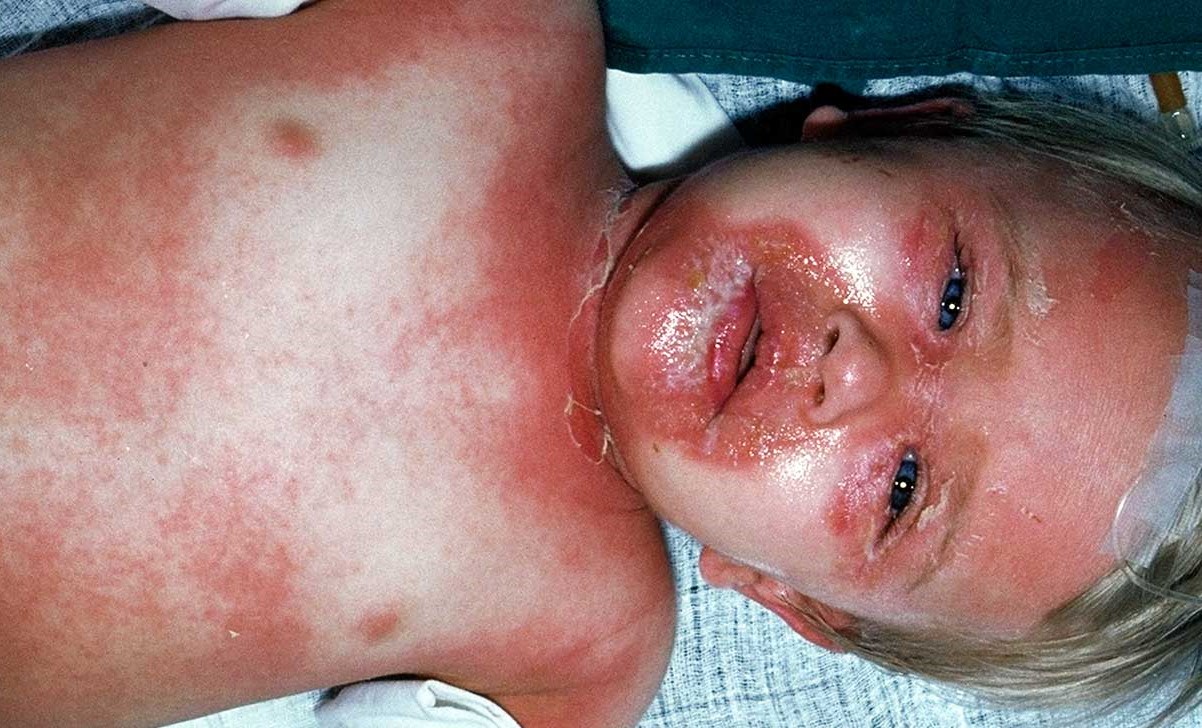
Ritter Disease, also known as Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS), is a rare but serious skin condition primarily affecting infants and young children. Caused by a bacterial infection, it leads to red, blistering skin that looks like it has been scalded. The bacteria responsible for this condition produce toxins that damage the skin's outer layer, causing it to peel away. Early symptoms often include fever, irritability, and widespread redness of the skin. If untreated, it can lead to severe complications. Prompt medical attention is crucial for effective treatment and recovery. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments can help in managing and preventing this condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Ritter Disease, also known as Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome, is a severe skin condition caused by bacterial infection. It primarily affects infants and young children, causing red, blistering skin that peels off in sheets.
- Early recognition of symptoms and prompt treatment are crucial for managing Ritter Disease. Good hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and proper wound care can help prevent the spread of the bacteria.
What is Ritter Disease?
Ritter Disease, also known as Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS), is a severe skin condition primarily affecting infants and young children. It is caused by a bacterial infection that leads to the skin peeling off in sheets. Understanding this condition can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking prompt treatment.
- Ritter Disease is named after the German physician Gottfried Ritter von Rittershain, who first described the condition in 1878.
- The disease is caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, which produce toxins that affect the skin.
