Progeria, also known as Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS), is a rare genetic condition that causes children to age rapidly. Short stature is one of the most noticeable symptoms, as affected children often remain significantly smaller than their peers. Another common feature is pigmented nevi, which are dark, mole-like spots on the skin. These symptoms, along with others, make Progeria a unique and challenging condition to understand. In this post, we'll explore 50 intriguing facts about Progeria, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and the lives of those who live with it. Buckle up for a journey into the world of this rare syndrome.
Key Takeaways:
- Progeria, a rare genetic disorder causing rapid aging, affects children's appearance and lifespan. Research and support offer hope for improved treatments and understanding.
- Understanding the genetic basis of Progeria is key to developing effective treatments. Support and resources are available to help individuals and families affected by Progeria.
What is Progeria?
Progeria, also known as Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS), is a rare genetic disorder. It causes children to age rapidly. This condition affects various parts of the body and leads to a shortened lifespan.
- Progeria is extremely rare, affecting about 1 in 20 million people worldwide.
- The term "progeria" comes from the Greek words "pro" meaning "before" and "gēras" meaning "old age."
- Children with progeria typically appear normal at birth but start showing signs of rapid aging within the first two years.
- The average life expectancy for someone with progeria is around 13 years.
- Progeria is caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene, which produces the lamin A protein.
Symptoms of Progeria
Progeria presents a variety of symptoms that mimic aspects of aging. These symptoms can affect the skin, bones, and cardiovascular system.
- One of the earliest signs of progeria is growth failure during the first year of life.
- Children with progeria often have a distinctive appearance, including a small face and jaw, and a pinched nose.
- Hair loss, including eyelashes and eyebrows, is common in children with progeria.
- Skin changes, such as thin, wrinkled skin and visible veins, are typical in progeria patients.
- Joint stiffness and hip dislocations are frequent due to abnormal bone development.
Short Stature in Progeria
Short stature is a hallmark of progeria. Children with this condition do not grow at the same rate as their peers.
- Most children with progeria are significantly shorter than average for their age.
- Growth hormone therapy has been explored as a treatment to help increase height in children with progeria.
- Despite their short stature, children with progeria often have normal intelligence and can attend school.
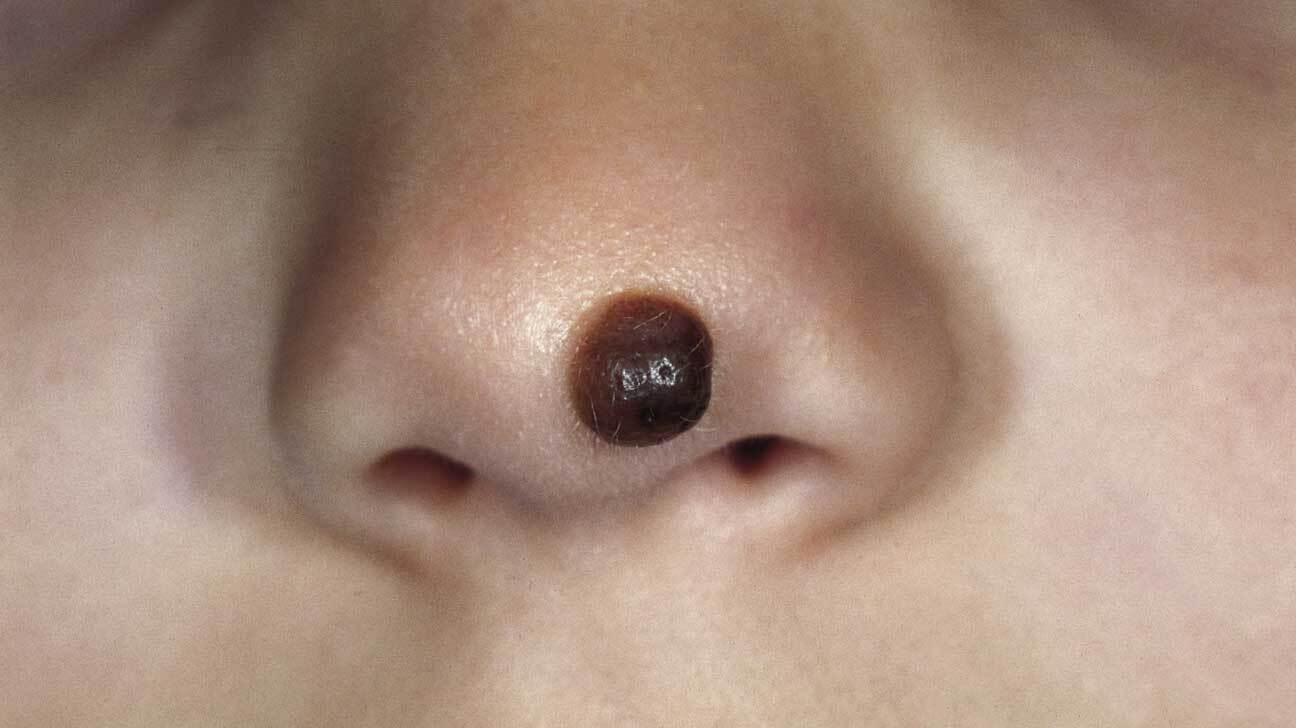
Pigmented Nevi in Progeria
Pigmented nevi, or moles, are common in individuals with progeria. These skin lesions can vary in size and color.
