What is Jaffe–Campanacci Syndrome? Jaffe–Campanacci Syndrome (JCS) is a rare genetic disorder that presents with a unique combination of clinical and radiological features. First described by Henry Lewis Jaffe in 1958 and later detailed by Mario Campanacci in 1983, this syndrome is characterized by multiple non-ossifying fibromas (NOFs) and café-au-lait macules (CALMs). These benign bone lesions and skin patches can lead to various complications, including intellectual disability, skeletal abnormalities, and cardiovascular malformations. While JCS shares some similarities with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), it has distinct features that set it apart. Understanding JCS is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management, as it impacts multiple aspects of a patient's health.
What is Jaffe–Campanacci Syndrome?
Jaffe–Campanacci Syndrome (JCS) is a rare genetic disorder that presents with a unique combination of clinical and radiological features. Named after Henry Lewis Jaffe and Mario Campanacci, this syndrome can be easily confused with other conditions due to overlapping symptoms. Let's dive into the key facts about JCS.
-
Definition and Classification: JCS is a rare genetic disorder marked by multiple non-ossifying fibromas (NOFs) and café-au-lait macules (CALMs). It shares some features with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), making diagnosis tricky.
-
Clinical Features: The main clinical signs include multiple non-ossifying fibromas, café-au-lait macules, and central giant cell granulomas of the jaw. Other possible features are intellectual disability, hypogonadism, cryptorchidism, ocular malformations, cardiovascular malformations, and various skeletal abnormalities.
Radiological and Skin Features
Radiological imaging and skin manifestations are crucial for diagnosing JCS. These features help differentiate it from other similar conditions.
-
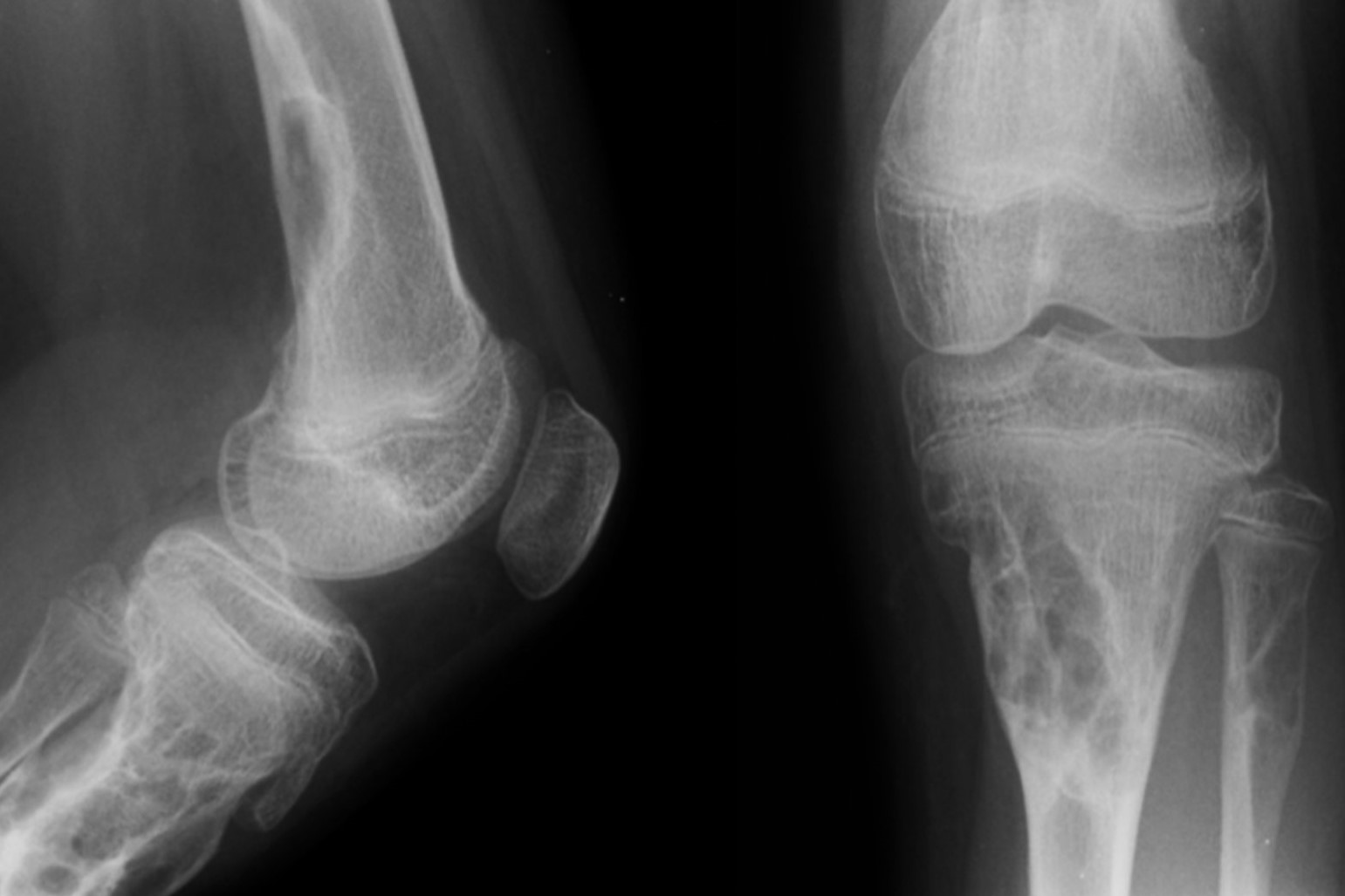
Radiological Characteristics: Radiological exams are key for diagnosing JCS. The syndrome shows multiple non-ossifying fibromas, which are benign bone lesions that can cause fractures. These fibromas appear as well-defined, lytic lesions in long bones and the jaw.
