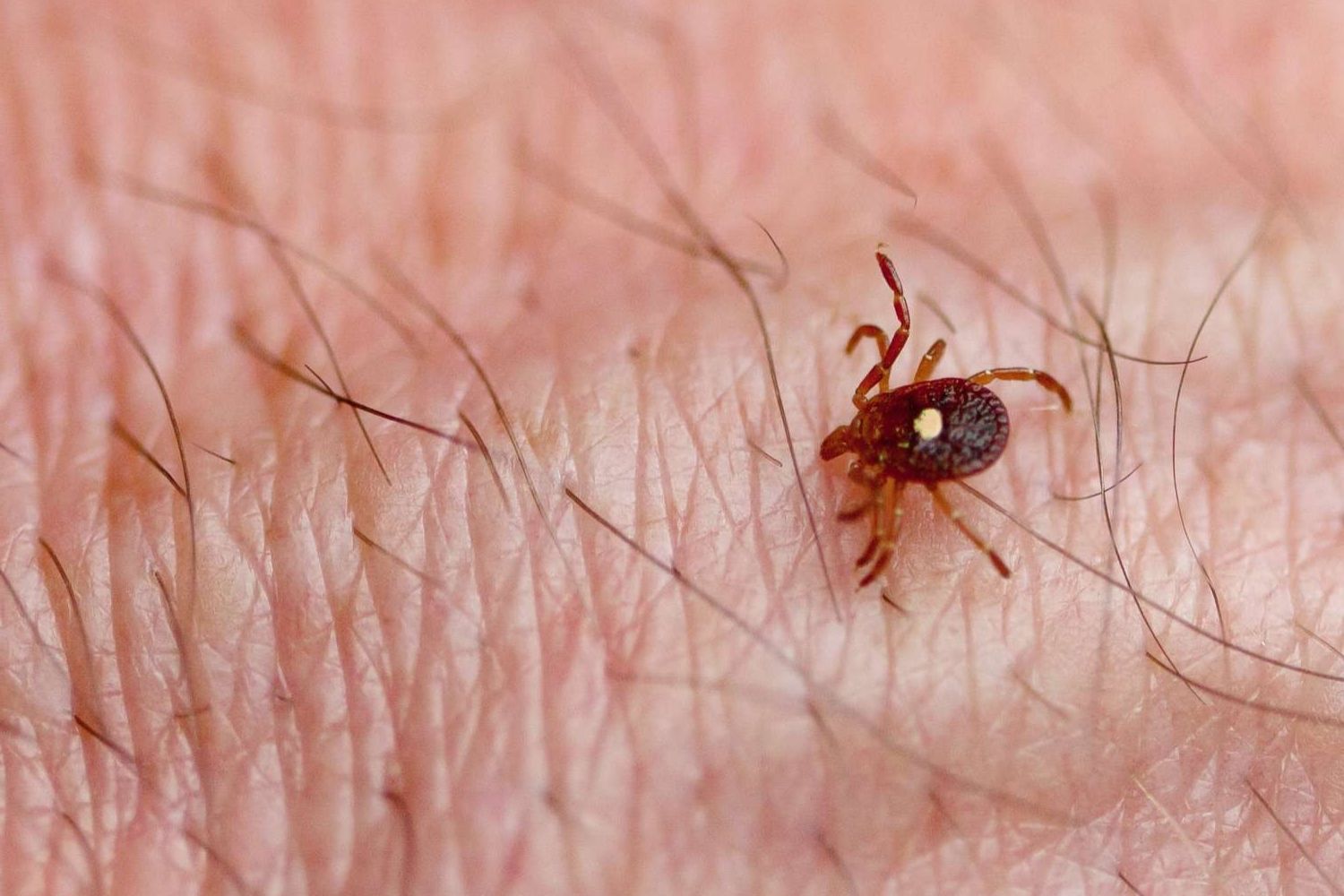
Ehrlichiosis is a tick-borne illness caused by bacteria from the Ehrlichia genus. These tiny creatures, often found in wooded areas, can transmit the disease to humans through bites. Symptoms might start with fever, chills, headache, and muscle aches, making it tricky to distinguish from other illnesses. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, usually involving antibiotics like doxycycline. While anyone can get ehrlichiosis, those spending time outdoors in tick-prone regions face higher risks. Preventing tick bites by using repellents, wearing protective clothing, and checking for ticks after outdoor activities can reduce the chances of infection. Understanding this disease helps in taking proactive steps to stay healthy and safe.
