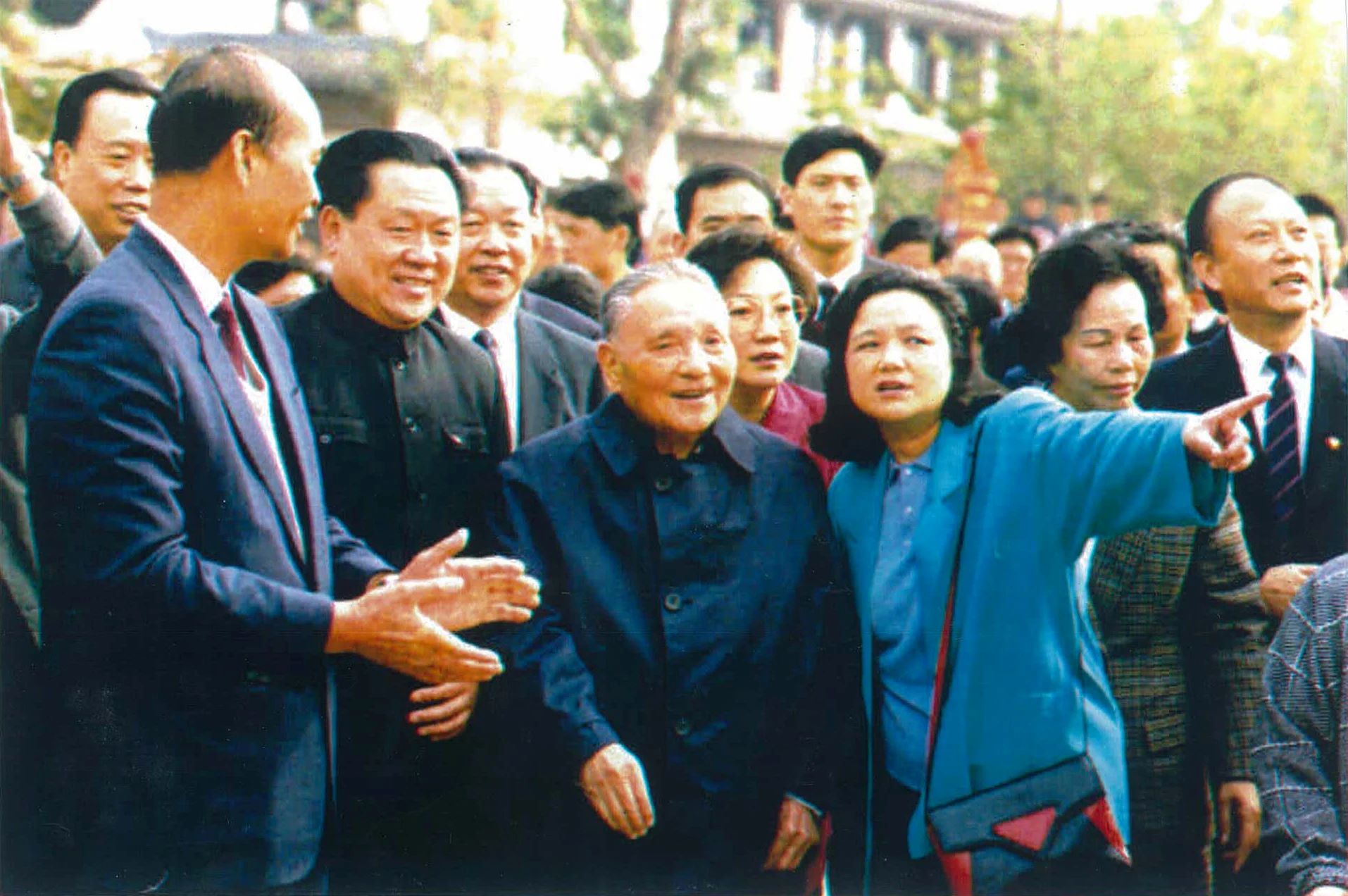
Known as one of the most influential figures in modern Chinese history, Deng Xiaoping’s legacy continues to fascinate and captivate people around the world. As the paramount leader of the People’s Republic of China from 1978 until his retirement in 1992, Deng Xiaoping played a pivotal role in shaping China’s economic and political landscape.
