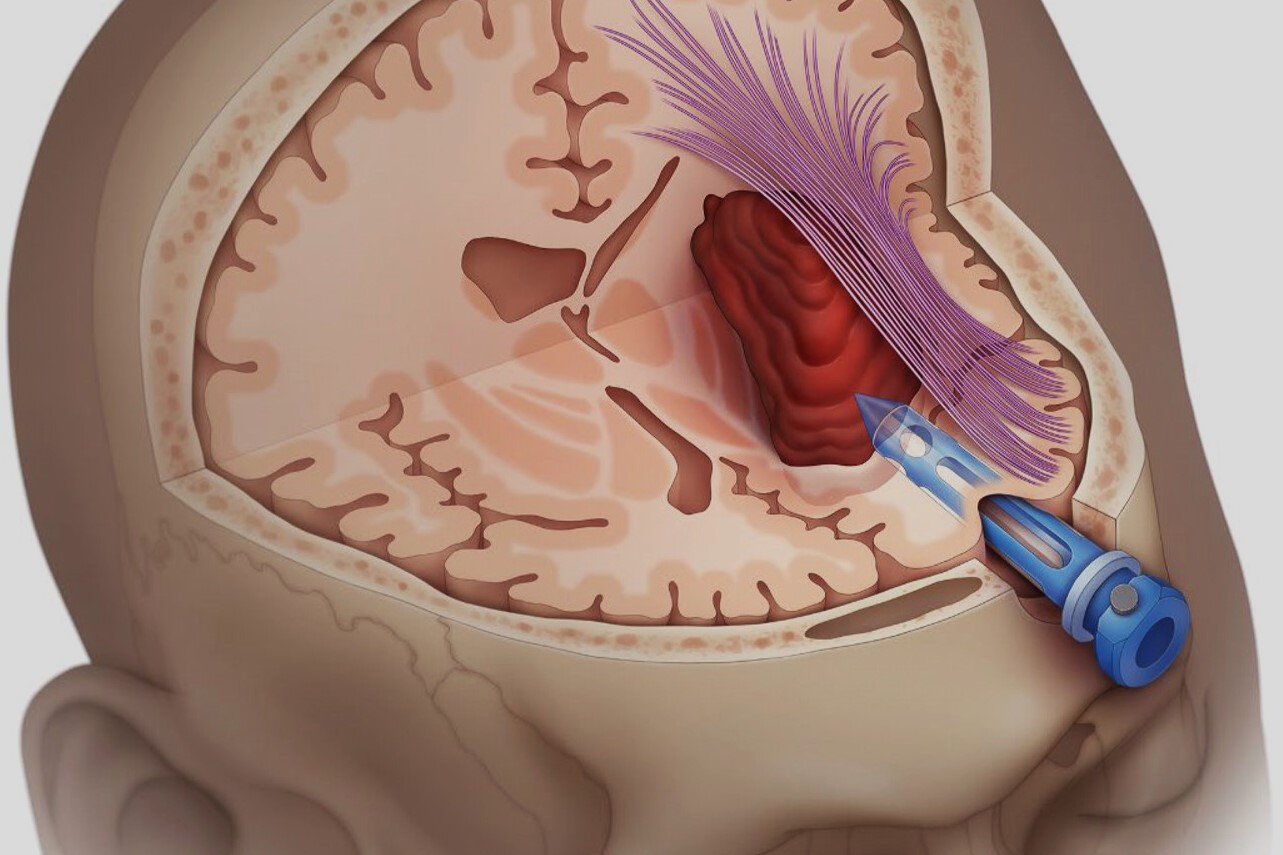
What is an intracranial hemorrhage? It's a type of bleeding that occurs inside the skull. This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. Intracranial hemorrhages can result from various causes, such as head trauma, high blood pressure, or blood vessel abnormalities. Symptoms might include a sudden headache, nausea, confusion, or even loss of consciousness. There are different types, including subdural hematomas, epidural hematomas, and intracerebral hemorrhages, each affecting different areas of the brain. Treatment often involves surgery to relieve pressure on the brain and stop the bleeding. Understanding the causes and symptoms can help in seeking timely medical care, which is crucial for recovery. Always remember, if someone shows signs of a stroke or head injury, getting help quickly can make a big difference.
