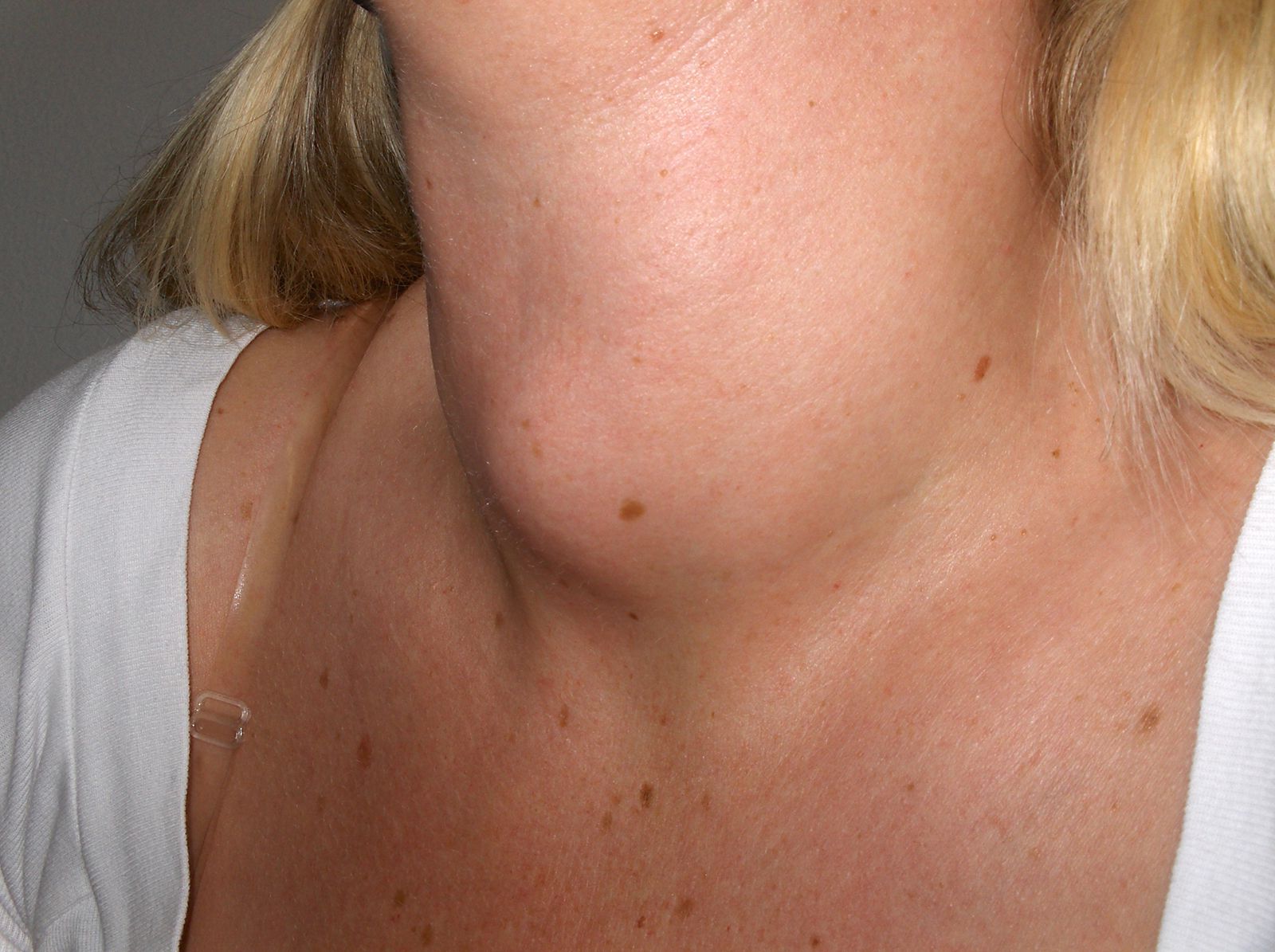
What is a goitre? A goitre is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, located at the base of the neck. This condition can cause visible swelling and may lead to symptoms like difficulty swallowing, coughing, and a tight feeling in the throat. Goitres can result from various factors, including iodine deficiency, autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and certain medications. While some goitres are harmless, others may indicate underlying thyroid issues that require medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of goitre can help manage this condition effectively. Let's dive into 50 intriguing facts about goitre to expand your knowledge.
Key Takeaways:
- Goitre is a condition where the thyroid gland enlarges, causing visible or invisible swelling in the neck. It can be caused by iodine deficiency, autoimmune diseases, genetics, hormonal changes, and radiation exposure.
- Recognizing the symptoms of goitre, such as visible swelling, tightness in the throat, difficulty swallowing, breathing problems, and voice changes, can lead to early diagnosis and treatment. Treatment options include iodine supplementation, medications, radioactive iodine therapy, surgery, and watchful waiting.
What is Goitre?
Goitre is a condition where the thyroid gland enlarges abnormally. This gland, located at the base of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about goitre.
-
Goitre can be visible or invisible. Sometimes, the swelling is noticeable, while other times, it can only be detected through medical imaging.
-
Iodine deficiency is a common cause. Lack of iodine in the diet can lead to thyroid enlargement.
-
Goitre can affect anyone. People of all ages and genders can develop this condition, though it is more common in women.
-
There are different types of goitre. These include diffuse goitre, where the entire thyroid swells, and nodular goitre, where lumps form within the gland.
-
Symptoms vary widely. Some people experience no symptoms, while others may have difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Causes of Goitre
Understanding what causes goitre can help in its prevention and treatment. Here are some key factors that contribute to its development.