- Infants and young children are most commonly affected due to their underdeveloped immune systems.
- The condition is characterized by red, blistering skin that looks like it has been scalded.
- Ritter Disease is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact or contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of Ritter Disease early can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment. Here are some key signs and diagnostic methods.
- Initial symptoms include fever, irritability, and redness of the skin.
- The skin may develop large, fluid-filled blisters that easily rupture.
- Peeling skin is a hallmark of the disease, often starting around the mouth and spreading.
- Nikolsky's sign is a diagnostic test where slight rubbing of the skin causes it to peel away.
- Blood tests and skin cultures can confirm the presence of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment is crucial for managing Ritter Disease and preventing complications. Here are some common treatment methods.
- Antibiotics are the primary treatment to combat the bacterial infection.
- Intravenous fluids may be necessary to prevent dehydration from fluid loss through the skin.
- Pain management is important, often requiring medications to alleviate discomfort.
- Wound care involves keeping the affected skin clean and protected to prevent secondary infections.
- In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for intensive care and monitoring.
Complications and Prognosis
While Ritter Disease can be severe, understanding potential complications and the prognosis can help in managing expectations and outcomes.
- Secondary infections are a common complication due to the damaged skin barrier.
- Dehydration can occur from fluid loss through the peeling skin.
- Electrolyte imbalances may result from extensive skin damage and fluid loss.
- With prompt treatment, the prognosis is generally good, and most children recover fully.
- Scarring is rare, but some children may experience temporary skin discoloration.
Preventing Ritter Disease
Prevention focuses on reducing the risk of infection and spreading the bacteria. Here are some preventive measures.
- Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoiding contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces is crucial.
- Proper wound care for cuts and abrasions can prevent bacterial entry.
- Early treatment of minor skin infections can stop them from progressing to Ritter Disease.
- Vaccination against Staphylococcus aureus is currently under research and may offer future prevention options.
Historical and Cultural Context
Understanding the historical and cultural context of Ritter Disease provides insight into its impact and recognition over time.
- Gottfried Ritter von Rittershain first described the disease in 1878, bringing attention to this severe condition.
- The disease was initially mistaken for burns due to the scalded appearance of the skin.
- Medical advancements in antibiotics and wound care have significantly improved outcomes for affected children.
- Public health campaigns have raised awareness about the importance of hygiene in preventing bacterial infections.
- Cultural beliefs about skin diseases have evolved, reducing stigma and promoting better care for affected individuals.
Interesting Facts
Here are some intriguing facts about Ritter Disease that highlight its unique aspects and challenges.
- Ritter Disease is also known as Pemphigus neonatorum in some medical literature.
- The condition can affect adults with weakened immune systems, though it is rare.
- Exfoliative toxins produced by the bacteria are responsible for the skin peeling.
- Outbreaks of Ritter Disease have been reported in neonatal units, emphasizing the need for strict hygiene practices.
- The disease can be mistaken for other skin conditions, such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, making accurate diagnosis essential.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of Ritter Disease. Here are some areas of focus.
- Genetic studies are exploring why some individuals are more susceptible to the toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus.
- New antibiotics are being developed to combat antibiotic-resistant strains of the bacteria.
- Immunotherapy is being investigated as a potential treatment to boost the body's defense against the infection.
- Public health initiatives continue to focus on preventing the spread of bacterial infections in healthcare settings.
- Patient education programs aim to increase awareness about the signs and symptoms of Ritter Disease for early detection and treatment.
Final Thoughts on Ritter Disease
Ritter Disease, also known as Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS), is a serious skin condition primarily affecting infants and young children. Caused by toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, it leads to red, blistering skin that looks like it’s been scalded. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. Antibiotics are the main treatment, and supportive care helps manage symptoms. While it can be alarming, most children recover fully with proper medical care. Understanding the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention can make a significant difference. Stay informed, and always consult healthcare professionals if you suspect Ritter Disease. Knowledge is key to ensuring the well-being of our little ones.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
