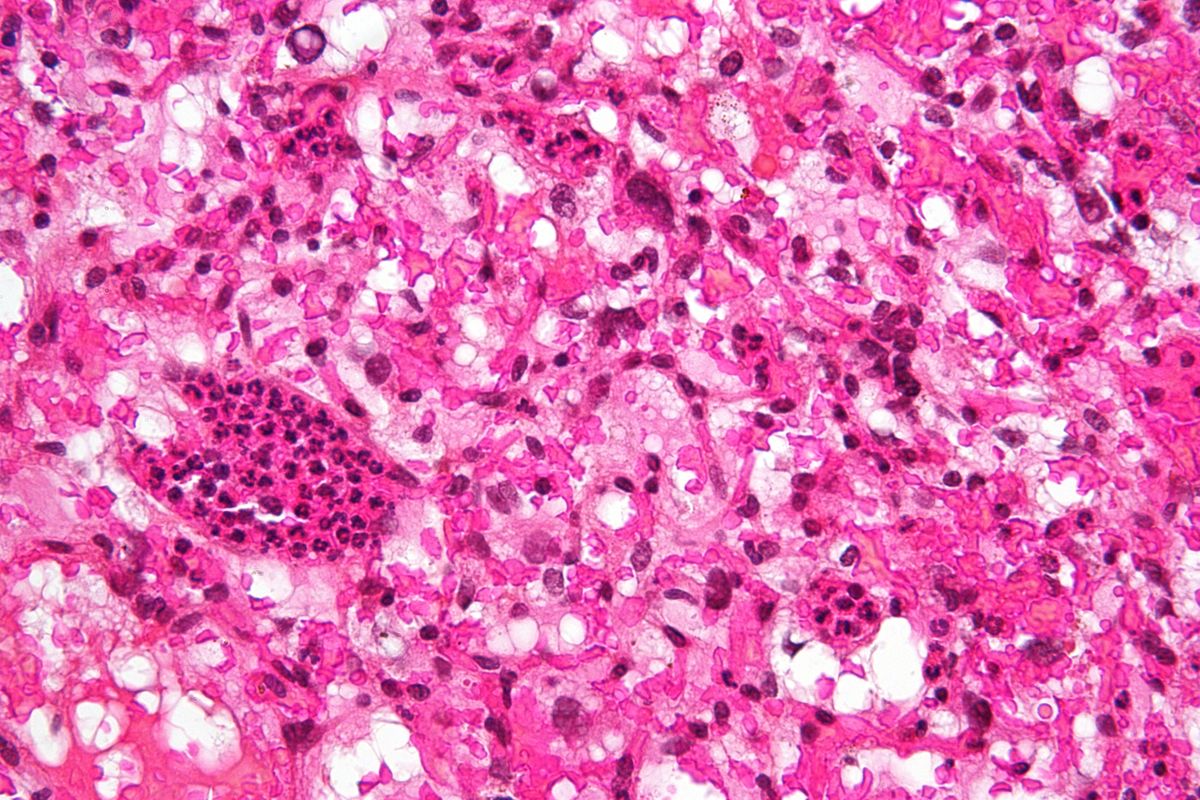
Hemangioblastoma is a rare, benign tumor primarily found in the brain and spinal cord. These tumors originate from the blood vessels and can cause a variety of symptoms depending on their location. Hemangioblastomas are often associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease, a genetic disorder that increases the risk of developing multiple types of tumors. While these tumors are non-cancerous, their growth can lead to serious complications such as headaches, balance issues, and even neurological deficits. Understanding hemangioblastoma is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This article will provide 50 essential facts about hemangioblastoma, covering everything from symptoms and diagnosis to treatment options and prognosis.
Key Takeaways:
- Hemangioblastoma is a rare, non-cancerous brain tumor associated with genetic factors, causing symptoms like headaches, balance problems, and vision issues. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
- Research on hemangioblastoma is advancing, with ongoing studies on genetic mutations, imaging techniques, and new treatment options. Patients can find support through regular check-ups, healthy living, and online communities.
What is Hemangioblastoma?
Hemangioblastoma is a rare, benign tumor that originates from the blood vessels in the brain, spinal cord, or retina. These tumors are often associated with a genetic condition called von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about hemangioblastomas.
-
Hemangioblastomas are most commonly found in the cerebellum, the part of the brain that controls balance and coordination.
-
These tumors can also occur in the spinal cord, brainstem, and retina.
-
Hemangioblastomas are typically slow-growing and non-cancerous.
-
They account for about 2% of all brain tumors.
-
Hemangioblastomas are more common in adults between the ages of 30 and 50.
Symptoms of Hemangioblastoma
The symptoms of hemangioblastoma can vary depending on the tumor's location. Here are some common symptoms associated with these tumors.
-
Headaches are a common symptom, especially if the tumor is in the brain.
-
Nausea and vomiting can occur due to increased pressure in the brain.
