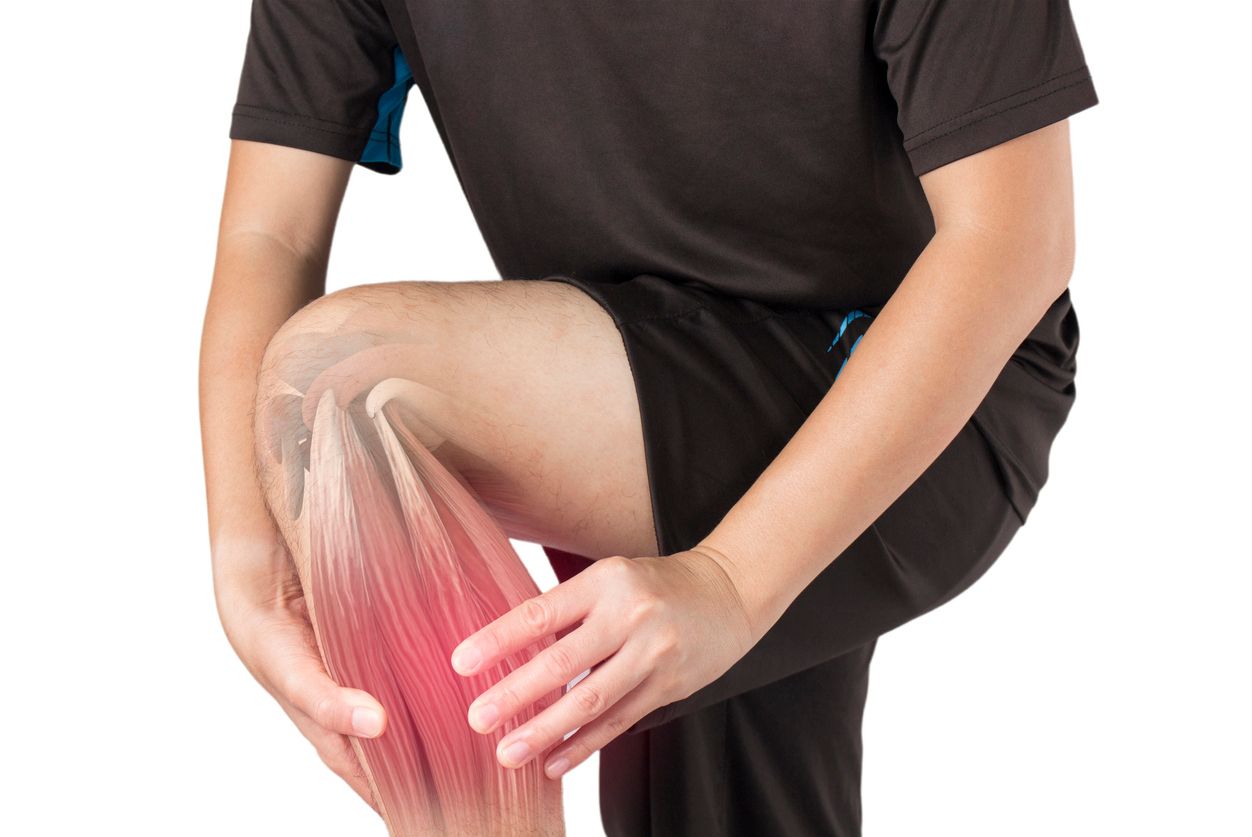
Rhabdomyolysis might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be crucial. This condition occurs when damaged muscle tissue releases proteins and electrolytes into the blood, potentially leading to serious complications. Common causes include trauma, extreme exercise, drug use, and infections. Symptoms often start with muscle pain, weakness, and dark urine. If left untreated, it can lead to kidney failure. Early detection and treatment are vital to prevent severe outcomes. Hydration and medical care can help manage the condition effectively. Ready to dive into 50 facts about this medical condition? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Rhabdomyolysis is a serious condition caused by muscle breakdown, releasing a harmful protein into the bloodstream. It can be prevented by staying hydrated and avoiding excessive exercise.
