Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be simpler than you think. This rare genetic disorder affects bone growth, particularly in the metaphyses, the wide parts of long bones. Symptoms often include short stature, bowed legs, and joint pain. While it can be challenging, knowing more about it helps in managing the condition better. Genetics play a crucial role, with mutations in specific genes being the culprits. Diagnosis usually involves X-rays and genetic testing. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms through physical therapy and sometimes surgery. Ready to dive into 40 intriguing facts about this condition? Let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia (MCD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects bone growth, causing unique symptoms and challenges for individuals. Genetic testing and early intervention are crucial for managing this condition effectively.
- Research and collaboration are driving exciting developments in understanding and treating MCD. From gene therapy to patient registries, the future holds promise for improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this rare disorder.
What is Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia?
Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia (MCD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting bone growth. It primarily impacts the metaphyses, the wider part of long bones where growth occurs. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
MCD is a group of disorders, not just one single condition. Each type has unique characteristics and genetic causes.
-
The three main types of MCD are Schmid, Jansen, and McKusick. Each type varies in severity and symptoms.
-
Schmid type is the most common form of MCD. It is usually less severe compared to other types.
-
Jansen type is extremely rare and often more severe. It can cause significant skeletal abnormalities.
-
McKusick type, also known as cartilage-hair hypoplasia, affects both the bones and hair. It can lead to short stature and fine, sparse hair.
Causes and Genetics of MCD
Understanding the genetic basis of MCD helps in diagnosing and managing the condition. Here are some key facts about its genetic origins.
-
MCD is usually inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. This means only one copy of the mutated gene is needed to cause the disorder.
-
The Schmid type is caused by mutations in the COL10A1 gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein essential for bone development.
-
Jansen type results from mutations in the PTH1R gene. This gene plays a crucial role in regulating bone growth and development.
-
McKusick type is linked to mutations in the RMRP gene. This gene is involved in the production of RNA, which is essential for protein synthesis.
-
Genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of MCD. It helps identify the specific type and guide treatment options.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of MCD is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Here are some common signs and diagnostic methods.
-
Short stature is a hallmark of MCD. Affected individuals often have shorter limbs compared to their torso.
-
Bowed legs or knock knees are common in MCD. These skeletal abnormalities can affect mobility.
-
Joint pain and stiffness may occur, especially in the knees and hips.
-
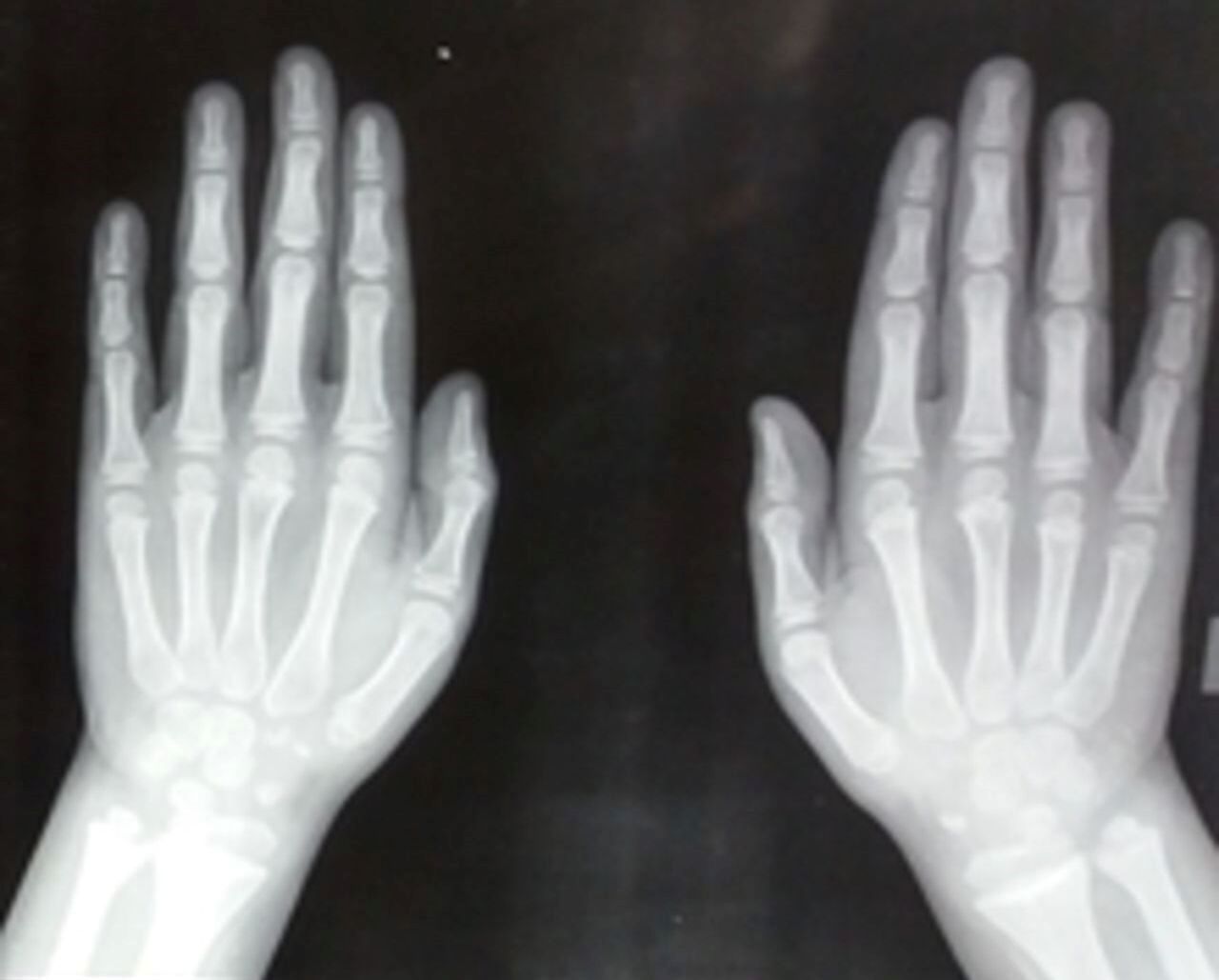
X-rays are essential for diagnosing MCD. They reveal characteristic changes in the metaphyses of long bones.
-
Growth charts help monitor the growth patterns of children with MCD. Deviations from normal growth can indicate the disorder.
Treatment and Management
Managing MCD involves addressing symptoms and improving quality of life. Here are some treatment options and strategies.
-
Physical therapy can help improve mobility and reduce joint pain.
-
Orthopedic surgery may be necessary to correct severe skeletal abnormalities.
-
Growth hormone therapy is sometimes used to promote growth in children with MCD.
-
