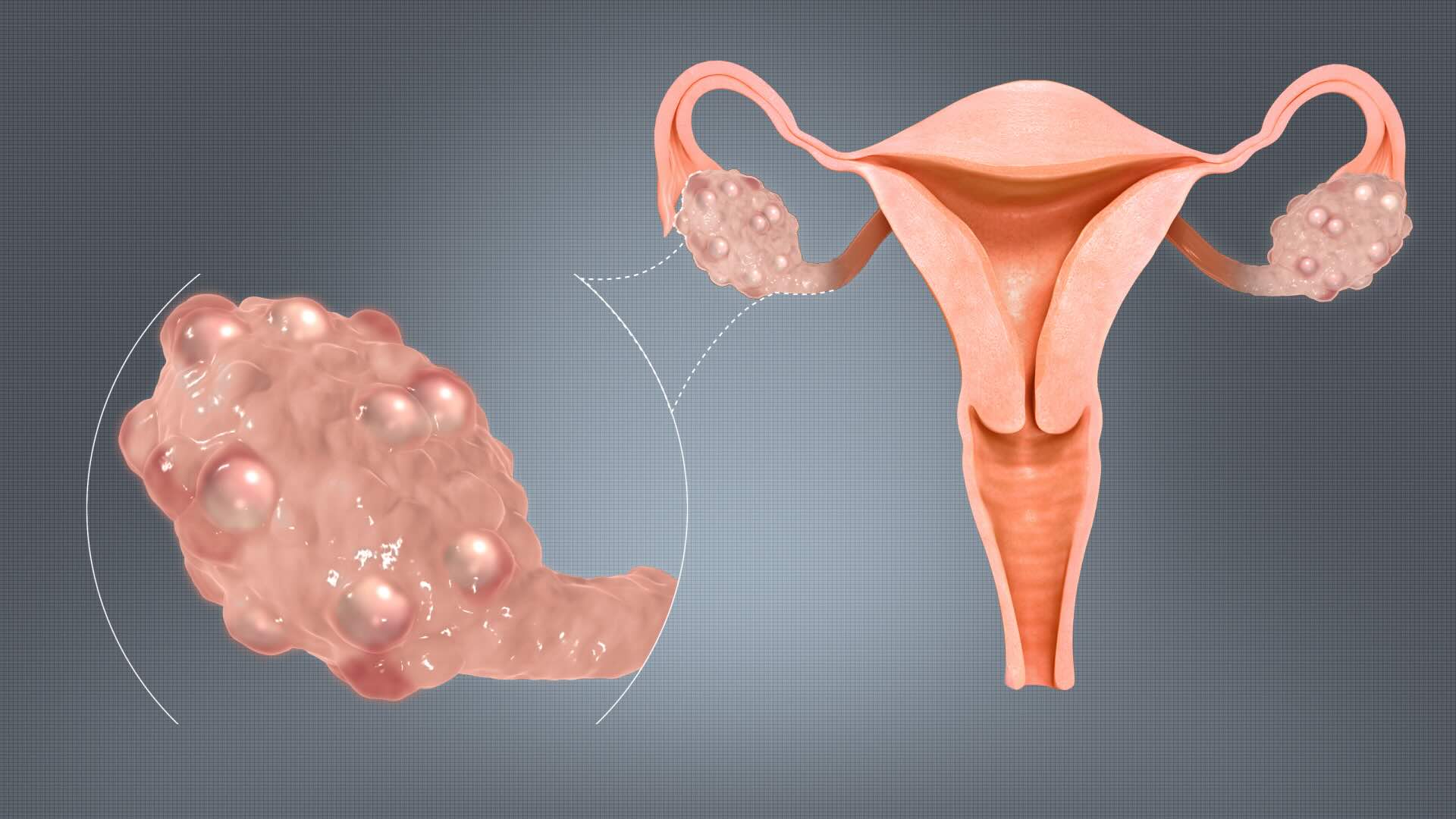
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD), often confused with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), affects millions of women worldwide. But what exactly is it? PCOD is a condition where a woman's ovaries produce immature or partially mature eggs in large numbers. These eggs can turn into cysts over time, leading to various health issues. Symptoms can range from irregular periods, weight gain, and acne to more severe complications like infertility and diabetes. Understanding PCOD is crucial for managing its symptoms and improving quality of life. This article dives into 40 essential facts about Polycystic Ovarian Disease to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Key Takeaways:
- PCOD affects 5-10% of women and can cause infertility, irregular periods, and weight gain. Early diagnosis and lifestyle changes are crucial for managing its effects and improving quality of life.
