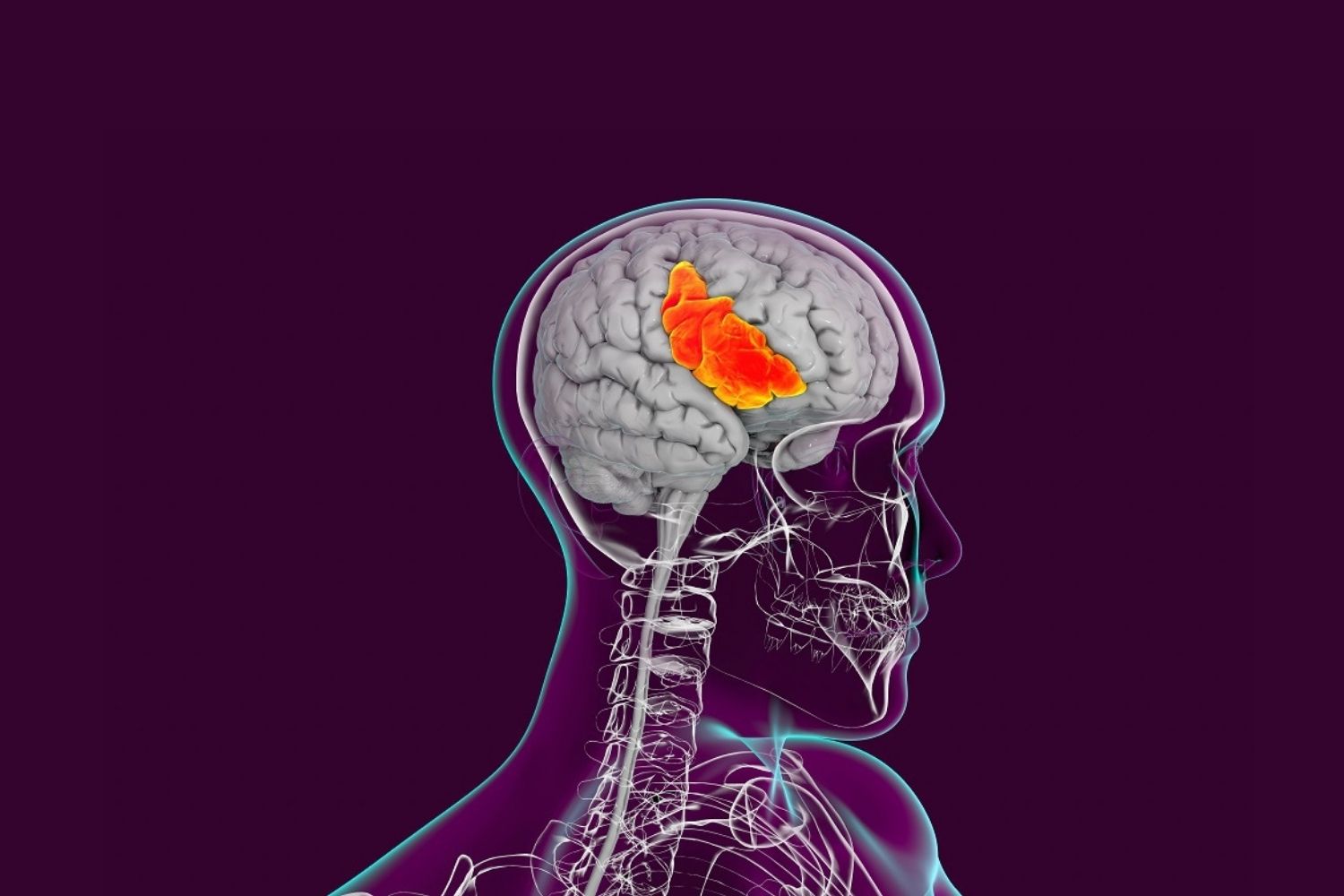
Broca's Aphasia is a type of language disorder that affects speech production and writing while leaving comprehension mostly intact. Named after French physician Pierre Paul Broca, who first linked it to brain damage in the 1860s, this condition often results from injury to the frontal lobe, specifically Broca's area. Symptoms include difficulty forming complete sentences, omitting small words like "is" or "the," and speaking in short, broken phrases. Despite these challenges, individuals with Broca's Aphasia usually understand spoken language well and can follow conversations. Treatment often involves speech therapy, which helps improve communication skills over time. Understanding this condition can foster empathy and support for those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- Broca's Aphasia affects speech production due to brain damage. It causes slow, broken speech and difficulty finding words. Support and therapy can improve communication and quality of life.
