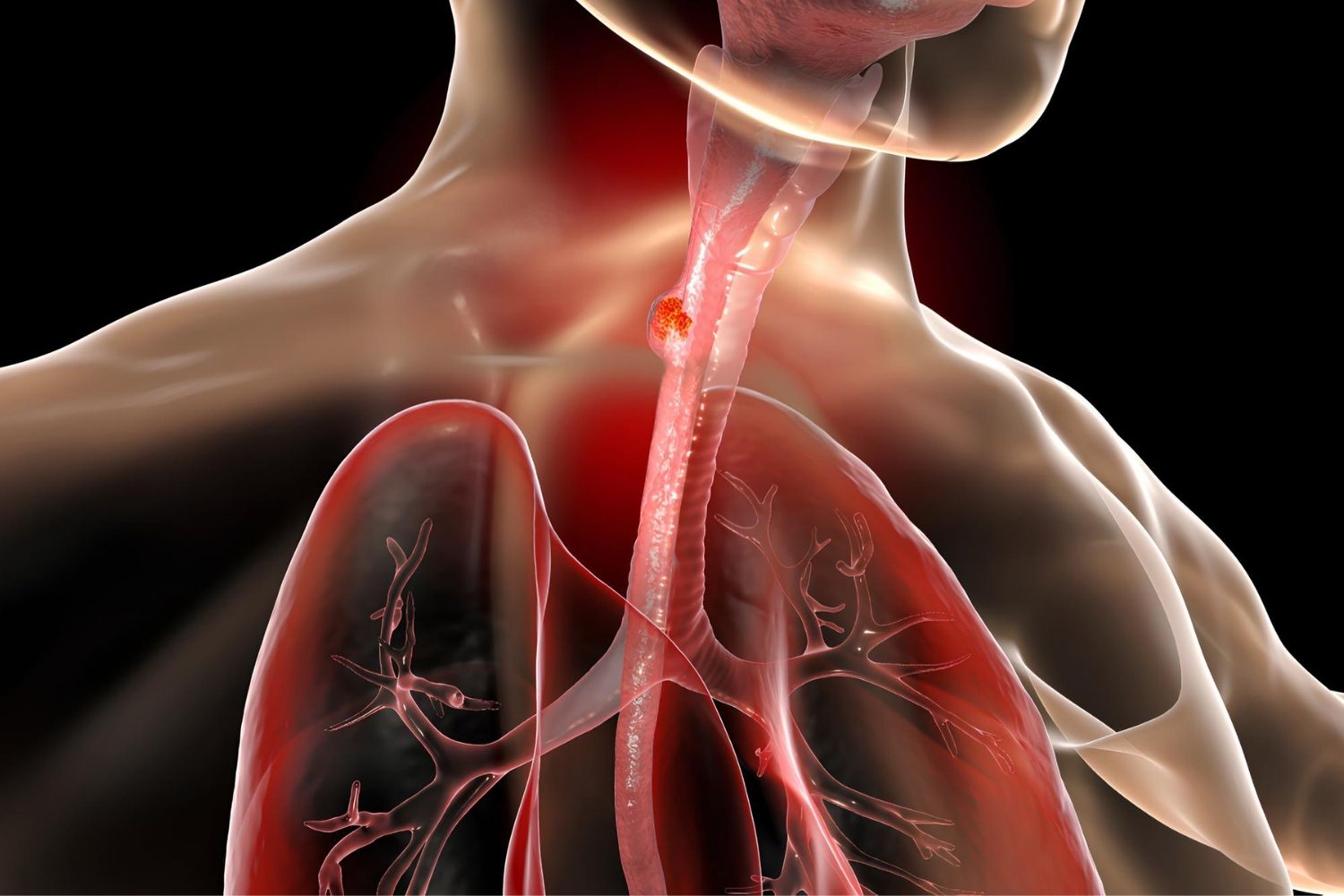
Esophageal varices are swollen veins in the lower part of the esophagus, often linked to serious liver conditions like cirrhosis. These veins can become life-threatening if they rupture, leading to severe bleeding. Understanding esophageal varices is crucial for anyone dealing with liver disease or caring for someone who is. This post will provide 50 facts about esophageal varices, covering everything from symptoms and causes to treatments and preventive measures. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or just curious, these facts will equip you with essential knowledge about this medical condition. Ready to dive in? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Esophageal varices are enlarged veins in the esophagus, often caused by liver diseases. Symptoms include vomiting blood and black stools. Treatment options include medications and surgical procedures.
- Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding alcohol and maintaining a healthy weight, can help prevent esophageal varices. Regular medical check-ups and support from healthcare providers are essential for managing the condition.
What are Esophageal Varices?
Esophageal varices are abnormal, enlarged veins in the lower part of the esophagus. They often develop in people with serious liver diseases. These veins can rupture and cause life-threatening bleeding.
- Esophageal varices are most commonly caused by cirrhosis of the liver.