- Recognizing symptoms like muscle pain and dark urine is crucial for timely treatment. Intravenous fluids and rest are key in managing rhabdomyolysis and preventing kidney damage.
What is Rhabdomyolysis?
Rhabdomyolysis is a serious medical condition caused by the breakdown of muscle tissue. This breakdown releases a protein called myoglobin into the bloodstream, which can lead to kidney damage. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
- Rhabdomyolysis comes from the Greek words "rhabdo" (rod), "myo" (muscle), and "lysis" (breakdown).
- Myoglobin is the protein released during muscle breakdown that can cause kidney damage.
- Symptoms include muscle pain, weakness, and dark urine.
- Causes range from severe exercise to drug use and trauma.
- Diagnosis often involves blood tests to check for elevated levels of creatine kinase.
- Treatment usually includes intravenous fluids to prevent kidney damage.
- Complications can include acute kidney injury and electrolyte imbalances.
- Prevention involves staying hydrated and avoiding excessive exercise.
- History of the condition dates back to World War II when it was first described in soldiers.
- Genetic factors can make some individuals more susceptible to rhabdomyolysis.
Causes of Rhabdomyolysis
Understanding the causes of rhabdomyolysis can help in its prevention and management. Here are some common and unusual causes.
- Severe exercise is a leading cause, especially in untrained individuals.
- Trauma such as crush injuries can lead to muscle breakdown.
- Drug use, including statins and recreational drugs, can trigger the condition.
- Infections like influenza and HIV can also cause rhabdomyolysis.
- Heatstroke and hyperthermia are risk factors.
- Electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium or calcium, can contribute.
- Genetic disorders like McArdle's disease increase risk.
- Alcohol abuse is another common cause.
- Snake bites and other venomous bites can lead to muscle breakdown.
- Seizures and prolonged immobilization are also risk factors.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for timely treatment.
- Muscle pain is often the first symptom.
- Weakness in the affected muscles is common.
- Dark urine resembling cola or tea is a key indicator.
- Swelling of the muscles can occur.
- Nausea and vomiting may accompany the condition.
- Confusion and altered mental state can be symptoms.
- Blood tests showing elevated creatine kinase levels confirm diagnosis.
- Urine tests can detect myoglobin.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) may be used to check for heart complications.
- Imaging tests like MRI can assess muscle damage.
Treatment and Management
Effective treatment and management strategies can prevent complications and promote recovery.
- Intravenous fluids are the cornerstone of treatment.
- Dialysis may be necessary in severe cases to support kidney function.
- Medications to manage pain and electrolyte imbalances are often used.
- Physical therapy can aid in muscle recovery.
- Avoiding certain drugs that can exacerbate the condition is crucial.
- Monitoring kidney function is essential during treatment.
- Rest and avoiding strenuous activity help in recovery.
- Nutritional support can aid in muscle repair.
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are important.
- Education on recognizing early symptoms can prevent recurrence.
Prevention and Risk Factors
Knowing how to prevent rhabdomyolysis and understanding the risk factors can help reduce its incidence.
- Staying hydrated is key to prevention.
- Gradual increase in exercise intensity helps avoid muscle strain.
- Avoiding alcohol and drugs that can cause muscle damage is important.
- Wearing protective gear can prevent trauma-related rhabdomyolysis.
- Managing chronic conditions like diabetes reduces risk.
- Regular check-ups for those on statins can catch early signs.
- Genetic counseling may be beneficial for those with a family history.
- Heat acclimatization can prevent heat-related rhabdomyolysis.
- Proper nutrition supports muscle health.
- Awareness campaigns can educate the public on risk factors and prevention strategies.
Final Thoughts on Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is a serious condition that can affect anyone, from athletes to those with certain medical conditions. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments is crucial for early detection and effective management. Muscle pain, weakness, and dark urine are key signs to watch for. Causes range from intense exercise to drug use and infections. Treatment often involves hydration and addressing the underlying cause. Early intervention can prevent complications like kidney damage. Staying informed and vigilant can make a significant difference in outcomes. If you suspect rhabdomyolysis, seek medical attention immediately. Knowledge is power, and being aware of this condition can help protect your health and well-being. Stay safe, stay informed, and take care of your muscles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
