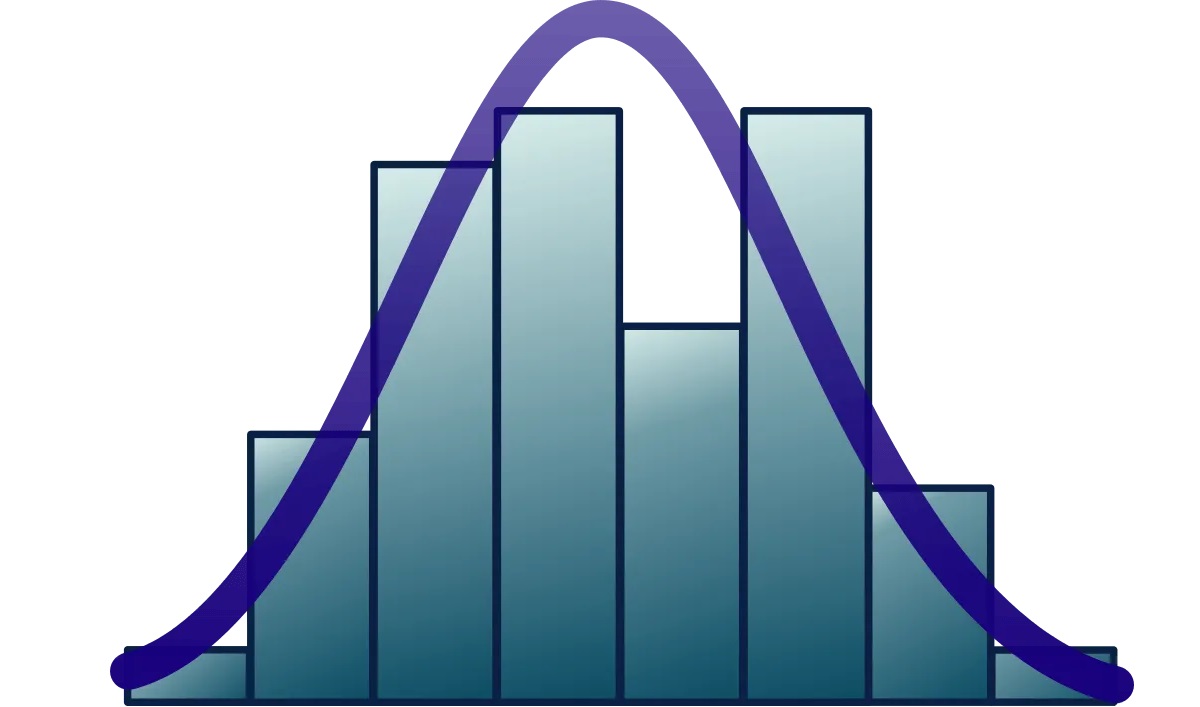
When it comes to analyzing data and understanding patterns, histograms play a crucial role. These graphical representations allow us to visualize the distribution of numerical data and gain valuable insights. Whether you are a data analyst, a researcher, or simply someone curious about statistics, understanding histograms is essential.
In this article, we are going to explore 10 fascinating facts about histograms. We will delve into their definition, purpose, construction, and interpretation. Whether you are new to histograms or already familiar with them, the facts presented here will deepen your knowledge and help you appreciate the power of this statistical tool.
So, buckle up and get ready to uncover some intriguing details about histograms that will enhance your understanding of data analysis and visualization.
Key Takeaways:
- Histograms are like data detectives! They help us see how data is spread out and find sneaky outliers that don’t fit in. They’re super useful for understanding trends and patterns in all kinds of information.
- Choosing the right bin size for a histogram is like picking the right magnifying glass. A smaller one shows tiny details, while a bigger one gives a broader view. It’s all about finding the best fit for the job!
Histograms provide a visual representation of data distribution.
Histograms are graphical representations that show the frequency or number of occurrences of data within certain intervals, commonly known as bins. They are widely used in statistics and data analysis to understand the distribution and patterns of data.
A histogram displays continuous data.
Histograms are specifically designed to showcase continuous data, which means that the data falls within a range of values rather than discrete categories. Continuous data examples include height, weight, temperature, and time duration.
The shape of a histogram provides insights into data distribution.
The shape of a histogram reveals important information about the nature of the data distribution. It can be symmetric (bell-shaped), skewed to the left or right, or have multiple peaks, indicating different patterns within the data.
Histograms assist in identifying outliers.
Outliers are data points that significantly deviate from the majority of the data. By examining a histogram, analysts can easily identify these outliers as they appear as data points that fall far outside the normal range of the distribution.
Histograms help in determining data trends.
By analyzing the height and width of the bars in a histogram, one can identify trends and patterns within the data. For example, a histogram with taller bars on the right side suggests that the data is skewed to the right, indicating a positive trend or increase.
Different bin sizes can alter the interpretation of a histogram.
The choice of bin sizes in a histogram affects the visual representation and interpretation of the data. Smaller bin sizes can reveal more detailed information and smaller variations, while larger bin sizes can generalize the data, potentially obscure certain patterns or trends.
Histograms can be used for data cleaning and outlier detection.
By examining the histogram, analysts can detect and remove any data entry errors or anomalies that may skew the overall analysis. This helps ensure the integrity and accuracy of the dataset.
Histograms are commonly used in fields such as market research and finance.
In market research, histograms are utilized to analyze customer demographics and purchasing behavior. In finance, histograms are used to study stock price movements, risk analysis, and portfolio performance.
Histograms can be created using various software and programming languages.
There are numerous software programs and programming languages available that enable the creation of histograms. Popular choices include Microsoft Excel, Python, R, and Tableau.
Histograms are a powerful tool for data visualization and analysis.
Histograms offer a visual and intuitive way to understand data patterns, distribution, and trends. They are widely utilized in various fields to make informed decisions based on data analysis and provide valuable insights into complex datasets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, histograms are a valuable tool in data analysis and visualization. They allow us to understand the distribution and frequency of data in a clear and concise manner. By representing data in bins and displaying the frequency of each bin on a bar graph, histograms provide insights into the pattern, shape, and outliers of a dataset. The key takeaways about histograms are that they provide a visual representation of data distribution, help identify trends and outliers, and are widely used in various fields such as statistics, data analysis, and finance. Utilizing histograms in your data analysis can lead to better decision-making and a deeper understanding of the underlying patterns in your data.
FAQs
Q: What is a histogram?
A: A histogram is a graphical representation of data distribution, where data is divided into intervals (bins) and the frequency of data falling into each bin is represented by the height of a bar.
Q: How do histograms help in data analysis?
A: Histograms provide insights into the shape, pattern, and outliers of a dataset. They allow us to understand the frequency of different values or ranges within the data, highlighting trends and providing a visual representation of data distribution.
Q: What are the key components of a histogram?
A: The key components of a histogram include bins (intervals) on the x-axis, frequency (or count) on the y-axis, bars representing the frequency in each bin, and a title that describes the variable being analyzed.
Q: Can histograms be used for any type of data?
A: Yes, histograms can be used for both numerical and categorical data. For numerical data, the x-axis represents the value range, whereas for categorical data, the x-axis represents the distinct categories.
Q: How can histograms be beneficial in decision-making?
A: Histograms allow us to identify trends, patterns, and outliers in data, making them useful in decision-making processes. They enable us to visualize data distributions and understand the relative frequency of different values or ranges, aiding in insightful analysis and informed decision-making.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