Key Takeaways:
- Ehrlichiosis is a bacterial illness transmitted by ticks, causing flu-like symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are crucial for a full recovery.
- Prevention is key to avoiding ehrlichiosis. Wearing protective clothing, using insect repellent, and performing tick checks can reduce the risk of infection.
What is Ehrlichiosis?
Ehrlichiosis is a bacterial illness transmitted by ticks. It can affect both humans and animals, causing flu-like symptoms. Understanding this disease is crucial for prevention and treatment.
-
Ehrlichiosis is caused by bacteria from the genus Ehrlichia. These bacteria are transmitted through tick bites, primarily from the lone star tick.
-
The disease was first identified in the United States in 1986. It was discovered in a patient from Arkansas, marking the beginning of its recognition as a public health concern.
-
Ehrlichiosis primarily affects white blood cells. The bacteria invade and multiply within these cells, leading to various symptoms.
-
Symptoms often resemble the flu. Fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches are common, making it difficult to distinguish from other illnesses without testing.
-
Ticks are the primary vectors. The lone star tick, American dog tick, and black-legged tick are known carriers of the bacteria.
How is Ehrlichiosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing ehrlichiosis can be tricky due to its non-specific symptoms. However, certain tests and methods help in identifying the disease accurately.
-
Blood tests are essential for diagnosis. They can detect the presence of Ehrlichia bacteria or antibodies produced in response to the infection.
-
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests are highly effective. These tests amplify the DNA of the bacteria, making it easier to identify.
-
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Delays can lead to more severe symptoms and complications.
-
Doctors often rely on clinical symptoms and history. A history of tick exposure combined with symptoms can lead to a presumptive diagnosis.
-
Ehrlichiosis can be mistaken for other tick-borne diseases. Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever have overlapping symptoms, complicating diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Ehrlichiosis
Once diagnosed, ehrlichiosis can be treated effectively with antibiotics. Early intervention is key to a full recovery.
-
Doxycycline is the antibiotic of choice. It is effective against Ehrlichia bacteria and is usually prescribed for 7 to 14 days.
-
Treatment should begin as soon as possible. Early administration of antibiotics can prevent severe complications.
-
Most patients recover fully with treatment. However, untreated ehrlichiosis can lead to severe illness or even death.
-
Hospitalization may be necessary for severe cases. Patients with complications may require supportive care in a hospital setting.
-
There is no vaccine for ehrlichiosis. Prevention relies on avoiding tick bites and using protective measures.
Preventing Ehrlichiosis
Prevention is the best strategy against ehrlichiosis. By taking certain precautions, you can reduce the risk of tick bites and infection.
-
Wearing protective clothing can help. Long sleeves, pants, and hats can reduce skin exposure to ticks.
-
Using insect repellent is effective. Products containing DEET or permethrin can repel ticks.
-
Performing tick checks is crucial. After spending time outdoors, check your body and clothing for ticks.
-
Keeping your yard tidy can reduce tick habitats. Mowing the lawn and removing leaf litter can help keep ticks away.
-
Pets can carry ticks indoors. Regularly check and treat pets with tick prevention products.
Ehrlichiosis in Animals
Ehrlichiosis doesn't just affect humans; animals, particularly dogs, can also contract the disease. Understanding its impact on pets is important for their health.
-
Dogs are commonly affected by ehrlichiosis. They can contract the disease from tick bites, just like humans.
-
Symptoms in dogs include fever, lethargy, and loss of appetite. These signs can be similar to other canine illnesses.
-
Veterinarians use blood tests to diagnose ehrlichiosis in dogs. These tests can detect the presence of Ehrlichia bacteria or antibodies.
-
Doxycycline is also used to treat dogs. The antibiotic is effective in clearing the infection in pets.
-
Preventative measures for pets are similar to those for humans. Regular tick checks and using tick prevention products are recommended.