- Pigmented nevi are more frequent in children with progeria compared to the general population.
- These moles can appear anywhere on the body but are often found on the face and limbs.
- Regular dermatological check-ups are important for monitoring pigmented nevi in progeria patients.
Cardiovascular Issues in Progeria
Cardiovascular problems are a major concern for individuals with progeria. These issues often lead to life-threatening complications.
- Atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries, is common in children with progeria.
- Heart attacks and strokes are leading causes of death in progeria patients.
- Regular cardiovascular monitoring is crucial for managing the health of children with progeria.
- Medications like statins and aspirin are sometimes used to manage cardiovascular risks in progeria.
Research and Treatment
Research into progeria has led to a better understanding of the condition and potential treatments. Scientists continue to explore ways to improve the quality of life for those affected.
- The Progeria Research Foundation was established in 1999 to support research and find a cure for progeria.
- In 2020, the FDA approved the first drug, lonafarnib, specifically for treating progeria.
- Gene therapy is being investigated as a potential treatment for progeria.
- Clinical trials are ongoing to test new medications and therapies for progeria.
Living with Progeria
Living with progeria presents unique challenges, but many children with the condition lead fulfilling lives.
- Children with progeria often have a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare providers.
- Many children with progeria participate in normal activities like school, sports, and hobbies.
- Raising awareness about progeria helps to reduce stigma and promote understanding.
Famous Cases of Progeria
Several individuals with progeria have gained public attention, helping to raise awareness about the condition.
- Sam Berns, a progeria patient, became well-known for his TEDx talk and documentary "Life According to Sam."
- Hayley Okines, another progeria patient, authored an autobiography and appeared in several documentaries.
- Adalia Rose, a social media personality with progeria, inspired millions with her positive outlook on life.
Genetic Aspects of Progeria
Understanding the genetic basis of progeria is key to developing effective treatments.
- Progeria is caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene, which affects the production of lamin A protein.
- This mutation leads to the production of an abnormal protein called progerin, which causes cells to age prematurely.
- Progeria is not typically inherited; it usually occurs as a new mutation.
- Genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of progeria.
Support and Resources
Various organizations and resources are available to support individuals with progeria and their families.
- The Progeria Research Foundation provides resources, support, and funding for research.
- Online communities and support groups offer a platform for families to connect and share experiences.
- Educational resources help schools and teachers support students with progeria.
Future Directions in Progeria Research
Ongoing research aims to find new treatments and improve the lives of those with progeria.
- Scientists are exploring the use of CRISPR technology to correct the genetic mutation that causes progeria.
- Research into the biology of aging may provide insights that benefit progeria patients.
- Collaborative efforts between researchers, clinicians, and families are essential for advancing progeria research.
Raising Awareness about Progeria
Raising awareness about progeria helps to promote understanding and support for those affected.
- World Progeria Day, observed on October 10th, aims to raise awareness and funds for research.
- Social media campaigns and documentaries have played a significant role in increasing public awareness of progeria.
- Advocacy efforts by families and organizations help to drive research funding and policy changes.
Challenges in Progeria Research
Researching a rare condition like progeria presents unique challenges.
- The rarity of progeria makes it difficult to conduct large-scale clinical trials.
- Funding for progeria research is limited compared to more common conditions.
- Collaboration between researchers and institutions is crucial for advancing progeria research.
The Impact of Progeria on Families
Progeria affects not only the individuals diagnosed but also their families.
- Families of children with progeria often face emotional and financial challenges.
- Support from healthcare providers, social workers, and community organizations is vital for families.
- Many families become advocates for progeria research and awareness.
Hope for the Future
Despite the challenges, there is hope for the future of progeria research and treatment.
- Advances in genetic research and therapy hold promise for finding a cure for progeria.
Final Thoughts on Progeria
Progeria, a rare genetic condition, affects children worldwide. Characterized by short stature, pigmented nevi, and rapid aging, it presents unique challenges. Understanding this condition helps raise awareness and support for those affected.
Research continues to uncover more about the genetic mutations causing Progeria. Advances in treatments offer hope for improved quality of life. Families and caregivers play a crucial role in providing care and emotional support.
Raising awareness about Progeria can lead to better resources and funding for research. Every bit of knowledge shared contributes to a brighter future for those living with this condition.
Stay informed, support research efforts, and spread awareness. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of children with Progeria.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