Pain management strategies, including medications and physical therapy, can help alleviate discomfort.
-
Regular monitoring by a healthcare team is essential. This ensures timely interventions and adjustments to treatment plans.
Living with MCD
Living with MCD presents unique challenges, but with the right support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some insights into daily life with MCD.
-
Adaptive devices, such as braces or orthotics, can aid mobility and reduce pain.
-
Support groups provide a sense of community and shared experiences for individuals with MCD and their families.
-
Educational accommodations may be necessary for children with MCD. This ensures they receive appropriate support in school.
-
Regular exercise, tailored to individual abilities, can help maintain joint function and overall health.
-
A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve our understanding of MCD and develop better treatments. Here are some exciting developments in the field.
-
Gene therapy holds promise for treating genetic disorders like MCD. Researchers are exploring ways to correct the underlying genetic mutations.
-
Advances in imaging technology are improving the accuracy of MCD diagnosis. This allows for earlier and more precise interventions.
-
Clinical trials are testing new medications to manage symptoms and improve bone health in individuals with MCD.
-
Patient registries are helping researchers gather valuable data on MCD. This information can guide future research and treatment strategies.
-
Collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and patient advocacy groups is essential. It drives progress in understanding and treating MCD.
Interesting Facts about MCD
Here are some lesser-known but intriguing facts about Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia.
-
MCD can affect both males and females equally. There is no gender predisposition for this disorder.
-
The severity of MCD can vary widely, even among individuals with the same type. This makes personalized treatment plans crucial.
-
Some individuals with MCD may have normal intelligence, while others may experience developmental delays.
-
Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes for children with MCD. Timely treatment can prevent or minimize complications.
-
MCD is often diagnosed in childhood, but symptoms can become more apparent with age.
-
The prevalence of MCD is not well-documented due to its rarity. It is estimated to affect fewer than 1 in 1,000,000 people.
-
MCD can sometimes be mistaken for other skeletal disorders. Accurate diagnosis requires careful evaluation by a specialist.
-
Family history plays a significant role in diagnosing MCD. A detailed family medical history can provide important clues.
-
Genetic counseling is recommended for families affected by MCD. It helps them understand the risks and implications of the disorder.
-
Advances in genetic research are paving the way for new treatments and improved outcomes for individuals with MCD.
Final Thoughts on Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia
Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia, a rare genetic disorder, affects bone growth, leading to short stature and skeletal abnormalities. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments is crucial for managing the condition. Early diagnosis can make a significant difference in the quality of life for those affected. Genetic counseling helps families understand the risks and implications. While there's no cure, treatments like physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgery can alleviate symptoms and improve mobility. Staying informed and connected with medical professionals ensures the best care. Awareness and education about this condition can lead to better support and resources for patients and their families. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with any health issue. Keep learning, stay proactive, and support those living with Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
