Waardenburg Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the pigmentation of the skin, hair, and eyes, and can also cause hearing loss. Named after Dutch ophthalmologist Petrus Johannes Waardenburg, who first described it in 1951, this condition is fascinating due to its unique characteristics. People with Waardenburg Syndrome often have strikingly blue eyes or different colored eyes, a white forelock of hair, or patches of white skin. Hearing loss can range from mild to profound. This syndrome is divided into several types, each with its own specific features. Understanding Waardenburg Syndrome is crucial for early diagnosis and management, helping those affected lead better lives. Let's dive into 50 intriguing facts about this captivating condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Waardenburg Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects pigmentation and hearing. It has unique types, and early diagnosis and support can help individuals lead normal, healthy lives.
- Understanding the genetic and physical aspects of Waardenburg Syndrome can lead to better diagnosis, treatment, and support for affected individuals.
What is Waardenburg Syndrome?
Waardenburg Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects pigmentation and can cause hearing loss. Named after Dutch ophthalmologist Petrus Johannes Waardenburg, this condition has several types, each with unique characteristics. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about Waardenburg Syndrome.
General Facts About Waardenburg Syndrome
Understanding the basics of Waardenburg Syndrome helps in grasping its complexity and impact.
- Waardenburg Syndrome is named after Petrus Johannes Waardenburg, who first described it in 1951.
- It affects approximately 1 in 40,000 people worldwide.
- This syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning one copy of the altered gene is enough to cause the disorder.
- There are four main types of Waardenburg Syndrome: Type 1, Type 2, Type 3 (Klein-Waardenburg), and Type 4 (Waardenburg-Shah).
- Types 1 and 2 are the most common, while Types 3 and 4 are rarer.
- The syndrome can affect both males and females equally.
- It is characterized by varying degrees of hearing loss and changes in pigmentation of the hair, skin, and eyes.
Symptoms and Physical Characteristics
The symptoms of Waardenburg Syndrome can vary widely, even among members of the same family.
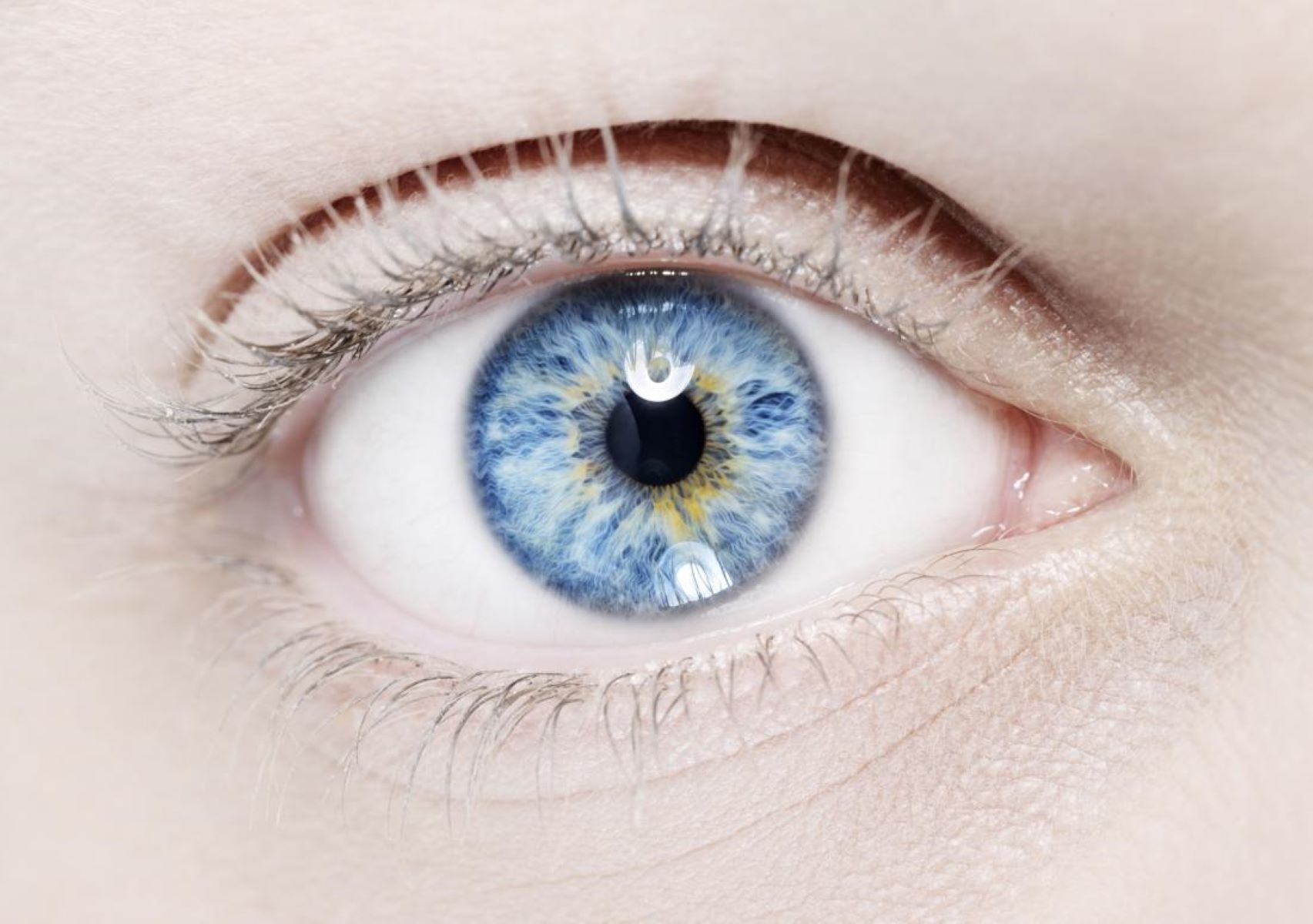
- One of the most recognizable features is heterochromia iridum, where a person has two different colored eyes.
