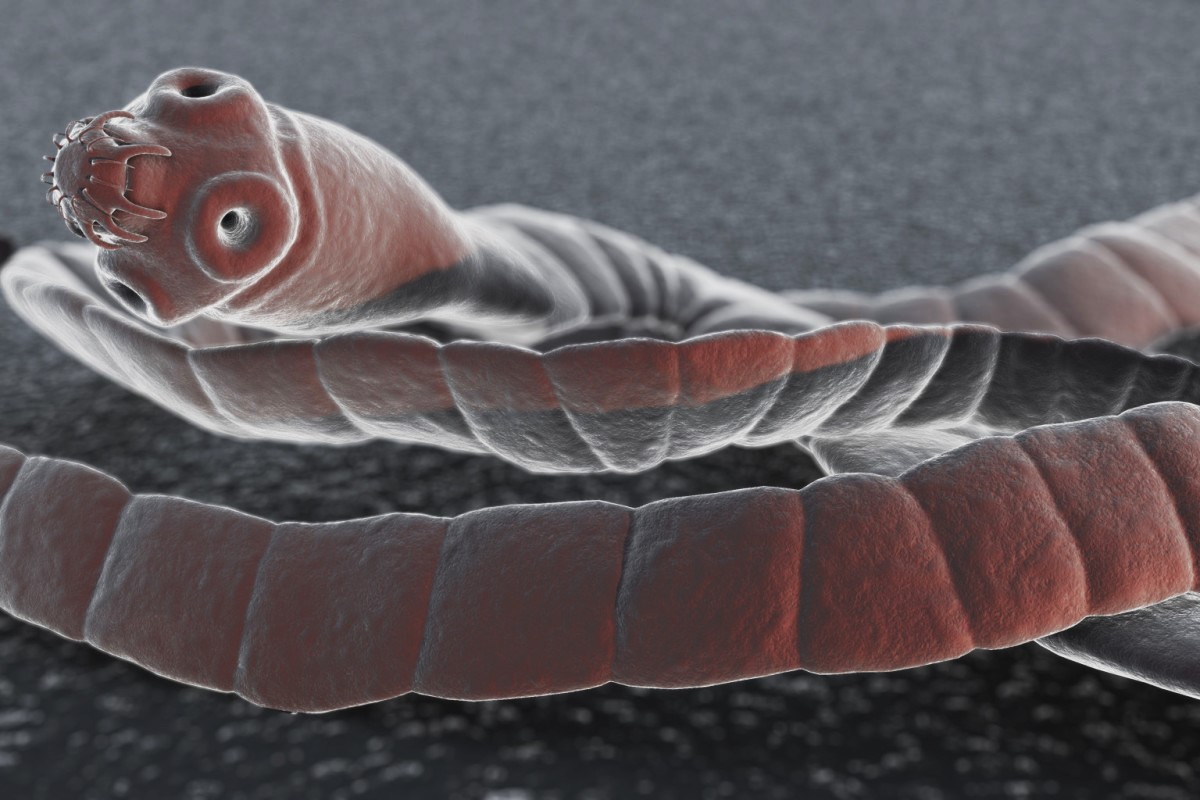
What is Taeniasis? Taeniasis is an infection caused by tapeworms, specifically the Taenia species. These parasites can enter the human body through the consumption of undercooked or contaminated pork or beef. Symptoms can range from mild digestive issues to more severe complications like cysticercosis, which affects muscles and the nervous system. Preventing taeniasis involves proper cooking of meat and maintaining good hygiene practices. Treatment typically includes antiparasitic medications prescribed by a healthcare professional. Understanding taeniasis is crucial for maintaining health, especially in regions where these infections are more common.
Key Takeaways:
- Taeniasis, caused by tapeworms from undercooked meat, can lead to abdominal pain, weight loss, and fatigue. Proper cooking and hygiene are crucial for prevention.
- Taeniasis can cause complications like cysticercosis and intestinal blockage. Public health efforts and WHO programs aim to control and eliminate this global health issue.
What is Taeniasis?
Taeniasis is an infection caused by tapeworms, specifically those from the genus Taenia. These parasites can live in the intestines of humans and animals, leading to various health issues. Here are some intriguing facts about taeniasis.
-
Caused by Tapeworms: Taeniasis is primarily caused by three types of tapeworms: Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm), Taenia solium (pork tapeworm), and Taenia asiatica (Asian tapeworm).
-
Transmission through Undercooked Meat: Consuming undercooked or raw beef or pork is the most common way to contract taeniasis.
-
Eggs in Feces: Tapeworm eggs are passed in the feces of an infected person or animal, contaminating the environment.
-
Larvae in Muscles: The larvae of Taenia species can encyst in the muscles of cattle and pigs, which then become a source of infection for humans.
-
Adult Tapeworms in Intestines: Once ingested, the larvae develop into adult tapeworms in the human intestines.
