Lesions can sound scary, but what exactly are they? Lesions are abnormal changes in tissue caused by disease or injury. They can appear anywhere on the body, from skin to internal organs. Some are harmless, while others might need medical attention. Understanding lesions helps in identifying potential health issues early. Knowing the types, causes, and treatments can make a big difference. Whether it's a mole that looks different or a strange bump, recognizing these signs is crucial. Ready to learn more? Here are 34 facts about lesions that will help you understand them better.
Lesions: An Overview
Lesions are abnormal changes in tissue caused by disease or injury. They can appear anywhere on the body and vary in size, shape, and severity. Understanding lesions helps in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
-
Lesions can be benign or malignant. Benign lesions are non-cancerous, while malignant ones are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body.
-
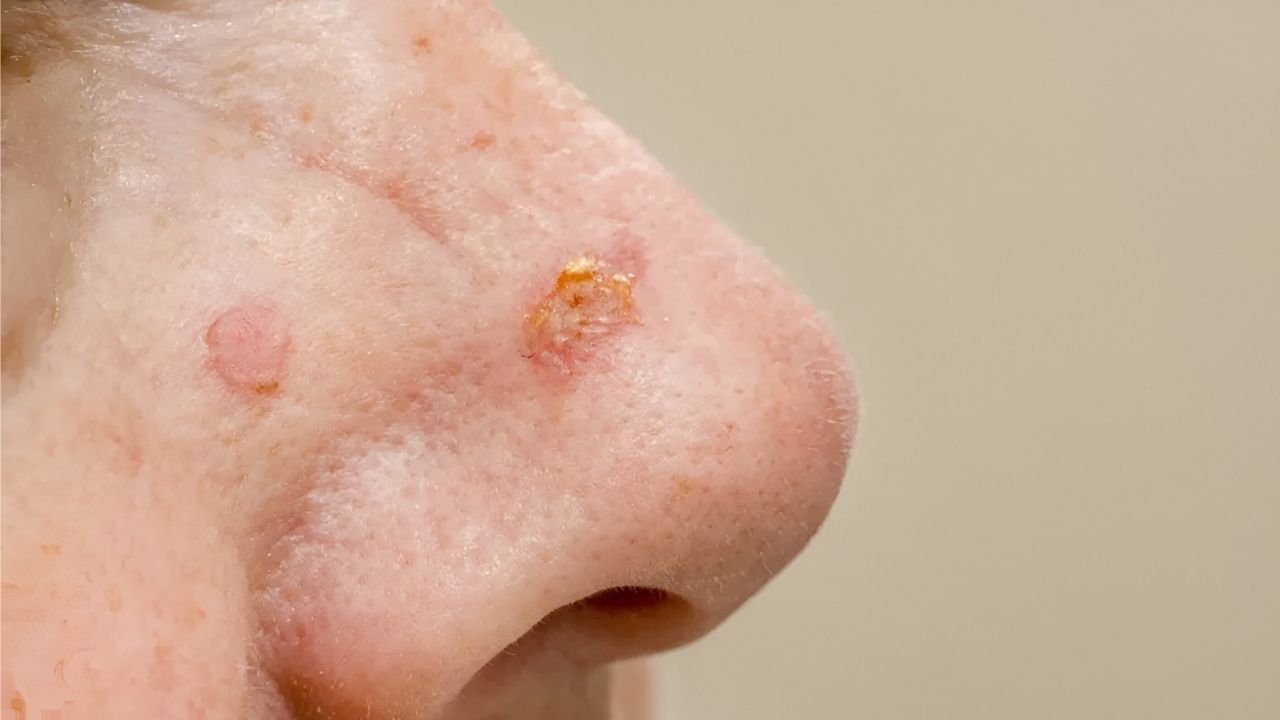
Skin lesions are the most common type. These include moles, warts, and rashes. They can be caused by infections, allergic reactions, or chronic skin conditions like eczema.
-
Brain lesions can result from trauma, infections, or diseases like multiple sclerosis. They often affect brain function, leading to symptoms like headaches, seizures, or cognitive difficulties.
-
Liver lesions are often detected through imaging tests. They can be benign, like hemangiomas, or malignant, such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
-
Lung lesions are usually found during chest X-rays or CT scans. They can be benign nodules or malignant tumors, often requiring a biopsy for diagnosis.
Causes of Lesions
Lesions can arise from various causes, including infections, injuries, and chronic diseases. Knowing the cause is crucial for effective treatment.
