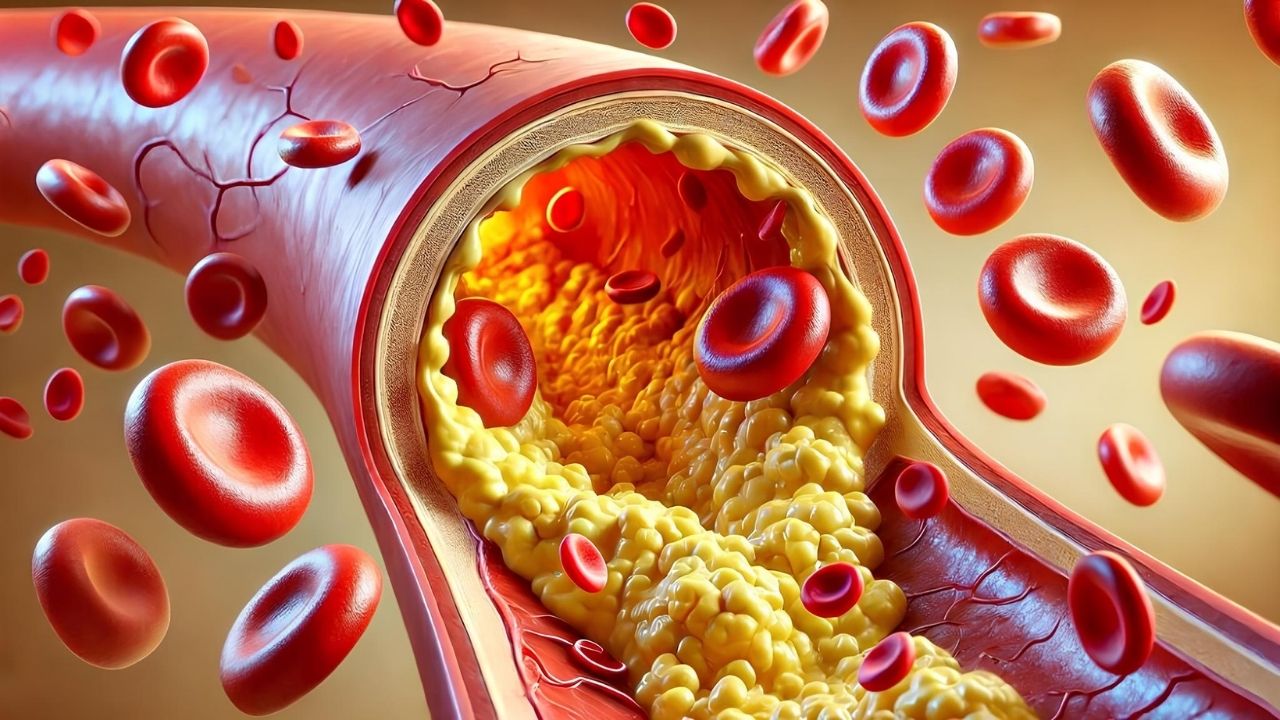
Hyperlipidemia might sound like a mouthful, but it’s a common condition affecting millions. What is hyperlipidemia? Hyperlipidemia is when you have high levels of fats, like cholesterol and triglycerides, in your blood. These fats can build up in your arteries, leading to heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems. Understanding hyperlipidemia is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This condition often sneaks up without symptoms, making regular check-ups vital. Factors like diet, exercise, and genetics play significant roles in managing it. By learning more about hyperlipidemia, you can take steps to keep your heart healthy and avoid complications. Ready to dive into some eye-opening facts? Let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Hyperlipidemia, or high cholesterol, is a condition with elevated levels of fats in the blood, increasing the risk of heart disease. It can be managed through healthy eating, exercise, and regular check-ups.
- Lifestyle choices, including a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, play a crucial role in preventing hyperlipidemia. Genetic factors, age, and gender also influence lipid levels.
What is Hyperlipidemia?
Hyperlipidemia is a medical condition characterized by high levels of lipids (fats) in the blood. These lipids include cholesterol and triglycerides. Understanding this condition is crucial for maintaining heart health and preventing cardiovascular diseases.
-
Hyperlipidemia is often referred to as high cholesterol. However, it encompasses more than just cholesterol; it includes elevated levels of triglycerides too.