-
Balance and coordination problems may arise if the tumor is in the cerebellum.
-
Weakness or numbness in the limbs can occur if the tumor is in the spinal cord.
-
Vision problems, such as blurred vision or loss of vision, can occur if the tumor is in the retina.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of hemangioblastoma can help in early detection and management.
-
The exact cause of hemangioblastoma is unknown, but genetic factors play a significant role.
-
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease is a major risk factor for developing hemangioblastomas.
-
VHL disease is an inherited disorder caused by mutations in the VHL gene.
-
People with VHL disease have a higher risk of developing multiple hemangioblastomas.
-
Sporadic hemangioblastomas, which occur without a family history of VHL disease, are less common.
Diagnosis of Hemangioblastoma
Diagnosing hemangioblastoma involves various imaging techniques and tests. Here are some key facts about the diagnosis process.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most common imaging technique used to diagnose hemangioblastomas.
-
Computed tomography (CT) scans can also be used to detect these tumors.
-
Angiography, an imaging technique that visualizes blood vessels, can help in diagnosing hemangioblastomas.
-
Genetic testing for VHL disease may be recommended if multiple tumors are present.
-
A biopsy, where a small sample of the tumor is removed and examined, can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hemangioblastoma depends on the tumor's size, location, and symptoms. Here are some common treatment options.
-
Surgery is the primary treatment for hemangioblastomas, especially if the tumor is causing symptoms.
-
Complete surgical removal of the tumor is often possible due to its well-defined borders.
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery, a non-invasive treatment that uses focused radiation, can be an option for small tumors.
-
Regular monitoring with MRI scans may be recommended for small, asymptomatic tumors.
-
Medications to manage symptoms, such as pain relievers and anti-nausea drugs, can be used alongside other treatments.
Prognosis and Outcomes
The prognosis for hemangioblastoma patients can vary. Here are some important facts about outcomes and prognosis.
-
The prognosis for hemangioblastoma patients is generally good, especially if the tumor is completely removed.
-
Recurrence of the tumor is possible, particularly in patients with VHL disease.
-
Regular follow-up with imaging studies is essential to monitor for recurrence.
-
Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
-
Patients with VHL disease require lifelong monitoring for new tumors.
Interesting Facts About Hemangioblastoma
Let's explore some intriguing and lesser-known facts about hemangioblastomas.
-
Hemangioblastomas can sometimes produce a protein called erythropoietin, leading to increased red blood cell production.
-
These tumors are highly vascular, meaning they have a rich blood supply.
-
Hemangioblastomas can sometimes be mistaken for other types of brain tumors due to similar symptoms.
-
The first description of hemangioblastoma dates back to the early 20th century.
-
Hemangioblastomas are more common in males than females.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research is crucial for understanding hemangioblastomas better and developing new treatments. Here are some recent advances and research findings.
-
Researchers are studying the genetic mutations involved in VHL disease to develop targeted therapies.
-
Advances in imaging techniques are improving the accuracy of hemangioblastoma diagnosis.
-
Clinical trials are exploring new treatment options, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies.
-
Researchers are investigating the role of angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, in hemangioblastoma growth.
-
Collaborative efforts between researchers and clinicians are leading to better management strategies for hemangioblastoma patients.
Living with Hemangioblastoma
Living with hemangioblastoma can be challenging, but support and resources are available. Here are some tips for managing life with this condition.
-
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring the condition.
-
Support groups and online communities can provide emotional support and valuable information.
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can improve overall well-being.
-
Patients should be aware of the symptoms of recurrence and seek medical attention if they experience any changes.
-
Genetic counseling can be beneficial for patients with VHL disease and their families.
Hemangioblastoma in Pop Culture
While not commonly featured in pop culture, hemangioblastomas have made occasional appearances. Here are a few examples.
-
Some medical TV shows have featured episodes about rare brain tumors, including hemangioblastomas.
-
Documentaries about rare diseases sometimes highlight conditions like VHL disease and associated tumors.
-
Awareness campaigns for rare diseases occasionally mention hemangioblastomas to educate the public.
-
Medical journals and books often include case studies and research articles about hemangioblastomas.
-
Social media platforms have patient advocacy groups that share stories and raise awareness about hemangioblastomas.
Final Thoughts on Hemangioblastoma
Hemangioblastomas, though rare, are significant due to their impact on the central nervous system. These tumors, often found in the brain and spinal cord, can cause a variety of symptoms like headaches, nausea, and balance issues. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing these symptoms and improving patient outcomes. Advances in medical imaging and surgical techniques have made it easier to diagnose and treat hemangioblastomas effectively. While they can be challenging to manage, ongoing research offers hope for better treatments and understanding. Staying informed about the latest developments in hemangioblastoma research can make a big difference for patients and their families. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options. Knowledge is power, and being aware of the facts about hemangioblastomas can help navigate this complex condition with more confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
