Lymphocytic vasculitis might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be simpler than you think. This condition involves inflammation of blood vessels due to an immune response, often leading to symptoms like skin rashes or ulcers. Why should you care? Because recognizing the signs early can make a big difference in managing it effectively. From its causes to treatment options, knowing the basics can help you stay informed and proactive about your health. Whether you're a curious student, a concerned parent, or someone experiencing symptoms, this guide will break down 40 essential facts about lymphocytic vasculitis in a way that's easy to grasp. Ready to dive in? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Lymphocytic vasculitis is a rare condition where the body's immune system attacks its own blood vessels, causing inflammation and skin symptoms like red or purple spots. Treatment involves medications and lifestyle adjustments for effective management.
- Factors like genetics, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices can contribute to the development of lymphocytic vasculitis. Understanding these factors can help in prevention and early detection of the condition.
What is Lymphocytic Vasculitis?
Lymphocytic vasculitis is a rare condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own blood vessels. This can lead to inflammation, pain, and various other symptoms. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Lymphocytic vasculitis primarily affects small blood vessels, including capillaries, arterioles, and venules.
-
Inflammation caused by lymphocytic vasculitis can lead to damage in the blood vessel walls, resulting in leakage and swelling.
-
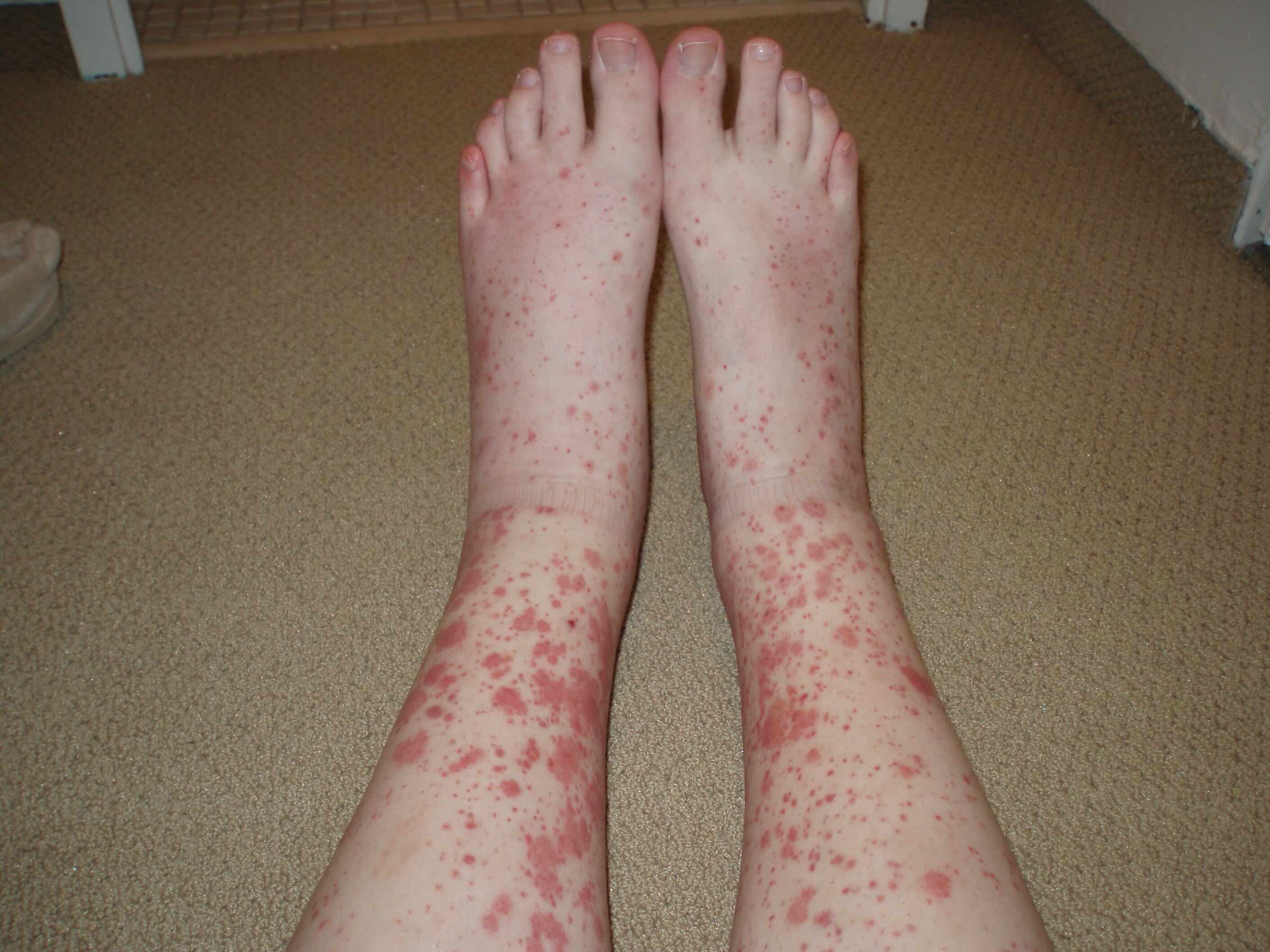
Symptoms often include red or purple spots on the skin, known as purpura, which can be itchy or painful.
-
Diagnosis typically involves a skin biopsy, where a small sample of affected tissue is examined under a microscope.
-
Lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, are the main immune cells involved in this condition.
-
Autoimmune disorders such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can increase the risk of developing lymphocytic vasculitis.
-
Medications like certain antibiotics or diuretics have been linked to triggering lymphocytic vasculitis in some individuals.
-
Infections can also act as a trigger, with viruses like hepatitis B and C being common culprits.
-
Treatment often involves corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
-
Immunosuppressive drugs may be prescribed for severe cases to prevent further immune system attacks on blood vessels.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how lymphocytic vasculitis is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively.
-
Skin lesions are the most common symptom, appearing as raised, red patches or bumps.