Key Takeaways:
- Intracranial hemorrhage, or bleeding within the skull, can have various causes and symptoms. Understanding risk factors and early intervention are crucial for prevention and better outcomes.
- Advances in research and technology, along with global awareness, are improving the understanding and treatment of intracranial hemorrhages. Support systems and holistic care are essential for recovery.
Understanding Intracranial Hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage is a serious medical condition involving bleeding within the skull. It can occur due to various reasons and affects people of all ages. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Types of Intracranial Hemorrhage: There are several types, including subdural hematoma, epidural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and intracerebral hemorrhage. Each type has distinct causes and symptoms.
-
Common Causes: Head trauma, high blood pressure, aneurysms, and blood vessel abnormalities are frequent causes. Trauma is often linked to accidents or falls.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms can range from headaches and nausea to confusion and loss of consciousness. The severity and location of the bleed influence the symptoms.
-
Age Factor: While it can affect anyone, older adults and infants are more susceptible. In older adults, falls are a common cause, while in infants, it might be due to birth trauma.
-
Diagnosis Tools: CT scans and MRIs are crucial for diagnosing intracranial hemorrhages. These imaging techniques help determine the location and extent of the bleed.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding the risk factors can help in preventing intracranial hemorrhages. Some factors are modifiable, while others are not.
-
Hypertension: High blood pressure is a significant risk factor. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication can reduce risk.
-
Lifestyle Choices: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption increase the risk. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can be beneficial.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to aneurysms or blood vessel abnormalities, increasing their risk.
-
Preventive Measures: Wearing helmets during sports and seat belts in cars can prevent head injuries, reducing the risk of hemorrhages.
-
Medication Awareness: Blood thinners, while necessary for some conditions, can increase bleeding risk. Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare providers are essential.
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment varies based on the type and severity of the hemorrhage. Early intervention is crucial for better outcomes.
-
Surgical Intervention: In some cases, surgery is necessary to relieve pressure on the brain or repair damaged blood vessels.
-
Medication: Medications may be used to control blood pressure, prevent seizures, or reduce swelling in the brain.
-
Rehabilitation: Recovery often involves rehabilitation, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, to regain lost functions.
-
Prognosis: The prognosis depends on the hemorrhage's location, size, and the patient's overall health. Early treatment improves chances of recovery.
-
Long-term Effects: Some individuals may experience long-term effects, such as cognitive or physical impairments, requiring ongoing support.
Intracranial Hemorrhage in Special Populations
Certain populations face unique challenges and considerations regarding intracranial hemorrhages.
-
Infants and Children: In children, causes can include birth trauma or congenital conditions. Symptoms might differ from adults, requiring specialized care.
-
Pregnant Women: Pregnancy can increase the risk due to changes in blood pressure and blood volume. Careful monitoring is essential.
-
Athletes: Contact sports increase the risk of head injuries, leading to potential hemorrhages. Protective gear and proper techniques are vital.
-
Elderly: Age-related changes in blood vessels and increased fall risk make the elderly more susceptible. Regular health check-ups are important.
-
People with Blood Disorders: Conditions like hemophilia or thrombocytopenia can increase bleeding risk, necessitating careful management.
Advances in Research and Technology
Ongoing research and technological advancements are improving the understanding and treatment of intracranial hemorrhages.
-
Neuroimaging Innovations: Advances in neuroimaging provide clearer, more detailed images, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
-
Minimally Invasive Techniques: New surgical techniques are less invasive, reducing recovery time and improving outcomes.
-
Genetic Research: Studies on genetic factors are helping identify individuals at higher risk, paving the way for preventive strategies.
-
Telemedicine: Telemedicine allows for remote monitoring and consultation, improving access to care, especially in remote areas.
-
Artificial Intelligence: AI is being used to analyze imaging data, potentially speeding up diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Global Impact and Awareness
Intracranial hemorrhages have a significant global impact, affecting millions worldwide. Awareness and education are key to prevention and early intervention.
-
Global Statistics: Intracranial hemorrhages account for a substantial number of strokes worldwide, with varying incidence rates across regions.