- Stroke, brain tumors, and infections can cause Broca's Aphasia. Therapy, family support, and technology help manage the condition and enhance communication skills.
What is Broca's Aphasia?
Broca's Aphasia, also known as non-fluent or expressive aphasia, is a language disorder that affects speech production. It occurs due to damage in a specific area of the brain called Broca's area. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
- Broca's Aphasia was first identified by French physician Pierre Paul Broca in the 1860s.
- It primarily affects the left hemisphere of the brain, which is responsible for language processing.
- Individuals with Broca's Aphasia often understand speech better than they can produce it.
- Writing abilities are usually impaired, mirroring the difficulties in speech production.
- Reading comprehension remains relatively intact, although it can be challenging.
- People with this condition often speak in short, broken sentences.
- Common phrases and automatic speech, like greetings, are usually easier to produce.
- Broca's area is located in the frontal lobe of the brain.
- Damage to this area is often caused by a stroke.
- Traumatic brain injury can also lead to Broca's Aphasia.
Symptoms and Characteristics
Understanding the symptoms and characteristics of Broca's Aphasia can help in identifying and managing the condition effectively.
- Speech is typically slow and laborious.
- Grammar and syntax are often incorrect or missing.
- Patients may struggle to find the right words, a condition known as anomia.
- Repetition of words or phrases is common.
- Non-verbal communication, like gestures, becomes more prominent.
- Emotional expression through speech is usually preserved.
- Patients are often aware of their speech difficulties.
- Frustration and depression can occur due to communication challenges.
- Comprehension of complex sentences can be difficult.
- Naming objects or people can be particularly challenging.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of Broca's Aphasia. Knowing these can aid in prevention and early intervention.
- Stroke is the leading cause of Broca's Aphasia.
- Brain tumors can also damage Broca's area.
- Infections like encephalitis may lead to this condition.
- Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's, can be a risk factor.
- Aneurysms in the brain can cause localized damage.
- Genetic predisposition may play a role.
- High blood pressure increases the risk of stroke-related aphasia.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are risk factors.
- Diabetes can contribute to vascular issues leading to strokes.
- Age is a significant risk factor, with older adults being more susceptible.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with Broca's Aphasia.
- Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive language assessment.
- Brain imaging techniques, like MRI and CT scans, are used to identify the damage.
- Speech and language therapy is the primary treatment.
- Therapy focuses on improving speech production and comprehension.
- Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices can be helpful.
- Group therapy sessions provide social support and practice.
- Family involvement is crucial for effective therapy.
- Medications may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions.
- Neuroplasticity allows the brain to reorganize and compensate for damaged areas.
- Consistent practice and repetition are key to improvement.
Living with Broca's Aphasia
Adapting to life with Broca's Aphasia involves various strategies and support systems to enhance communication and overall well-being.
- Patience and understanding from family and friends are vital.
- Simplifying language and using visual aids can aid communication.
- Encouraging the use of gestures and facial expressions helps convey messages.
- Technology, like speech-generating apps, can be beneficial.
- Support groups offer emotional and practical assistance.
- Occupational therapy can help with daily living skills.
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet support overall brain health.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques reduce stress.
- Setting realistic goals and celebrating small achievements boosts morale.
- Continuous learning and adaptation are essential for managing Broca's Aphasia.
The Power of Understanding
Broca's Aphasia, a condition affecting speech and language, highlights the brain's complexity. Named after Paul Broca, this disorder shows how specific brain areas control language. People with Broca's Aphasia often struggle with speaking but can understand others well. This condition can result from strokes, head injuries, or brain tumors.
Treatment involves speech therapy, which helps patients regain communication skills. Understanding Broca's Aphasia not only aids those affected but also deepens our knowledge of the brain's functions.
Recognizing symptoms early and seeking medical advice can make a significant difference. Awareness and support are crucial for those living with this condition. By learning about Broca's Aphasia, we can better support individuals and appreciate the intricacies of human communication.
Stay curious, keep learning, and remember the importance of empathy in understanding such conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