But beyond his widely recognized accomplishments, there are some lesser-known and enigmatic facts about Deng Xiaoping that add an intriguing layer to his persona. From his early life struggles to his complex relationship with power, here are 12 facts that shed light on the enigmatic character of Deng Xiaoping.
Key Takeaways:
- Deng Xiaoping transformed China’s economy and lifted millions out of poverty with his pragmatic leadership and famous quote “To get rich is glorious.”
- His “One Child Policy” and “One Country, Two Systems” policy for Hong Kong show his enigmatic and influential legacy in Chinese history.
Deng Xiaoping started his political career as a guerrilla fighter.
In his early years, Deng Xiaoping joined the Communist Party of China and fought as a guerrilla soldier during the Chinese Civil War. This experience shaped his revolutionary spirit and commitment to the communist ideology.
Deng Xiaoping played a key role in modernizing China.
As the paramount leader of China from the late 1970s until the early 1990s, Deng Xiaoping implemented a series of economic reforms and policies that transformed the country into the global economic powerhouse we know today. His “Four Modernizations” campaign focused on agriculture, industry, national defense, and science and technology.
Deng Xiaoping advocated for “socialism with Chinese characteristics.”
One of Deng Xiaoping’s defining contributions to Chinese political and economic ideology was the concept of “socialism with Chinese characteristics.” This philosophy emphasized that China could pursue its own unique path to socialism, taking into account its specific historical, cultural, and economic circumstances.
Deng Xiaoping was the architect behind the ‘One Child Policy’.
Recognizing the overpopulation challenges in China, Deng Xiaoping introduced the controversial “One Child Policy” in While it successfully curbed population growth, the policy also had unintended consequences on issues such as gender imbalance and aging population.
Deng Xiaoping played a pivotal role in the resolution of the Hong Kong issue.
Deng Xiaoping formulated the “One Country, Two Systems” policy, which provided a framework for the peaceful transition of Hong Kong from British rule to Chinese sovereignty in This policy allowed Hong Kong to maintain its own legal and economic systems, ensuring its unique status within China.
Deng Xiaoping was known for his pragmatic approach to governance.
Unlike his predecessor, Mao Zedong, Deng Xiaoping believed in practical policies and reforms rather than relying solely on ideology. He famously stated, “It doesn’t matter if a cat is black or white, as long as it catches mice.
Deng Xiaoping was the first Chinese leader to visit the United States.
In 1979, Deng Xiaoping made a historic trip to the United States, marking the first visit by a Chinese leader since the establishment of the People’s Republic of China. This visit paved the way for diplomatic and economic relations between the two nations.
Deng Xiaoping’s economic reforms lifted millions of Chinese people out of poverty.
Under Deng Xiaoping’s leadership, China experienced significant economic growth, resulting in the lifting of millions of people out of poverty. His policies promoted market-oriented reforms, opening up China’s economy to foreign investment and trade.
Deng Xiaoping emphasized collective leadership.
Unlike the cult of personality that surrounded Mao Zedong, Deng Xiaoping believed in collective leadership. He advocated for a system where decisions were made by a group of leaders rather than relying on a single individual.
Deng Xiaoping’s famous quote: “To get rich is glorious.”
Deng Xiaoping famously encouraged economic development and individual prosperity with his statement, “To get rich is glorious.” This statement reinforced his commitment to economic reform and motivated people to strive for personal success.
Deng Xiaoping retired from politics but continued to influence Chinese policies.
After retiring from his official positions, Deng Xiaoping remained highly influential in Chinese politics. His economic and political ideologies, known as “Dengism,” continued to shape China’s policies and reforms even after his passing.
Deng Xiaoping’s legacy continues to spark debates and discussions.
