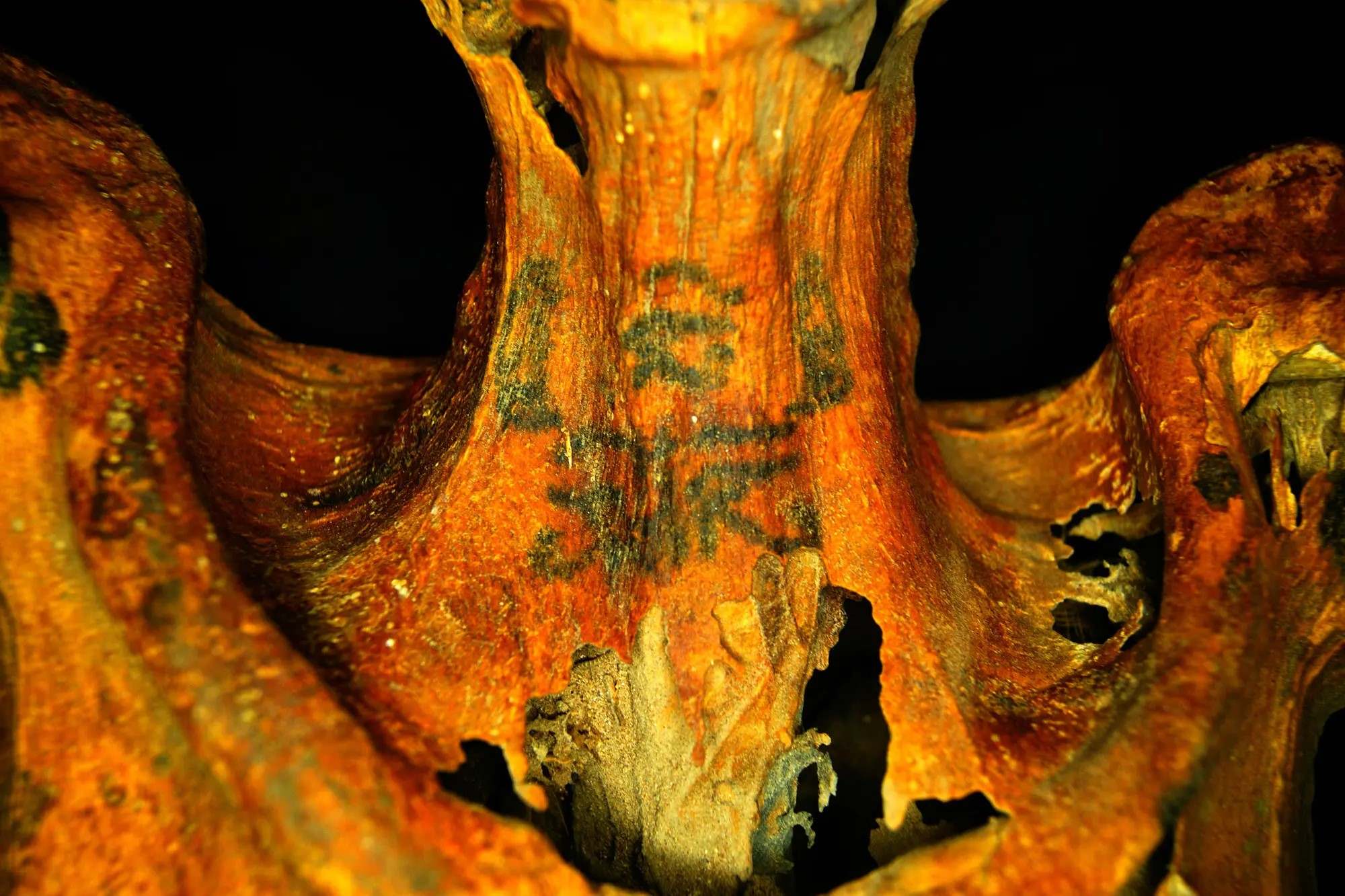
Did you know that the world's oldest tattoo mummies date back over 5,000 years? These ancient inked individuals provide a fascinating glimpse into early human culture and practices. Found in various parts of the world, including Egypt, Siberia, and the Alps, these mummies reveal that tattooing was a widespread phenomenon. Ötzi the Iceman, discovered in the Alps, sports 61 tattoos, primarily lines and crosses, believed to have been used for therapeutic purposes. In Egypt, mummies like Amunet showcase intricate designs, indicating tattoos might have held religious or social significance. These ancient body arts not only highlight the creativity of early civilizations but also their understanding of health and spirituality. Dive into these 35 intriguing facts to uncover more about the world's oldest tattoo mummies!
Key Takeaways:
- Ancient tattoos have been found on mummies dating back thousands of years, revealing their therapeutic, spiritual, and cultural significance in ancient civilizations.
- The preservation and study of tattooed mummies provide valuable insights into ancient tattooing techniques, meanings, and their influence on modern tattoo culture.