Geographic Distribution of Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is more prevalent in certain regions, primarily due to the distribution of tick vectors. Knowing where the disease is common can help in prevention efforts.
-
The southeastern and south-central United States have higher incidence rates. These regions are home to the lone star tick, a primary vector.
-
Cases have been reported in other parts of the world. While less common, ehrlichiosis has been identified in Europe, Africa, and Asia.
-
Tick habitats influence the distribution of ehrlichiosis. Areas with dense vegetation and wildlife are more likely to harbor ticks.
-
Climate change may affect the spread of ehrlichiosis. Warmer temperatures can expand tick habitats, potentially increasing the disease's range.
-
Travelers to endemic areas should take precautions. Awareness and preventive measures can reduce the risk of infection.
Complications of Untreated Ehrlichiosis
If left untreated, ehrlichiosis can lead to serious health issues. Understanding potential complications underscores the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
-
Severe cases can cause respiratory failure. The infection can lead to difficulty breathing and require medical intervention.
-
Kidney failure is a possible complication. The bacteria can affect kidney function, leading to serious health problems.
-
Neurological issues may arise. Confusion, seizures, and other neurological symptoms can occur in severe cases.
-
Blood disorders are a risk. Anemia, low platelet count, and other blood-related issues can develop.
-
Death is a rare but possible outcome. Without treatment, the disease can be fatal, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Research and Developments in Ehrlichiosis
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of ehrlichiosis. Scientific advancements continue to shed light on this tick-borne disease.
-
New diagnostic tests are being developed. These aim to improve accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
-
Research is exploring potential vaccines. While none are available yet, efforts continue to find a preventive solution.
-
Studies are examining tick behavior and ecology. Understanding tick habitats and behaviors can aid in prevention strategies.
-
Genetic research is uncovering more about Ehrlichia bacteria. Insights into bacterial genetics can lead to better treatments.
-
Public health initiatives focus on awareness and prevention. Educating communities about tick-borne diseases is a key component of control efforts.
Interesting Facts About Ehrlichiosis
Beyond the medical and scientific aspects, there are intriguing facts about ehrlichiosis that highlight its complexity and impact.
-
Ehrlichiosis is named after Paul Ehrlich. The German scientist made significant contributions to immunology and bacteriology.
-
The disease can affect multiple species. Besides humans and dogs, other animals like cats and horses can also contract ehrlichiosis.
-
Ticks can carry multiple pathogens. A single tick bite can transmit more than one disease, complicating diagnosis and treatment.
-
Ehrlichiosis is considered an emerging infectious disease. Its incidence has increased over the years, raising public health concerns.
-
The bacteria can survive in tick saliva. This adaptation helps them infect hosts during a tick bite.
Myths and Misconceptions About Ehrlichiosis
Misunderstandings about ehrlichiosis can lead to confusion and improper prevention or treatment. Clearing up these myths is important for public awareness.
-
Myth: Only outdoor enthusiasts are at risk. While outdoor activities increase exposure, anyone can be bitten by a tick.
-
Myth: Ticks only live in rural areas. Ticks can be found in urban parks and gardens, not just forests.
-
Myth: All tick bites lead to ehrlichiosis. Not all ticks carry the bacteria, and not all bites result in infection.
-
Myth: Ehrlichiosis is not serious. While often mild, untreated cases can lead to severe complications.
-
Myth: You can feel a tick bite. Tick bites are usually painless, making it easy to miss them.
Final Thoughts on Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis, a tick-borne illness, often flies under the radar, yet understanding it is crucial. This disease, caused by Ehrlichia bacteria, can lead to serious health issues if not caught early. Symptoms like fever, chills, and muscle aches mimic other illnesses, making diagnosis tricky. Prevention is key—wear protective clothing and use tick repellents when in wooded or grassy areas. If bitten, remove ticks promptly and monitor for symptoms. Early detection and treatment with antibiotics can prevent complications. Awareness is your best defense. Knowing the risks and signs can help protect you and your loved ones. Stay informed, stay safe, and don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect exposure. Remember, a little knowledge goes a long way in keeping ehrlichiosis at bay. Stay vigilant and proactive in safeguarding your health against this sneaky tick-borne threat.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