The impact of Deng Xiaoping’s leadership and reforms on China’s development is a topic of ongoing debate and analysis. His contributions and decisions continue to shape the economic, social, and political landscape of China.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Deng Xiaoping is undoubtedly one of the most enigmatic figures in modern Chinese history. His impact on the country’s political, economic, and social landscape cannot be overstated. From his role in transforming China into a global powerhouse to his nuanced approach to leadership and governance, Deng Xiaoping’s legacy continues to shape the nation today.While his contributions are widely recognized, there are still many aspects of Deng Xiaoping’s life and career that remain shrouded in mystery. The 12 enigmatic facts highlighted in this article provide a glimpse into the complexities of his persona and the challenges he faced in steering China towards progress.As we strive to understand the intricate layers of Deng Xiaoping’s character, it is essential to acknowledge his pivotal role in shaping China’s modernization and opening up to the world. His visionary leadership and pragmatic approach have left an indelible mark on the country and continue to influence its trajectory in the 21st century. Deng Xiaoping will always be remembered as a transformative figure who guided China through a period of remarkable change and growth.
FAQs
1. What were Deng Xiaoping’s major accomplishments?
Deng Xiaoping was instrumental in modernizing China’s economy and implementing market-oriented reforms. He played a crucial role in opening up China to foreign investment, which transformed the country into a global economic powerhouse.
2. What was Deng Xiaoping’s role during the Tiananmen Square protests in 1989?
Deng Xiaoping was not directly involved in the Tiananmen Square protests. However, he was a key decision-maker in the subsequent crackdown, which resulted in the loss of numerous lives.
3. How did Deng Xiaoping impact China’s foreign policy?
Deng Xiaoping’s “Four Modernizations” policy aimed to strengthen China’s military, agriculture, industry, and science and technology sectors. He also sought to improve diplomatic relations with other countries.
4. Did Deng Xiaoping hold any official positions after stepping down from power?
After stepping down from key leadership positions, Deng Xiaoping retained influence through his protégés. However, he did not hold any official government positions.
5. What were Deng Xiaoping’s views on political reform?
Deng Xiaoping believed in maintaining strong central leadership and prioritizing economic development over political reform. He famously stated, “It doesn’t matter whether a cat is black or white, as long as it catches mice.”
6. How did Deng Xiaoping influence China’s education system?
Deng Xiaoping emphasized the importance of education and the need to produce skilled professionals to support economic growth. He introduced significant reforms in China’s education system, including the expansion of higher education opportunities.
7. What impact did Deng Xiaoping have on China’s military?
Deng Xiaoping modernized China’s military by investing in advanced weapons systems and improving training and organization. He prioritized strengthening the defense capabilities of the People’s Liberation Army.
8. Did Deng Xiaoping face any opposition during his tenure?
Yes, Deng Xiaoping faced opposition from various factions within the Communist Party. However, his ability to navigate complex political dynamics allowed him to maintain a firm grip on power.
9. How did Deng Xiaoping handle the issue of Hong Kong’s sovereignty?
Deng Xiaoping proposed the “One Country, Two Systems” policy, which allowed Hong Kong to maintain its capitalist system and legal framework after its return to Chinese sovereignty in 1997.
10. What was Deng Xiaoping’s stance on free-market capitalism?
Deng Xiaoping embraced elements of free-market capitalism and encouraged foreign investment and entrepreneurship. However, he believed in maintaining state control over key sectors and strategic industries.
11. How did Deng Xiaoping contribute to China’s poverty alleviation efforts?
Deng Xiaoping’s economic reforms lifted millions of Chinese citizens out of poverty. His emphasis on job creation and improved living standards had a significant impact on reducing poverty levels in the country.
12. What was Deng Xiaoping’s relationship with Mao Zedong?
Deng Xiaoping served under Mao Zedong during the early years of the People’s Republic of China. However, he faced political persecution during the Cultural Revolution and was only able to regain power after Mao’s death.
Deng Xiaoping's enigmatic legacy continues to shape China's political landscape, sparking discussions about his impact on the nation's development. As you ponder his influence, consider exploring the captivating story of another transformative leader, Manmohan Singh, whose economic reforms reshaped India's trajectory. Uncover the fascinating facts behind these two giants of Asian politics and gain a deeper understanding of their lasting contributions to their respective countries.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.