-
Café-au-lait Macules: Café-au-lait macules are flat, light-brown or dark-brown skin patches that can appear anywhere on the body. They are often present at birth or appear early in life, serving as a diagnostic marker for JCS.
-
Non-Ossifying Fibromas: These benign bone tumors are the most distinctive radiological feature of JCS. They can cause significant morbidity due to their potential to cause pathological fractures. They are typically found in long bones and the jaw.
Jaw and Intellectual Features
JCS also affects the jaw and intellectual capabilities, adding to the complexity of the syndrome.
-
Giant Cell Granulomas: Central giant cell granulomas of the jaw are another characteristic feature. These benign lesions can cause discomfort and dental issues, potentially leading to jaw deformities if untreated.
-
Intellectual Disability: Intellectual disability is common in JCS patients. The degree of impairment varies widely, ranging from mild to severe.
Skeletal and Cardiovascular Abnormalities
Skeletal and cardiovascular abnormalities are frequent in JCS, impacting the patient's quality of life.
-
Skeletal Abnormalities: These can include kyphoscoliosis, a curvature of the spine, and other congenital skeletal anomalies. These abnormalities can significantly affect the patient's daily life.
-
Cardiovascular Malformations: Cardiovascular issues like mitral insufficiency and stenosis of the aortic isthmus are common. These congenital heart defects require careful monitoring and management.
Ocular and Endocrine Features
JCS also affects the eyes and endocrine system, adding more layers to its complexity.
-
Ocular Malformations: Eye issues such as cataracts and glaucoma are associated with JCS. These abnormalities can affect vision and overall eye health.
-
Hypogonadism and Cryptorchidism: Endocrine and urogenital abnormalities like hypogonadism (low sex hormone levels) and cryptorchidism (undescended testes) are often present.
Genetic and Molecular Basis
Understanding the genetic and molecular basis of JCS is crucial for accurate diagnosis and potential future treatments.
-
Genetic Basis: The genetic basis of JCS is not fully understood but is believed to be related to mutations in the NF1 gene, also associated with neurofibromatosis type 1. This gene provides instructions for making a protein called neurofibromin, involved in cell growth and division.
-
Molecular Analysis: Molecular analysis of the NF1 gene in JCS patients has revealed various mutations. One such mutation, c.2789_2791delATC(p.Tyr930_Pro931delinsSer), has been identified in patients with both JCS and NF1 features.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management of JCS. This involves a combination of clinical, radiological, and genetic assessments.
-
Clinical Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves physical exams, radiological imaging, and genetic testing. The presence of multiple non-ossifying fibromas, café-au-lait macules, and central giant cell granulomas of the jaw are key diagnostic criteria.
-
Differential Diagnosis: JCS can be confused with conditions like neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and fibrous dysplasia. However, its unique combination of features helps distinguish it from these disorders.
Treatment and Prognosis
While there is no specific treatment for JCS, managing symptoms and complications can improve the patient's quality of life.
-
Treatment and Management: Management focuses on addressing symptoms and complications. This includes surgical intervention for fractures, dental care for jaw lesions, and endocrine management for hypogonadism and other abnormalities.
-
Prognosis: Prognosis varies widely depending on the severity of associated features. Regular follow-up and multidisciplinary care are essential for effective management.
Family Screening and Education
Family screening and education are crucial for early intervention and better management of JCS.
-
Family Screening: Screening is recommended for siblings and relatives of JCS patients. This can help identify individuals at risk and allow for early intervention and management.
-
Awareness and Education: Educating patients and families about JCS is crucial. Understanding the benign nature of non-ossifying fibromas and associated features can help alleviate anxiety and improve quality of life.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand JCS and develop more effective management strategies.
- Research and Future Directions: Research into JCS continues to uncover its genetic basis and improve diagnostic accuracy. Advances in genetic testing and imaging technologies are expected to enhance treatment outcomes for JCS patients.
Final Thoughts on Jaffe–Campanacci Syndrome
Jaffe–Campanacci Syndrome (JCS) is a rare genetic disorder with unique features like non-ossifying fibromas, café-au-lait macules, and central giant cell granulomas of the jaw. These characteristics, along with other congenital anomalies, make it a complex condition often confused with neurofibromatosis type 1. Diagnosis involves a mix of physical exams, radiological imaging, and genetic testing. While there's no specific cure, managing symptoms through surgical interventions, dental care, and endocrine treatments can improve quality of life. Family screening and education are crucial for early intervention and better management. Ongoing research aims to uncover more about its genetic basis and develop targeted treatments. Understanding JCS helps in providing better care and support for those affected.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