Symptoms of Taeniasis
Symptoms of taeniasis can vary widely. Some people may not experience any symptoms, while others may have noticeable signs of infection.
-
Abdominal Pain: One of the most common symptoms is abdominal pain, which can range from mild to severe.
-
Digestive Issues: Infected individuals may experience nausea, diarrhea, or constipation.
-
Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can occur due to the parasite consuming nutrients from the host.
-
Appetite Changes: Some people may experience increased appetite, while others may lose their appetite.
-
Fatigue: Persistent fatigue and weakness can result from the body's struggle to fight the infection.
Diagnosis of Taeniasis
Diagnosing taeniasis involves several methods to detect the presence of tapeworms or their eggs.
-
Stool Sample Analysis: Examining stool samples under a microscope can reveal tapeworm eggs or segments.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests can detect antibodies against tapeworms, indicating an infection.
-
Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans may be used to identify cysts in tissues.
-
Endoscopy: An endoscopy can help visualize the tapeworms in the intestines.
-
PCR Testing: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests can detect tapeworm DNA in stool samples.
Treatment of Taeniasis
Treating taeniasis typically involves medications to eliminate the tapeworms from the body.
-
Antiparasitic Medications: Drugs like praziquantel and albendazole are commonly used to treat taeniasis.
-
Single-Dose Treatment: In many cases, a single dose of medication is sufficient to clear the infection.
-
Follow-Up Tests: Follow-up stool tests are often necessary to ensure the infection has been completely eradicated.
-
Surgical Intervention: In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove cysts or tapeworms from tissues.
-
Supportive Care: Supportive care, including hydration and nutrition, is important during treatment.
Prevention of Taeniasis
Preventing taeniasis involves measures to reduce the risk of infection from tapeworms.
-
Proper Cooking: Cooking meat thoroughly to an internal temperature of at least 145°F (63°C) can kill tapeworm larvae.
-
Freezing Meat: Freezing meat at -4°F (-20°C) for at least 24 hours can also kill tapeworm larvae.
-
Good Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands with soap and water, can prevent the spread of tapeworm eggs.
-
Safe Food Handling: Avoiding cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods is crucial.
-
Regular Deworming: Regular deworming of livestock can reduce the risk of taeniasis in humans.
Complications of Taeniasis
While taeniasis is often treatable, complications can arise, especially if the infection is left untreated.
-
Cysticercosis: Taenia solium can cause cysticercosis, where larvae form cysts in tissues, including the brain.
-
Neurocysticercosis: When cysts form in the brain, it can lead to seizures, headaches, and other neurological issues.
-
Intestinal Blockage: Large tapeworms can cause blockages in the intestines, leading to severe pain and digestive problems.
-
Malnutrition: Chronic infection can result in malnutrition due to nutrient absorption issues.
-
Organ Damage: In rare cases, tapeworms can cause damage to organs like the liver and lungs.
Global Impact of Taeniasis
Taeniasis is a global health issue, affecting millions of people worldwide.
-
Endemic Regions: Taeniasis is most common in regions where raw or undercooked meat is consumed, such as parts of Africa, Latin America, and Asia.
-
Economic Impact: The infection can have significant economic impacts, particularly in developing countries where livestock is a major source of income.
-
Public Health Efforts: Public health initiatives, including education and improved sanitation, are crucial in reducing the prevalence of taeniasis.
-
WHO Involvement: The World Health Organization (WHO) has programs aimed at controlling and eliminating taeniasis and cysticercosis.
-
Research and Development: Ongoing research is focused on developing better diagnostic tools, treatments, and vaccines for taeniasis.
Interesting Facts about Taeniasis
Here are some additional fascinating facts about taeniasis that you might not know.
-
Longest Tapeworm: The longest tapeworm ever recorded in a human was over 82 feet (25 meters) long.
-
Tapeworm Segments: Tapeworms are made up of segments called proglottids, each containing eggs.
-
Ancient Infection: Evidence of tapeworm infections has been found in ancient Egyptian mummies.
-
Zoonotic Disease: Taeniasis is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can be transmitted between animals and humans.
-
Self-Infection: In some cases, individuals can self-infect by ingesting tapeworm eggs from their own feces, leading to cysticercosis.
Key Takeaways on Taeniasis
Taeniasis, caused by tapeworms, is a condition that can be prevented with proper hygiene and cooking practices. Consuming undercooked or contaminated pork and beef often leads to infection. Symptoms might be mild or severe, ranging from digestive issues to neurological problems. Regular deworming, especially in areas where taeniasis is common, helps reduce the risk. If you suspect an infection, seek medical advice promptly. Early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing complications. Educating communities about safe food handling and sanitation can significantly lower infection rates. Remember, maintaining good hygiene and being cautious about food sources are your best defenses against taeniasis. Stay informed, stay safe, and keep those tapeworms at bay!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