- People with Waardenburg Syndrome often have very pale blue eyes or one blue eye and one brown eye.
- Another common feature is a white forelock, a patch of white hair near the forehead.
- Some individuals may have early graying of the hair.
- Skin pigmentation changes, such as patches of skin that are lighter than the surrounding area, can occur.
- Hearing loss is present in about 20-60% of individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome.
- The degree of hearing loss can range from mild to profound.
- Some individuals may have a wide nasal bridge, making the eyes appear farther apart (dystopia canthorum).
- Type 3 (Klein-Waardenburg) can include limb abnormalities, such as underdeveloped muscles or joints.
Genetic and Molecular Basis
The genetic underpinnings of Waardenburg Syndrome are complex and fascinating.
- Mutations in several genes, including PAX3, MITF, SOX10, EDN3, and EDNRB, are associated with the syndrome.
- PAX3 mutations are primarily linked to Types 1 and 3.
- MITF mutations are often found in Type 2.
- SOX10, EDN3, and EDNRB mutations are associated with Type 4.
- These genes play crucial roles in the development of neural crest cells, which contribute to the formation of various tissues, including melanocytes and auditory cells.
- Genetic testing can help confirm a diagnosis of Waardenburg Syndrome.
- Prenatal testing is available for families with a known history of the syndrome.
Diagnosis and Management
Early diagnosis and management can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected.
- Diagnosis is usually based on clinical features and family history.
- Audiological tests are essential to assess the degree of hearing loss.
- Genetic counseling is recommended for affected individuals and their families.
- There is no cure for Waardenburg Syndrome, but various treatments can manage symptoms.
- Hearing aids or cochlear implants can help those with hearing loss.
- Regular eye exams are crucial to monitor and manage vision issues.
- Skin protection from the sun is advised for those with pigmentation changes.
- Speech therapy may benefit children with hearing loss to develop communication skills.
Living with Waardenburg Syndrome
Living with Waardenburg Syndrome involves adapting to its challenges and embracing its unique aspects.
- Many individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome lead normal, healthy lives.
- Support groups and communities can provide emotional and social support.
- Awareness and education about the syndrome can reduce stigma and promote understanding.
- Advances in genetic research continue to improve diagnosis and treatment options.
- Early intervention programs can help children with hearing loss develop language and social skills.
- Some individuals with Waardenburg Syndrome may experience psychological challenges due to their appearance or hearing loss.
- Counseling and mental health support can be beneficial.
- Inclusive education and workplace accommodations can help individuals achieve their full potential.
- Advocacy for accessibility and equal opportunities is crucial for improving the lives of those affected.
Interesting Tidbits and Lesser-Known Facts
Here are some intriguing and lesser-known aspects of Waardenburg Syndrome.
- The syndrome is named after a Dutch ophthalmologist, yet it affects more than just the eyes.
- Some famous individuals, including musicians and actors, have Waardenburg Syndrome.
- The white forelock seen in some individuals is sometimes referred to as a "Mallen Streak."
- Waardenburg Syndrome can be part of other syndromes, such as Hirschsprung disease in Type 4.
- The condition is often featured in medical textbooks and genetic studies due to its distinct characteristics.
- Research into Waardenburg Syndrome has contributed to broader understanding of neural crest cell development.
- Some individuals with the syndrome may have a heightened sense of smell.
- The syndrome can sometimes be misdiagnosed as other conditions with similar features.
- Public awareness campaigns can help increase understanding and support for those affected.
- Ongoing research aims to uncover more about the genetic and molecular mechanisms behind Waardenburg Syndrome.
Final Thoughts on Waardenburg Syndrome
Waardenburg Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder affecting pigmentation and hearing. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected lead better lives. Genetic mutations in the PAX3, MITF, and other genes cause this condition, leading to unique physical traits like different-colored eyes, white forelocks, and hearing loss.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families. Treatments focus on managing symptoms, such as hearing aids for hearing loss and cosmetic options for pigmentation issues.
Raising awareness about Waardenburg Syndrome can foster empathy and support for those living with it. By sharing knowledge, we can help reduce stigma and improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition. Stay informed, spread awareness, and support those affected by Waardenburg Syndrome.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