-
Public Health Campaigns: Campaigns focusing on stroke awareness often include information about hemorrhagic strokes, promoting early recognition of symptoms.
-
Healthcare Access: Access to timely and adequate healthcare can vary, affecting outcomes. Efforts are ongoing to improve healthcare infrastructure globally.
-
Cultural Factors: Cultural beliefs and practices can influence how individuals perceive and respond to symptoms, impacting treatment-seeking behavior.
-
Educational Programs: Educational initiatives aim to inform the public about risk factors, symptoms, and the importance of seeking medical help promptly.
Intracranial Hemorrhage and Mental Health
The impact of an intracranial hemorrhage extends beyond physical health, affecting mental well-being as well.
-
Psychological Impact: Survivors may experience anxiety, depression, or PTSD due to the trauma and its aftermath.
-
Support Systems: Strong support systems, including family, friends, and support groups, play a crucial role in recovery and mental health.
-
Cognitive Rehabilitation: Cognitive rehabilitation can help address memory, attention, and problem-solving difficulties resulting from the hemorrhage.
-
Counseling Services: Access to counseling and mental health services is vital for addressing emotional and psychological challenges.
-
Holistic Approach: A holistic approach to recovery, addressing both physical and mental health, is essential for comprehensive care.
Intracranial Hemorrhage in the Media
Media coverage can influence public perception and awareness of intracranial hemorrhages.
-
High-Profile Cases: When celebrities or public figures experience intracranial hemorrhages, it often brings attention to the condition.
-
Documentaries and Films: Documentaries and films can educate the public about the causes, symptoms, and impact of intracranial hemorrhages.
-
Social Media: Social media platforms provide a space for sharing personal stories and raising awareness about intracranial hemorrhages.
-
Health Campaigns: Media campaigns by health organizations aim to educate the public about stroke symptoms, including those related to hemorrhages.
-
Public Figures as Advocates: Some public figures become advocates for stroke awareness, using their platform to promote education and prevention.
Future Directions in Intracranial Hemorrhage Research
Research continues to evolve, offering hope for better prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of intracranial hemorrhages.
-
Stem Cell Research: Investigating the potential of stem cells in repairing brain damage caused by hemorrhages is an exciting area of research.
-
Biomarker Discovery: Identifying biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of intracranial hemorrhages could revolutionize diagnosis and treatment.
-
Personalized Medicine: Advances in personalized medicine may lead to tailored treatment plans based on an individual's genetic makeup and risk factors.
-
Preventive Strategies: Research into preventive strategies, including lifestyle interventions and medications, aims to reduce the incidence of hemorrhages.
-
Collaborative Efforts: International collaborations among researchers and healthcare providers are driving progress in understanding and managing intracranial hemorrhages.
Intracranial Hemorrhage and Technology Integration
Technology integration is transforming the landscape of intracranial hemorrhage management and care.
-
Wearable Devices: Wearable devices that monitor vital signs and detect falls can alert healthcare providers to potential issues in real-time.
-
Virtual Reality: Virtual reality is being used in rehabilitation to help patients regain motor skills and cognitive functions.
-
Mobile Health Apps: Mobile health apps provide patients with tools to track symptoms, medication, and appointments, enhancing self-management.
-
Robotic Surgery: Robotic-assisted surgery offers precision and control, improving outcomes in complex cases of intracranial hemorrhage.
-
Data Analytics: Big data analytics is helping identify patterns and trends in intracranial hemorrhage cases, informing public health strategies and research.
Understanding Intracranial Hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage is a serious medical condition that demands immediate attention. Knowing the symptoms like sudden headaches, nausea, or confusion can save lives. Quick action is crucial because time is of the essence when dealing with brain bleeds. Risk factors such as high blood pressure, head trauma, or certain medications increase the likelihood of experiencing this condition. Prevention involves managing these risks through lifestyle changes and regular check-ups. Treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the hemorrhage, ranging from medication to surgery. Awareness and education about intracranial hemorrhage can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. By understanding the facts, people can better protect themselves and their loved ones. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize health. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to preventing and managing serious health issues like intracranial hemorrhage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