-
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood. While your body needs cholesterol to build healthy cells, high levels can increase the risk of heart disease.
-
Triglycerides are another type of fat in the blood. When you eat, your body converts any calories it doesn't need into triglycerides, which are stored in fat cells.
Causes of Hyperlipidemia
Several factors contribute to hyperlipidemia. Some are within your control, while others are not. Knowing these causes can help you manage and prevent the condition.
-
Genetics play a significant role. If your family has a history of hyperlipidemia, you are more likely to develop it.
-
Diet is a major factor. Consuming foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can raise your lipid levels.
-
Lack of exercise can lead to weight gain, which is a risk factor for hyperlipidemia. Regular physical activity helps maintain healthy lipid levels.
-
Obesity is closely linked to hyperlipidemia. Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, increases the risk.
-
Age and gender also influence lipid levels. Men are generally at higher risk before age 50, while women's risk increases after menopause.
Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia often shows no symptoms until it leads to more serious conditions. However, there are some signs to watch out for.
-
Xanthomas are fatty deposits that can form under the skin, often around the eyes, elbows, or knees.
-
Corneal arcus is a gray or white arc visible around the cornea of the eye, indicating high cholesterol levels.
-
Chest pain or angina can occur if hyperlipidemia leads to coronary artery disease.
Diagnosing Hyperlipidemia
Early diagnosis is key to managing hyperlipidemia effectively. Several tests can help identify the condition.
-
Lipid panel is a blood test that measures total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
-
Fasting blood test is often required to get accurate triglyceride levels. Patients are usually asked to fast for 9-12 hours before the test.
-
Genetic testing may be recommended if there is a strong family history of hyperlipidemia.
Treatment Options for Hyperlipidemia
Managing hyperlipidemia involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are some common treatments.
-
Statins are medications that lower LDL cholesterol by reducing its production in the liver.
-
Fibrates help reduce triglyceride levels and can also increase HDL cholesterol.
-
Niacin is a B vitamin that can lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while raising HDL cholesterol.
-
Lifestyle changes such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking are crucial.
Diet and Hyperlipidemia
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing hyperlipidemia. Making the right food choices can significantly impact your lipid levels.
-
Fiber-rich foods like oats, beans, and fruits help lower cholesterol levels.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon and mackerel can reduce triglycerides.
-
Plant sterols and stanols found in fortified foods can help block the absorption of cholesterol.
-
Avoiding trans fats is essential. These fats, often found in processed foods, can raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol.
Exercise and Hyperlipidemia
Physical activity is another key component in managing hyperlipidemia. Regular exercise can help control lipid levels and improve overall health.
-
Aerobic exercises like walking, running, and cycling can lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol.
-
Strength training helps build muscle mass, which can increase metabolism and aid in weight management.
-
Consistency is crucial. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Complications of Hyperlipidemia
If left untreated, hyperlipidemia can lead to several serious health issues. Understanding these complications can motivate better management of the condition.
-
Atherosclerosis is the buildup of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in and on the artery walls, which can restrict blood flow.
-
Heart attack occurs when a blood clot blocks blood flow to the heart, often due to atherosclerosis.
-
Stroke happens when blood flow to a part of the brain is blocked, which can be a result of atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to the brain.
-
Peripheral artery disease is a condition where narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs, often causing pain and mobility issues.
Prevention of Hyperlipidemia
Preventing hyperlipidemia involves making healthy lifestyle choices. Here are some tips to keep your lipid levels in check.
-
Healthy eating is crucial. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
-
Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and improves lipid levels.
-
Avoid smoking as it can lower HDL cholesterol and increase the risk of heart disease.
-
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor your lipid levels and catch any issues early.
Wrapping Up Hyperlipidemia Facts
Hyperlipidemia, a condition marked by high levels of lipids in the blood, affects millions worldwide. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help manage and prevent serious health issues like heart disease and stroke. Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, play a crucial role in controlling lipid levels. Medications can also be effective, but they should be used under medical supervision.
Regular check-ups and blood tests are essential for early detection and management. Knowing your family history can provide insights into your risk factors. Remember, small changes in daily habits can make a big difference in your lipid levels and overall health.
Stay informed, stay proactive, and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Hyperlipidemia may be common, but with the right knowledge and actions, it’s manageable. Keep these facts in mind to lead a healthier life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
