Hodgkin's Disease, also known as Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system. Named after Dr. Thomas Hodgkin, who first described the condition in 1832, this disease primarily targets lymph nodes but can spread to other organs. Early symptoms often include painless swelling of lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss. Treatment options have significantly improved over the years, making it one of the most treatable cancers if detected early. Understanding Hodgkin's Disease is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This article will provide 50 essential facts to help you better grasp this condition, its symptoms, treatments, and the latest research. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or just curious, these facts will offer valuable insights into Hodgkin's Disease.
Key Takeaways:
- Hodgkin's Disease is a highly treatable cancer that affects the lymphatic system. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely treatment can lead to a better prognosis and higher survival rates.
- Understanding risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options for Hodgkin's Disease can help individuals assess their personal risk and make informed decisions about their health.
What is Hodgkin's Disease?
Hodgkin's Disease, also known as Hodgkin's Lymphoma, is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system. This system is part of the immune system, which helps the body fight infections. Understanding this disease can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment.
- Named after Thomas Hodgkin, who first described abnormalities in the lymph system in 1832.
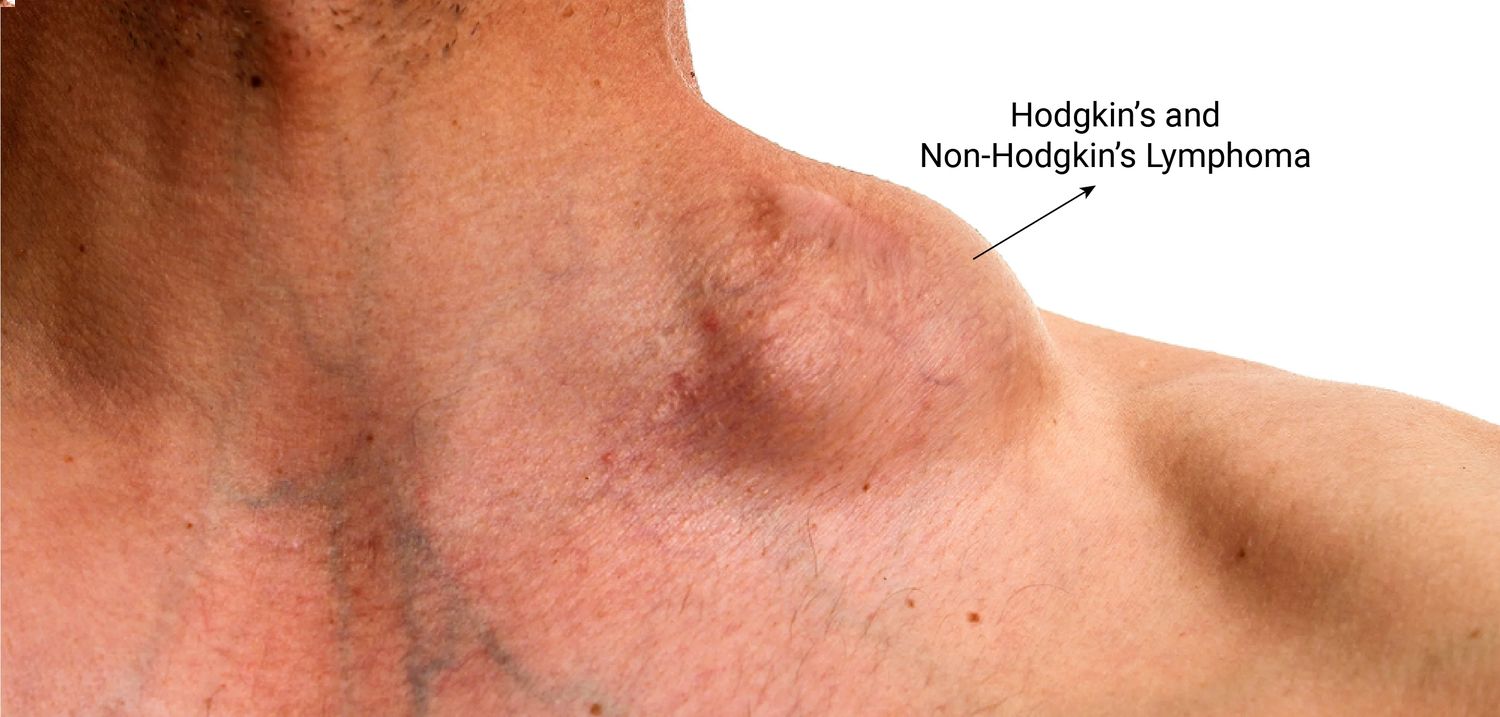
- It primarily affects lymph nodes, which are small, bean-shaped structures that produce and store cells that fight infection.
- Hodgkin's Disease is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, a type of abnormal cell.
- It is one of the most treatable forms of cancer, especially if detected early.
