OFD1 often have distinctive facial features, such as a broad nasal bridge, wide-set eyes, and a cleft lip or palate.
Symptoms and Characteristics
OFD1 presents a wide range of symptoms and characteristics that can vary significantly from one person to another. Understanding these can help in early diagnosis and management.
- 04
Oral cavity issues: Common oral problems include missing teeth, extra teeth, and abnormalities in tooth shape and size.
- 05
Digital abnormalities: Fingers and toes may be webbed, shortened, or have extra digits (polydactyly).
- 06
Developmental delays: Many children with OFD1 experience delays in motor skills and speech development.
- 07
Kidney problems: Some individuals may develop polycystic kidney disease, which can lead to kidney failure.
Diagnosis and Testing
Early diagnosis of OFD1 is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Various tests and evaluations are used to confirm the presence of this syndrome.
- 08
Genetic testing: A definitive diagnosis is often made through genetic testing to identify mutations in the OFD1 gene.
- 09
Prenatal diagnosis: In some cases, OFD1 can be diagnosed before birth through amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling.
- 10
Physical examination: Doctors may identify physical signs of OFD1 through a thorough physical examination, focusing on facial features, oral cavity, and digits.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for OFD1, various treatments and management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
- 11
Surgical interventions: Surgeries may be required to correct cleft lip/palate, extra digits, or other physical abnormalities.
- 12
Speech therapy: Many children with OFD1 benefit from speech therapy to address speech delays and improve communication skills.
- 13
Occupational therapy: This can help children develop motor skills and adapt to physical limitations.
- 14
Regular monitoring: Ongoing medical evaluations are essential to monitor kidney function and other potential complications.
Genetic Counseling and Family Planning
Genetic counseling can provide valuable information and support for families affected by OFD1, helping them make informed decisions about family planning.
- 15
Inheritance pattern: Understanding the X-linked dominant inheritance pattern is crucial for family planning and assessing risks for future pregnancies.
- 16
Carrier testing: Female relatives may undergo genetic testing to determine if they are carriers of the OFD1 mutation.
- 17
Reproductive options: Families may explore reproductive options such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) to reduce the risk of passing on the disorder.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand OFD1 and develop new treatments to improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
- 18
Gene therapy: Researchers are exploring the potential of gene therapy to correct the underlying genetic mutation in OFD1.
- 19
Stem cell research: Studies are investigating the use of stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues in individuals with OFD1.
- 20
Clinical trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new treatments and contribute to advancing medical knowledge about OFD1.
Support and Resources
Living with OFD1 can be challenging, but various support networks and resources are available to help individuals and families cope.
- 21
Support groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand the challenges of living with OFD1.
- 22
Educational resources: Access to educational materials can help families better understand the condition and navigate the healthcare system.
- 23
Advocacy organizations: Organizations dedicated to rare genetic disorders can offer assistance with finding medical care, financial support, and advocacy.
Interesting Facts About OFD1
Here are some lesser-known facts about Orofaciodigital Syndrome 1 that highlight the complexity and uniqueness of this condition.
- 24
Named by Papillon-Léage and Psaume: The syndrome was first described by French physicians Papillon-Léage and Psaume in 1954.
- 25
Multiple subtypes: There are several subtypes of orofaciodigital syndromes, but OFD1 is the most common and well-studied.
- 26
Variable expressivity: The severity and range of symptoms can vary widely even among individuals with the same genetic mutation.
- 27
Rare occurrence: OFD1 is extremely rare, with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 50,000 to 1 in 250,000 live births.
- 28
Research advancements: Advances in genetic research are continually improving our understanding of OFD1 and paving the way for new treatments.
Final Thoughts on Orofaciodigital Syndrome 1
Orofaciodigital Syndrome 1 (OFD1) is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body, including the face, oral cavity, and digits. Understanding its symptoms and genetic basis helps in early diagnosis and better management. OFD1 primarily affects females due to its X-linked dominant inheritance pattern. Key symptoms include facial abnormalities, oral defects, and digital malformations. Early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Genetic counseling is crucial for families to understand the risks and implications. While there's no cure, ongoing research offers hope for better treatments. Awareness and education about OFD1 can lead to earlier detection and support for affected individuals and their families. Stay informed and proactive in seeking medical advice if you suspect OFD1 in yourself or a loved one.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


