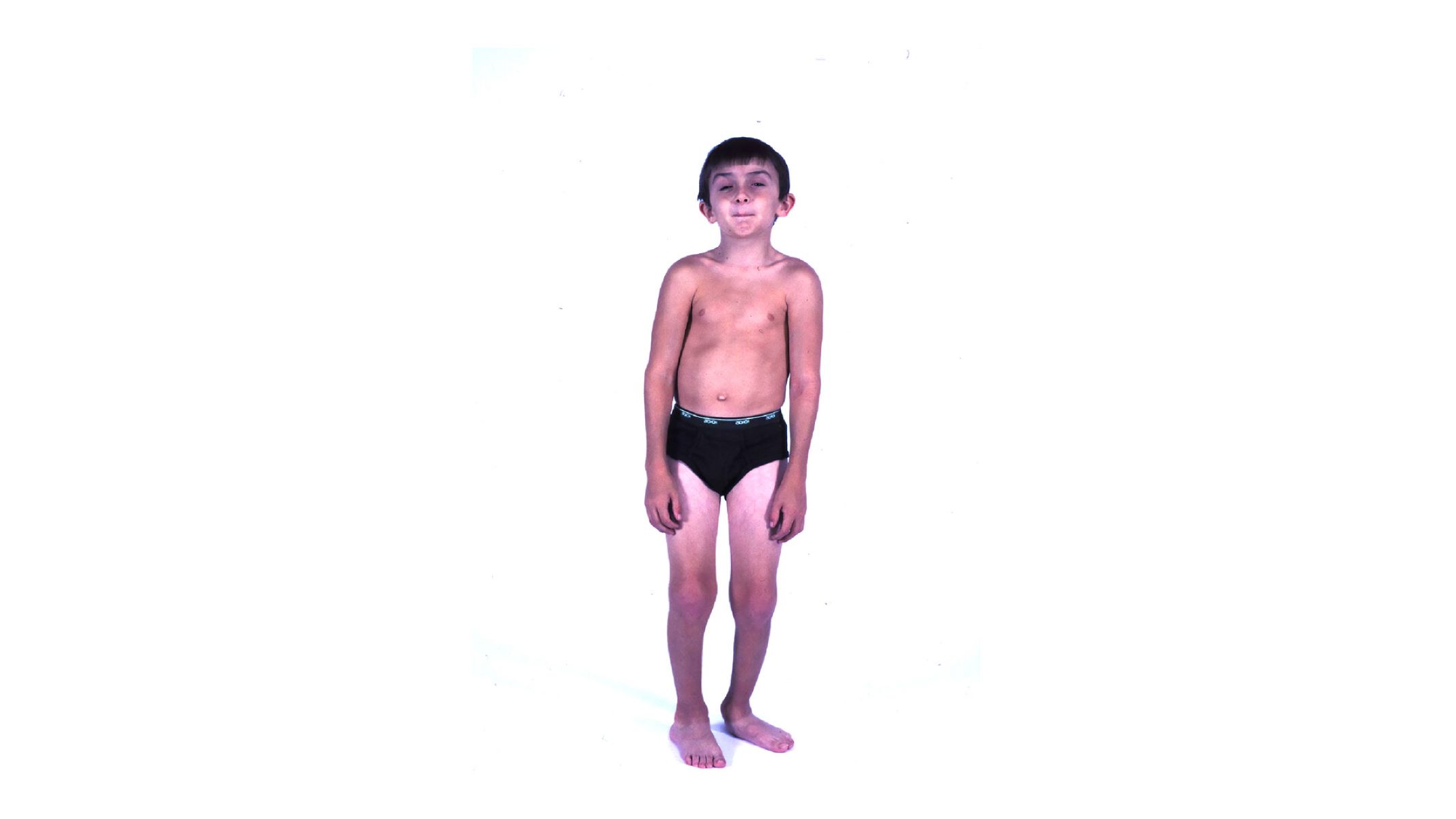
Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects muscle and bone development. Characterized by muscle stiffness, joint deformities, and distinctive facial features, this condition can significantly impact daily life. Caused by mutations in the HSPG2 gene, it disrupts the production of a protein essential for muscle function. Symptoms often appear in early childhood and can vary in severity. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms through physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgery. Understanding Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome is crucial for those affected and their families. Here are 40 facts to help you learn more about this complex condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome (SJS) is a rare genetic disorder causing muscle stiffness and bone abnormalities. It can lead to eye, hearing, and respiratory issues, but with proper support and treatment, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
- SJS is diagnosed through genetic testing and managed with physical therapy, medications, and surgeries. Support groups, adaptive equipment, and regular medical check-ups are crucial for individuals living with SJS.
What is Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome?
Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome (SJS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects muscle and bone development. It leads to muscle stiffness, bone abnormalities, and other physical issues. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
SJS was first identified in 1962 by Dr. Oscar Schwartz and Dr. Robert Jampel. They described two siblings with unique muscle and bone symptoms.
-
It is also known as chondrodystrophic myotonia. This name highlights the two main features: bone growth issues (chondrodystrophy) and muscle stiffness (myotonia).
-
SJS is caused by mutations in the HSPG2 gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein called perlecan, crucial for muscle and bone development.
-
The condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. This means both parents must carry one copy of the mutated gene for their child to be affected.
-
SJS affects males and females equally. There is no gender preference in the occurrence of this syndrome.
-
Symptoms usually appear in infancy or early childhood. Muscle stiffness and bone abnormalities are often noticeable from a young age.
-
Muscle stiffness in SJS is continuous. Unlike other conditions where stiffness comes and goes, SJS causes persistent muscle tightness.
-
Individuals with SJS often have a distinctive facial appearance. Features include a small mouth, pursed lips, and a flat nasal bridge.
-
Bone abnormalities can lead to short stature. Many individuals with SJS are shorter than average due to their bone growth issues.
-
Joint contractures are common. This means that joints may become permanently bent or stiff, limiting movement.
Symptoms and Complications
Understanding the symptoms and potential complications of SJS can help in managing the condition better. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Eye problems are frequent. These can include nearsightedness, cataracts, and glaucoma.
-
Hearing loss is another common issue. Many individuals with SJS experience varying degrees of hearing impairment.
-
Respiratory problems can occur. Muscle stiffness can affect breathing, leading to respiratory complications.
-
SJS can cause difficulties with speech. Muscle stiffness around the mouth and throat can make speaking challenging.
-
Feeding difficulties are often present. Infants and children with SJS may struggle with eating due to muscle stiffness.
-
Scoliosis, or curvature of the spine, is common. This can lead to additional physical complications and discomfort.
-
Dental issues are frequent. These can include crowded teeth and problems with jaw alignment.
-
Growth delays are typical. Children with SJS often grow more slowly than their peers.
-
Muscle weakness can develop over time. While stiffness is a primary symptom, muscle strength may also be affected.
-
Fatigue is a common complaint. The constant muscle stiffness can lead to overall tiredness and fatigue.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and treating SJS involves a multidisciplinary approach. Here are some important facts about how this condition is managed.
-
Diagnosis often involves genetic testing. Identifying mutations in the HSPG2 gene can confirm the diagnosis.
-
Electromyography (EMG) can be used. This test measures muscle electrical activity and can help diagnose myotonia.
-
X-rays and MRI scans are common diagnostic tools. These imaging techniques help identify bone abnormalities.
-
Physical therapy is a key treatment. Regular exercises can help maintain muscle flexibility and joint mobility.
-
Medications can help manage symptoms. Muscle relaxants and pain relievers are often prescribed.
-
Orthopedic surgery may be necessary. Procedures can correct bone deformities and improve mobility.
-
Speech therapy can be beneficial. This helps individuals with SJS improve their communication skills.
-
Hearing aids are often needed. These devices can help manage hearing loss.
-
Regular eye exams are crucial. Early detection and treatment of eye problems can prevent further complications.
-
Respiratory support may be required. In severe cases, breathing assistance might be necessary.
Living with Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome
Living with SJS presents unique challenges, but with proper support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some insights into daily life with this condition.
-
Support groups can be invaluable. Connecting with others who have SJS can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Adaptive equipment can improve quality of life. Tools like special utensils and mobility aids can help with daily tasks.
-
Educational support is often needed. Children with SJS may require special accommodations in school.
-
Regular medical check-ups are essential. Ongoing monitoring helps manage symptoms and prevent complications.
-
A balanced diet is important. Proper nutrition supports overall health and can help manage symptoms.
-
Mental health support is crucial. Counseling and therapy can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of SJS.
-
Family education is key. Teaching family members about SJS can improve understanding and support.
-
Occupational therapy can aid daily living. This therapy focuses on improving the ability to perform everyday activities.
-
Hydrotherapy can be beneficial. Water-based exercises can help maintain muscle flexibility without added strain.
-
Positive outlook and resilience are vital. Maintaining a hopeful attitude can make a significant difference in managing SJS.
Final Thoughts on Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome
Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome (SJS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects muscle and bone development. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improving quality of life. Regular medical check-ups, physical therapy, and medications can alleviate some symptoms. Genetic counseling is also beneficial for families with a history of SJS. Though living with SJS presents challenges, advancements in medical research offer hope for better management and potential treatments in the future. Staying informed and connected with support groups can make a significant difference. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with rare conditions like SJS.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