- Portal hypertension, increased blood pressure in the portal vein, leads to the formation of esophageal varices.
- Alcoholic liver disease is a significant risk factor for developing esophageal varices.
- Hepatitis B and C infections can also lead to cirrhosis and subsequent varices.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an emerging cause of cirrhosis and varices.
Symptoms of Esophageal Varices
Recognizing the symptoms of esophageal varices is crucial for timely medical intervention. Symptoms often appear only when the varices bleed.
- Vomiting blood is a common symptom of bleeding esophageal varices.
- Black, tarry stools indicate the presence of digested blood.
- Lightheadedness or fainting can occur due to significant blood loss.
- Jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes, may be present in individuals with liver disease.
- Ascites, or fluid accumulation in the abdomen, often accompanies varices in liver disease patients.
Diagnosis of Esophageal Varices
Diagnosing esophageal varices involves several medical tests and procedures. Early detection can prevent severe complications.
- Endoscopy is the most reliable method for diagnosing esophageal varices.
- Ultrasound of the liver can help identify cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
- CT scans provide detailed images of the liver and surrounding blood vessels.
- MRI can be used to assess liver structure and blood flow.
- Blood tests can reveal liver function and the presence of hepatitis viruses.
Treatment Options for Esophageal Varices
Treatment aims to prevent bleeding and manage underlying liver disease. Various medical and surgical options are available.
- Beta-blockers are medications that reduce blood pressure in the portal vein.
- Endoscopic band ligation involves placing bands around varices to prevent bleeding.
- Sclerotherapy injects a solution into varices to shrink them.
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a procedure that creates a new pathway for blood flow in the liver.
- Liver transplantation may be necessary for patients with severe liver disease.
Preventing Esophageal Varices
Preventing esophageal varices involves managing liver health and avoiding risk factors. Lifestyle changes can make a significant difference.
- Avoiding alcohol is crucial for preventing liver damage and varices.
- Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Regular exercise helps improve overall liver health.
- Vaccination against hepatitis B can prevent liver infections that lead to cirrhosis.
- Healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports liver function.
Complications of Esophageal Varices
Complications from esophageal varices can be severe and life-threatening. Understanding these risks is important for patients and caregivers.
- Bleeding is the most serious complication of esophageal varices.
- Hypovolemic shock can occur due to massive blood loss.
- Infection risk increases after variceal bleeding.
- Hepatic encephalopathy is a decline in brain function due to liver disease.
- Kidney failure can result from severe liver disease and variceal bleeding.
Living with Esophageal Varices
Living with esophageal varices requires ongoing medical care and lifestyle adjustments. Support from healthcare providers and loved ones is essential.
- Regular medical check-ups are necessary to monitor liver health and varices.
- Medications may be prescribed to manage liver disease and prevent bleeding.
- Avoiding NSAIDs like ibuprofen can reduce the risk of bleeding.
- Limiting salt intake helps manage fluid retention and ascites.
- Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve the understanding and treatment of esophageal varices. Advances in medical science offer hope for better outcomes.
- Stem cell therapy is being explored as a potential treatment for liver disease.
- New medications are being developed to reduce portal hypertension.
- Genetic research may identify individuals at higher risk for liver disease and varices.
- Improved imaging techniques can enhance the early detection of varices.
- Clinical trials offer patients access to cutting-edge treatments.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths and misconceptions about esophageal varices. Clearing up these misunderstandings can help patients make informed decisions.
- Myth: Only alcoholics get esophageal varices. Fact: Many conditions, including hepatitis and NAFLD, can cause varices.
- Myth: Esophageal varices always cause symptoms. Fact: Varices often remain asymptomatic until they bleed.
- Myth: Surgery is the only treatment option. Fact: Medications and less invasive procedures are also effective.
- Myth: Esophageal varices are rare. Fact: They are common in individuals with advanced liver disease.
- Myth: Lifestyle changes can't help. Fact: Healthy habits can significantly reduce the risk of varices.
Support and Resources
Support and resources are available for individuals with esophageal varices and their families. Accessing these can improve quality of life and outcomes.
- Liver disease foundations offer information and support for patients.
- Online forums provide a platform for sharing experiences and advice.
- Counseling services can help patients cope with the emotional impact of chronic illness.
- Educational materials from healthcare providers can enhance understanding of the condition.
- Community health programs may offer screenings and support for liver disease patients.
Key Takeaways on Esophageal Varices
Esophageal varices are swollen veins in the esophagus that can lead to serious health issues if they rupture. Often linked to liver disease, these varices develop when blood flow to the liver is obstructed, causing increased pressure in the veins. Symptoms might include vomiting blood, black stools, or lightheadedness. Early detection through endoscopy and managing underlying liver conditions are crucial for preventing complications. Treatments range from medications to procedures like banding or sclerotherapy. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding alcohol and maintaining a healthy diet, also play a significant role in managing this condition. Understanding the risks and symptoms can help in seeking timely medical intervention, potentially saving lives. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options. Stay informed, stay healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