Ancient Tattoo Traditions
Tattooing has been a part of human culture for thousands of years. The oldest tattooed mummies provide a fascinating glimpse into ancient practices and beliefs.
- The oldest known tattooed mummy is Ötzi the Iceman, discovered in the Alps. He lived around 3300 BCE.
- Ötzi's tattoos are mostly simple lines and crosses, believed to be therapeutic rather than decorative.
- The second oldest tattooed mummy is a Chinchorro mummy from Chile, dating back to around 3000 BCE.
- Chinchorro mummies often have tattoos of animals and geometric patterns, indicating a possible spiritual significance.
- In ancient Egypt, tattoos were found on female mummies dating back to 2000 BCE, often symbolizing fertility and protection.
Cultural Significance of Tattoos
Tattoos were not just body art; they held deep cultural and spiritual meanings for ancient civilizations.
- The Pazyryk mummies from Siberia, dating back to around 500 BCE, have intricate animal tattoos, reflecting their shamanistic beliefs.
- Ancient Nubian mummies from around 400 BCE have tattoos that resemble the goddess Bes, a protector of women and children.
- The Scythian mummies, also from Siberia, have tattoos depicting mythical creatures, symbolizing strength and protection.
- In ancient China, tattoos were often used to mark criminals, but some mummies from around 300 BCE have decorative tattoos, indicating a shift in cultural perception.
- The Maori people of New Zealand have a long tradition of tattooing, with mummies dating back to 1200 CE showing intricate facial tattoos called moko.
Tattoo Techniques and Tools
The methods and tools used for tattooing have evolved, but ancient techniques were surprisingly advanced.
- Ötzi's tattoos were made by rubbing charcoal into small cuts in the skin.
- The Chinchorro people used sharp cactus spines to create their tattoos.
- Ancient Egyptians used bronze needles to apply tattoos, a technique still used in some cultures today.
- The Pazyryk people used bone needles and soot to create their detailed tattoos.
- Maori tattoos were made using chisels called uhi, which created deep grooves in the skin.
Preservation of Tattooed Mummies
The preservation of tattooed mummies provides valuable insights into ancient tattooing practices.
- Ötzi's body was naturally mummified by the cold, preserving his tattoos for over 5,000 years.
- The Chinchorro mummies were intentionally mummified using a complex process involving clay and reeds.
- Egyptian mummies were preserved using a combination of embalming and dry desert conditions.
- The Pazyryk mummies were preserved in permafrost, keeping their tattoos remarkably intact.
- Maori mummies were preserved using a combination of natural and artificial methods, including smoking and drying.
Tattoo Meanings and Symbolism
The meanings behind ancient tattoos can be complex and varied, reflecting the beliefs and values of the time.
- Ötzi's tattoos are thought to have been therapeutic, possibly used to treat arthritis.
- Chinchorro tattoos may have been used to mark social status or spiritual beliefs.
- Egyptian tattoos often symbolized protection, fertility, and religious devotion.
- Pazyryk tattoos depicted animals and mythical creatures, representing power and spiritual guidance.
- Maori tattoos were deeply personal, telling the story of the individual's life and achievements.
Modern Discoveries and Research
Ongoing research continues to uncover new information about ancient tattooed mummies.
- Advanced imaging techniques, such as infrared photography, have revealed previously unseen tattoos on mummies.
- DNA analysis of tattooed mummies can provide insights into the health and ancestry of ancient peoples.
- Chemical analysis of tattoo pigments helps researchers understand the materials and methods used in ancient tattooing.
- Archaeologists continue to discover new tattooed mummies, expanding our understanding of ancient cultures.
- Collaborative research between historians, anthropologists, and tattoo artists helps to preserve and revive ancient tattooing traditions.
Impact on Modern Tattoo Culture
Ancient tattooed mummies have had a significant influence on contemporary tattoo practices and designs.
- Many modern tattoo artists draw inspiration from the designs found on ancient mummies.
- The therapeutic use of tattoos, as seen with Ötzi, has inspired modern practices such as medical tattoos for cancer patients.
- Cultural appreciation of ancient tattooing practices has led to a resurgence of traditional techniques and designs.
- Museums and exhibitions showcasing tattooed mummies have increased public interest in the history of tattooing.
- The study of ancient tattoos has helped to legitimize tattooing as an important and respected art form.
Ancient Ink's Timeless Tale
Ancient tattoos on mummies reveal a lot about early cultures. These inked markings weren't just for decoration. They had deep meanings, often linked to rituals, status, or health. The oldest known tattoos, found on Ötzi the Iceman, date back over 5,000 years. His 61 tattoos might have been used for pain relief. Egyptian mummies also sported tattoos, showing their importance in society. These ancient body arts give us a glimpse into the past, showing how humans have always used skin as a canvas for expression. Studying these tattoos helps us understand ancient beliefs and practices. It's fascinating to see how something as personal as a tattoo can connect us to our ancestors. So next time you see a tattoo, remember its roots run deep in history, linking us to the ancient world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