- Lifestyle tips like a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and adequate sleep can help manage PCOD effectively. Dispelling myths and seeking emotional support are also important for holistic care.
What is Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD)?
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) is a common hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It involves the presence of multiple cysts in the ovaries and can lead to various symptoms and health issues. Understanding PCOD is crucial for managing its effects.
- PCOD affects about 5-10% of women of childbearing age worldwide.
- It is one of the leading causes of infertility in women.
- The exact cause of PCOD is unknown, but genetics and lifestyle factors play a role.
- Women with PCOD often have higher levels of androgens, male hormones, which can cause symptoms like excess hair growth and acne.
- Insulin resistance is common in women with PCOD, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of PCOD
PCOD manifests through a variety of symptoms that can vary in severity. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking timely medical intervention.
- Irregular menstrual cycles are a hallmark of PCOD.
- Many women with PCOD experience heavy bleeding during periods.
- Weight gain, especially around the abdomen, is a common symptom.
- Thinning hair or hair loss on the scalp can occur.
- Darkening of the skin, particularly around the neck, groin, and under the breasts, is another symptom.
Diagnosis of PCOD
Diagnosing PCOD involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, and specific tests. Early diagnosis can lead to better management of the condition.
- Ultrasound imaging is used to detect the presence of ovarian cysts.
- Blood tests measure hormone levels to identify hormonal imbalances.
- A pelvic exam helps in assessing the health of reproductive organs.
- Doctors may also check for insulin resistance and glucose tolerance.
- Family history is considered, as PCOD can run in families.
Treatment Options for PCOD
While there is no cure for PCOD, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment plans are often tailored to individual needs.
- Birth control pills regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels.
- Metformin, a diabetes medication, helps improve insulin resistance.
- Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, are crucial.
- Anti-androgen medications reduce symptoms like excess hair growth and acne.
- Fertility treatments, including ovulation induction, assist women trying to conceive.
Impact of PCOD on Mental Health
PCOD doesn't just affect physical health; it can also have significant mental health implications. Addressing these aspects is essential for holistic care.
- Women with PCOD are at a higher risk of developing anxiety and depression.
- Body image issues due to symptoms like weight gain and acne can affect self-esteem.
- The stress of managing a chronic condition can lead to emotional strain.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support.
- Mindfulness and stress-reduction techniques can improve mental well-being.
Long-term Health Risks Associated with PCOD
PCOD can lead to several long-term health risks if not managed properly. Awareness of these risks can encourage proactive health measures.
- Women with PCOD have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- There is an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases due to associated risk factors like obesity and insulin resistance.
- Sleep apnea is more common in women with PCOD.
- Endometrial cancer risk is higher due to irregular menstrual cycles and prolonged exposure to estrogen.
- Managing weight and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can mitigate some of these risks.
Myths and Misconceptions about PCOD
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding PCOD. Dispelling these can lead to better understanding and management of the condition.
- Myth: PCOD and PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) are the same. Fact: They are related but distinct conditions.
- Myth: Only overweight women get PCOD. Fact: Women of all body types can have PCOD.
- Myth: PCOD always causes infertility. Fact: Many women with PCOD can conceive with appropriate treatment.
- Myth: Birth control pills cure PCOD. Fact: They manage symptoms but do not cure the condition.
- Myth: PCOD is rare. Fact: It is a common condition affecting millions of women worldwide.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing PCOD
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve the management of PCOD. Here are some practical tips to help manage the condition effectively.
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help manage weight and insulin levels.
- Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can improve overall health and reduce symptoms.
- Reducing stress through activities like meditation, deep breathing, or hobbies can positively impact hormone levels.
- Getting enough sleep is crucial, as poor sleep can exacerbate symptoms.
- Regular medical check-ups and monitoring can help in early detection and management of associated health risks.
Final Thoughts on Polycystic Ovarian Disease
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) affects many women worldwide, causing a range of symptoms from irregular periods to weight gain. Understanding PCOD is crucial for managing its impact on daily life. Lifestyle changes, like a balanced diet and regular exercise, can significantly improve symptoms. Medical treatments, including hormonal therapy, also play a vital role in managing the condition. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent long-term complications like diabetes and heart disease. Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends is essential for those dealing with PCOD. Knowledge empowers women to take control of their health, ensuring a better quality of life. Stay informed, seek medical advice, and remember, you're not alone in this journey. By staying proactive, women can effectively manage PCOD and lead fulfilling lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