-
Infections like bacteria, viruses, and fungi can cause lesions. For example, chickenpox leads to itchy skin lesions, while tuberculosis can cause lung lesions.
-
Trauma or injury can result in lesions. Cuts, burns, and bruises are common examples of traumatic lesions.
-
Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can cause lesions. These conditions make the immune system attack healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and lesions.
-
Cancer is a significant cause of lesions. Tumors form as abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, creating lesions in various organs.
-
Chronic conditions like diabetes can lead to lesions. Diabetic ulcers are a common type of lesion in people with poorly controlled diabetes.
Diagnosing Lesions
Accurate diagnosis of lesions involves various medical tests and procedures. Early detection is key to effective treatment.
-
Biopsies are often performed to diagnose lesions. A small tissue sample is taken and examined under a microscope to determine if it's benign or malignant.
-
Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help visualize internal lesions. These tests provide detailed images of organs and tissues, aiding in diagnosis.
-
Blood tests can detect infections or markers of inflammation that cause lesions. Elevated white blood cell counts often indicate an infection.
-
Endoscopy involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the body to examine internal lesions. This procedure is commonly used for gastrointestinal lesions.
-
Dermatoscopy is used to examine skin lesions. A dermatoscope magnifies the skin, allowing doctors to see details not visible to the naked eye.
Treatment of Lesions
Treating lesions depends on their type, cause, and location. Various medical and surgical options are available.
-
Medications can treat lesions caused by infections or inflammation. Antibiotics, antivirals, and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly prescribed.
-
Surgical removal is often necessary for malignant lesions. Removing the lesion prevents the spread of cancerous cells.
-
Cryotherapy involves freezing lesions with liquid nitrogen. This method is effective for treating warts and some skin cancers.
-
Laser therapy uses focused light to remove or reduce lesions. It's commonly used for skin lesions like moles and birthmarks.
-
Radiation therapy targets malignant lesions with high-energy rays. This treatment is often used for cancerous tumors.
Interesting Facts about Lesions
Lesions have fascinating aspects that go beyond their medical implications. Here are some intriguing facts.
-
Lesions can heal on their own. Minor lesions like small cuts or bruises often heal without medical intervention.
-
Some lesions are genetic. Conditions like neurofibromatosis cause benign tumors to form on nerves, leading to skin lesions.
-
Lesions can be painless. Not all lesions cause discomfort. Some, like certain skin cancers, may not hurt but still require treatment.
-
Lesions can change over time. They may grow, shrink, or change color, indicating changes in the underlying condition.
-
Lesions can be a sign of systemic disease. For example, skin lesions can indicate internal diseases like liver cirrhosis or HIV.
Prevention of Lesions
Preventing lesions involves lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Here are some ways to reduce the risk.
-
Good hygiene can prevent infections that cause lesions. Regular handwashing and proper wound care are essential.
-
Sun protection reduces the risk of skin lesions. Using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing can prevent sunburns and skin cancer.
-
Healthy diet supports overall health and can prevent lesions. Nutrient-rich foods boost the immune system and promote skin health.
-
Regular check-ups help detect lesions early. Routine medical exams can catch lesions before they become serious.
-
Vaccinations can prevent infections that cause lesions. Vaccines for diseases like chickenpox and HPV reduce the risk of related lesions.
Lesions in Animals
Animals can also develop lesions. Understanding these helps in veterinary care and animal health.
-
Pets can get skin lesions from allergies, infections, or parasites. Regular grooming and vet visits help keep pets healthy.
-
Wild animals can develop lesions from injuries or diseases. Wildlife rehabilitation centers treat these lesions to help animals recover.
-
Livestock can suffer from lesions due to poor living conditions. Proper care and hygiene in farms prevent these issues.
-
Zoo animals receive regular health checks to detect and treat lesions. Veterinarians ensure these animals remain healthy and lesion-free.
Final Thoughts on Lesions
Lesions, those pesky disruptions in tissue, can tell us a lot about our health. Whether they're benign or malignant, understanding them is key. They can appear anywhere on the body, from skin to internal organs. Some are harmless, like freckles or moles, while others need medical attention, like tumors or ulcers.
Early detection is crucial. Regular check-ups and being aware of changes in your body can make a big difference. Treatments vary widely, from simple removal to more complex procedures.
Remember, not all lesions are a cause for alarm, but staying informed helps. If you notice something unusual, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Knowledge is power when it comes to your health. Stay vigilant, stay healthy!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