- The exact cause of Hodgkin's Disease remains unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Symptoms of Hodgkin's Disease
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to a better prognosis. Symptoms can vary, but some are more common than others.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin are often the first sign.
- Persistent fatigue is a common symptom that can affect daily activities.
- Unexplained weight loss can be a red flag for Hodgkin's Disease.
- Fever and chills that come and go without any apparent cause.
- Night sweats that drench clothing and sheets.
- Itchy skin, which can be widespread or localized.
- Coughing, trouble breathing, or chest pain if the disease affects lymph nodes in the chest.
Risk Factors for Hodgkin's Disease
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing Hodgkin's Disease. Knowing these can help in assessing personal risk.
- Age is a significant factor; it most commonly affects people between 15 and 40 years old and those over 55.
- Family history can play a role; having a close relative with Hodgkin's Disease increases risk.
- Males are slightly more likely to develop Hodgkin's Disease than females.
- A weakened immune system, such as from HIV/AIDS or organ transplants, can increase risk.
- Past Epstein-Barr virus infection, which causes mononucleosis, has been linked to Hodgkin's Disease.
Diagnosis of Hodgkin's Disease
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various tests and procedures are used to diagnose Hodgkin's Disease.
- Physical exams often reveal swollen lymph nodes.
- Blood tests can indicate abnormalities that suggest Hodgkin's Disease.
- Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans help locate affected lymph nodes.
- A lymph node biopsy is the definitive test for diagnosing Hodgkin's Disease.
- Bone marrow biopsy may be performed to check if the disease has spread.
Treatment Options for Hodgkin's Disease
Treatment varies depending on the stage and severity of the disease. Multiple options are available to manage and potentially cure Hodgkin's Disease.
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and is often the first line of treatment.
- Radiation therapy targets specific areas affected by cancer.
- Immunotherapy helps the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Stem cell transplant may be considered for advanced cases or relapses.
- Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates can provide hope and perspective for those diagnosed with Hodgkin's Disease.
- The five-year survival rate for Hodgkin's Disease is about 86%.
- Early-stage Hodgkin's Disease has a higher survival rate, often exceeding 90%.
- Advanced stages have lower survival rates but still offer a good chance of remission with treatment.
- Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor for recurrence and manage long-term side effects.
- Advances in treatment have significantly improved survival rates over the past few decades.
Living with Hodgkin's Disease
Living with Hodgkin's Disease involves managing symptoms, treatment side effects, and emotional well-being.
- Support groups can provide emotional and practical support.
- Nutrition and exercise play a crucial role in maintaining strength and energy.
- Mental health support, including counseling and therapy, can help cope with the emotional impact.
- Palliative care focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Survivorship programs offer resources and support for life after treatment.
Research and Advances in Hodgkin's Disease
Ongoing research continues to improve understanding and treatment of Hodgkin's Disease. Staying informed about these advances can offer hope and new options.
- Clinical trials test new treatments and therapies.
- Genetic research aims to identify specific mutations involved in Hodgkin's Disease.
- Advances in immunotherapy are providing new treatment options.
- Personalized medicine tailors treatment to individual genetic profiles.
- Research into the role of the microbiome in cancer development is ongoing.
Myths and Misconceptions about Hodgkin's Disease
Clearing up common myths and misconceptions can help in understanding Hodgkin's Disease better.
- Myth: Hodgkin's Disease is always fatal. Fact: It is one of the most treatable cancers.
- Myth: Only older adults get Hodgkin's Disease. Fact: It commonly affects young adults.
- Myth: Hodgkin's Disease is contagious. Fact: It cannot be spread from person to person.
- Myth: All lymphomas are the same. Fact: Hodgkin's Disease is distinct from non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Myth: Alternative therapies can cure Hodgkin's Disease. Fact: Conventional medical treatments are necessary.
Famous People with Hodgkin's Disease
Knowing that public figures have faced Hodgkin's Disease can provide inspiration and awareness.
- Actor Michael C. Hall, known for his role in "Dexter," was diagnosed in 2010 and is now in remission.
- Musician Delta Goodrem was diagnosed at age 18 and has since become an advocate for cancer awareness.
- Former NFL player Mark Herzlich overcame Hodgkin's Disease and returned to professional football.
Final Thoughts on Hodgkin's Disease
Hodgkin's disease, a type of lymphoma, affects the lymphatic system, which is crucial for immune function. Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes. Symptoms like swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and weight loss should prompt medical consultation. Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation, and sometimes stem cell transplants. Advances in medical research have improved survival rates, offering hope to many patients.
Understanding the disease's risk factors, such as age, family history, and certain infections, can aid in early diagnosis. Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms play a vital role in managing health. Hodgkin's disease, though serious, is treatable, and many people lead healthy lives post-treatment. Stay informed, seek medical advice if symptoms arise, and support ongoing research efforts. Knowledge and vigilance are key in the fight against Hodgkin's disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