-
Autoimmune diseases can trigger goitre. Conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease can cause the thyroid to enlarge.
-
Certain medications can lead to goitre. Drugs like lithium and amiodarone have been linked to thyroid enlargement.
-
Genetics play a role. A family history of thyroid disorders increases the risk of developing goitre.
-
Radiation exposure is a risk factor. Exposure to radiation, especially during childhood, can increase the likelihood of goitre.
-
Hormonal changes can influence thyroid size. Pregnancy, puberty, and menopause can all affect thyroid function and size.
Symptoms of Goitre
Recognizing the symptoms of goitre can lead to early diagnosis and treatment. Here are some common signs to watch for.
-
A visible swelling in the neck. This is the most obvious symptom of goitre.
-
Tightness in the throat. Some people feel a constant pressure in their neck.
-
Difficulty swallowing. An enlarged thyroid can press against the esophagus, making it hard to swallow.
-
Breathing problems. In severe cases, goitre can compress the windpipe, leading to breathing difficulties.
-
Hoarseness or voice changes. Pressure on the vocal cords can alter the voice.
Diagnosing Goitre
Medical professionals use various methods to diagnose goitre. Here are some common diagnostic tools and techniques.
-
Physical examination. Doctors often detect goitre through a simple neck palpation.
-
Blood tests. These can measure thyroid hormone levels and help identify underlying causes.
-
Ultrasound imaging. This non-invasive test provides detailed images of the thyroid gland.
-
Thyroid scan. A small amount of radioactive iodine is used to visualize the thyroid.
-
Biopsy. In some cases, a small tissue sample is taken to rule out cancer.
Treatment Options for Goitre
Treating goitre depends on its cause, size, and symptoms. Here are some common treatment methods.
-
Iodine supplementation. For iodine-deficient goitre, increasing iodine intake can help.
-
Medications. Drugs like levothyroxine can regulate thyroid hormone levels.
-
Radioactive iodine therapy. This treatment shrinks the thyroid gland by destroying overactive thyroid cells.
-
Surgery. In severe cases, part or all of the thyroid may be removed.
-
Watchful waiting. If the goitre is small and not causing symptoms, doctors may recommend regular monitoring.
Preventing Goitre
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some ways to reduce the risk of developing goitre.
-
Ensure adequate iodine intake. Eating iodized salt and iodine-rich foods can prevent deficiency.
-
Regular thyroid check-ups. Early detection of thyroid issues can prevent goitre.
-
Avoid exposure to radiation. Limiting unnecessary radiation exposure can reduce risk.
-
Manage autoimmune conditions. Proper treatment of autoimmune diseases can prevent thyroid enlargement.
-
Stay informed about medications. Be aware of the potential side effects of drugs that can affect the thyroid.
Interesting Facts About Goitre
Here are some lesser-known but intriguing facts about goitre.
-
Goitre has been known since ancient times. Historical texts from Egypt and China mention this condition.
-
The word "goitre" comes from Latin. It is derived from "guttur," meaning throat.
-
Goitre was once called "Derbyshire neck." This term was used in England due to the high prevalence in Derbyshire.
-
Seaweed can help prevent goitre. This iodine-rich food is beneficial for thyroid health.
-
Goitre can be a sign of both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. It indicates an imbalance in thyroid hormone levels.
Goitre Around the World
Goitre prevalence varies globally. Here are some facts about its occurrence in different regions.
-
Iodine deficiency is more common in developing countries. Lack of access to iodized salt contributes to higher goitre rates.
-
Goitre is rare in countries with iodine-rich diets. Nations like Japan, where seaweed is a staple, have lower incidence rates.
-
Endemic goitre occurs in certain regions. Areas with low iodine in the soil and water see higher goitre prevalence.
-
Public health initiatives have reduced goitre rates. Programs promoting iodized salt have significantly decreased cases.
-
Goitre can indicate other nutritional deficiencies. Lack of selenium and iron can also contribute to thyroid enlargement.
Myths and Misconceptions About Goitre
There are many myths surrounding goitre. Here are some common misconceptions debunked.
-
Goitre is not always cancerous. Most goitres are benign and not related to cancer.
-
Only older people get goitre. This condition can affect individuals of any age.
-
Goitre is not always due to iodine deficiency. Other factors like autoimmune diseases and genetics also play a role.
-
Goitre cannot be cured. Many treatment options are available, and some goitres resolve on their own.
-
All goitres cause symptoms. Some people with goitre experience no symptoms at all.
Famous People with Goitre
Even well-known individuals have dealt with goitre. Here are some notable cases.
-
George H.W. Bush. The former U.S. president had a goitre due to Graves' disease.
-
Barbara Bush. She also had Graves' disease, leading to thyroid issues.
-
Oprah Winfrey. The media mogul has openly discussed her thyroid problems.
-
Rod Stewart. The singer underwent surgery for thyroid nodules.
-
Gail Devers. The Olympic sprinter overcame Graves' disease and continued her athletic career.
Final Thoughts on Goitre
Goitre, a swelling of the thyroid gland, can be caused by various factors like iodine deficiency, autoimmune diseases, or nodules. Recognizing symptoms such as neck swelling, difficulty swallowing, or breathing issues is crucial for early diagnosis. Treatments range from iodine supplements to surgery, depending on the underlying cause.
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in iodine can help prevent goitre. Foods like fish, dairy, and iodized salt are excellent sources. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider ensure any thyroid issues are caught early.
Understanding goitre empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their thyroid health. Awareness and timely intervention can make a significant difference in outcomes. Stay informed, prioritize health, and consult professionals when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
