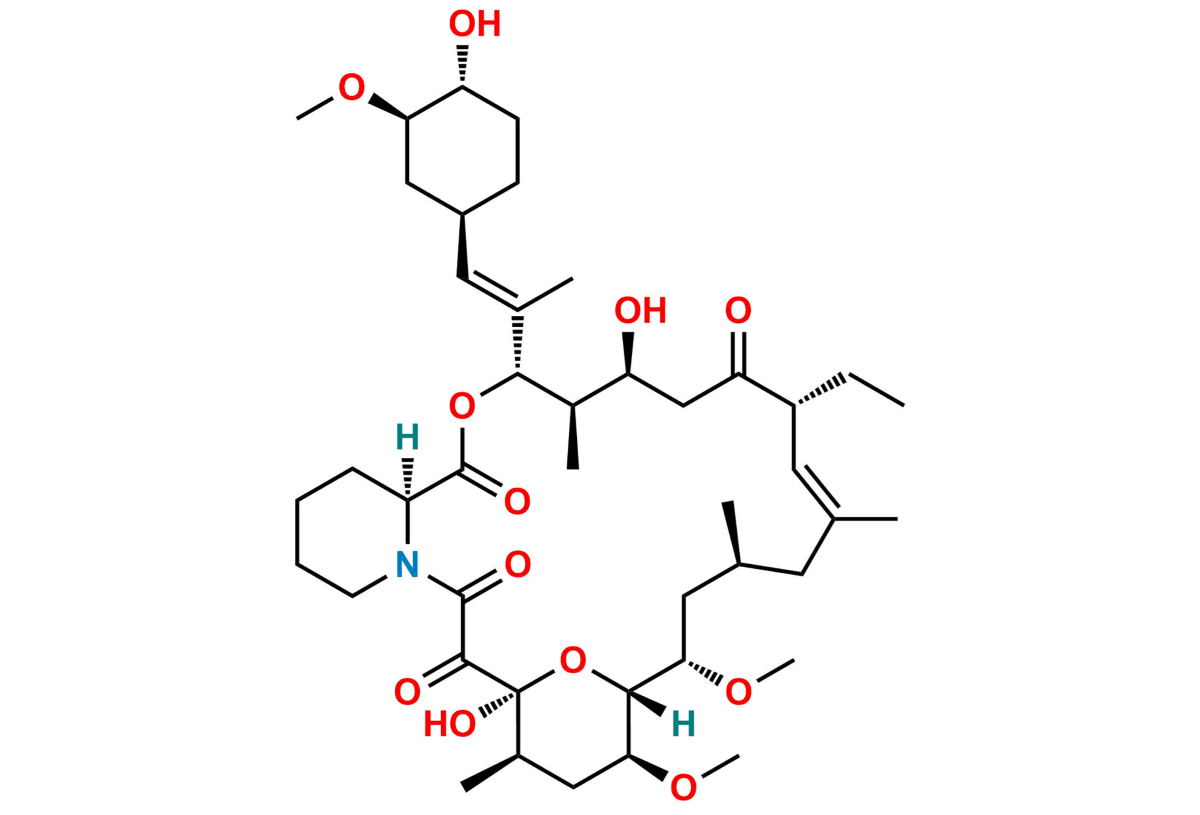
What is Ascomycin? Ascomycin is a powerful immunosuppressant derived from the bacterium Streptomyces hygroscopicus. This compound is closely related to tacrolimus, another well-known immunosuppressant. Ascomycin works by inhibiting T-cell activation, making it useful in preventing organ transplant rejection and treating autoimmune diseases. Unlike some other drugs, it has a unique mechanism that targets specific pathways in the immune system, reducing the risk of side effects. Ascomycin is also being studied for its potential in treating skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis. Understanding its benefits and applications can help in making informed decisions about its use.
What is Ascomycin?
Ascomycin is a fascinating compound with a range of applications, particularly in medicine. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this substance.
- Ascomycin is a macrolide immunosuppressant, meaning it helps suppress the immune system to prevent organ rejection after transplants.
- It was first isolated from a soil bacterium called Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. ascomyceticus.
- This compound is closely related to another well-known immunosuppressant, tacrolimus, which is also used in organ transplantation.
- Ascomycin works by inhibiting the activity of T-cells, a type of white blood cell involved in immune responses.
Medical Uses of Ascomycin
Ascomycin has several important medical applications, especially in treating skin conditions and preventing organ rejection.
- It is used topically to treat inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Ascomycin is effective in treating atopic dermatitis, a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed skin.
- The compound is also being studied for its potential to treat other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
- In organ transplantation, ascomycin helps prevent the body from rejecting the new organ by suppressing the immune system.
How Ascomycin Works
Understanding the mechanism of action of ascomycin can help us appreciate its effectiveness in various treatments.
- Ascomycin binds to a protein called FKBP-12, forming a complex that inhibits the activity of calcineurin, an enzyme involved in activating T-cells.
- By inhibiting calcineurin, ascomycin prevents the production of interleukin-2, a molecule that stimulates the growth and activity of T-cells.
- This inhibition reduces the immune response, making it useful in conditions where the immune system is overactive or attacking the body.
Side Effects and Precautions
Like any medication, ascomycin has potential side effects and precautions that need to be considered.
- Common side effects of topical ascomycin include burning, itching, and redness at the application site.
- Long-term use of ascomycin may increase the risk of skin infections and skin cancer due to its immunosuppressive effects.
- Patients using ascomycin should avoid excessive sun exposure and use sunscreen to protect their skin.
- Ascomycin should be used with caution in patients with a history of liver or kidney disease, as it can affect the function of these organs.
Research and Development
Ongoing research continues to explore new uses and formulations of ascomycin.
- Scientists are investigating the potential of ascomycin in treating other inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, such as multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- New formulations of ascomycin, including oral and injectable forms, are being developed to improve its effectiveness and ease of use.
- Researchers are also studying the molecular structure of ascomycin to develop new derivatives with enhanced properties and fewer side effects.
- Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ascomycin in various patient populations and conditions.
Interesting Facts About Ascomycin
Here are some additional intriguing tidbits about ascomycin that you might find interesting.
- Ascomycin is named after the Ascomycota, a phylum of fungi, because it was initially thought to be produced by a fungus rather than a bacterium.
Final Thoughts on Ascomycin
Ascomycin, a fascinating compound, has shown its potential in various medical applications. From its origins in soil bacteria to its role in treating skin conditions like eczema, this substance has proven its worth. Its immunosuppressive properties make it a valuable tool in organ transplants, helping prevent rejection. Despite its benefits, ascomycin isn't without risks, including potential side effects like increased infection susceptibility. However, ongoing research aims to maximize its benefits while minimizing drawbacks. Understanding ascomycin's complexities can lead to better treatments and improved patient outcomes. This compound's journey from nature to medicine highlights the importance of scientific discovery and innovation. As we continue to explore its potential, ascomycin remains a key player in the medical field, offering hope for many patients.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.