-
Pain and tenderness in the affected areas can occur, making daily activities uncomfortable.
-
Fever and general malaise may accompany the skin symptoms, indicating systemic involvement.
-
Blood tests can show elevated levels of inflammatory markers, aiding in the diagnosis.
-
Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans are sometimes used to assess the extent of blood vessel involvement.
-
Differential diagnosis is crucial, as symptoms can mimic other conditions like allergic reactions or infections.
-
Histopathology of the biopsy sample reveals lymphocytic infiltration around the blood vessels, confirming the diagnosis.
-
Direct immunofluorescence can be used on biopsy samples to detect immune complex deposits in the blood vessel walls.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of lymphocytic vasculitis. Knowing these can help in prevention and early detection.
-
Genetic predisposition plays a role, with certain genetic markers increasing susceptibility.
-
Environmental factors like exposure to certain chemicals or toxins can trigger the condition.
-
Chronic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension can exacerbate the risk.
-
Age is a factor, with middle-aged and older adults being more commonly affected.
-
Gender also plays a role, with women being slightly more prone to developing lymphocytic vasculitis.
-
Stress and emotional trauma have been linked to flare-ups in some patients.
-
Diet and lifestyle choices, including smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can impact the severity of the condition.
Treatment and Management
Effective management of lymphocytic vasculitis involves a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
-
Corticosteroids are the first line of treatment, helping to reduce inflammation quickly.
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used for pain relief and to reduce inflammation.
-
Antihistamines may be prescribed to alleviate itching and discomfort.
-
Topical treatments like corticosteroid creams can be applied directly to skin lesions.
-
Physical therapy might be recommended to maintain mobility and reduce pain in affected areas.
-
Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential to track the progression and response to treatment.
-
Patient education on recognizing early symptoms and triggers can help in managing flare-ups.
-
Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and coping strategies for patients.
-
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture or herbal remedies may offer additional relief for some individuals.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
Understanding the long-term outlook and potential complications can help patients and caregivers prepare for the future.
-
Prognosis varies, with some patients experiencing complete remission while others may have chronic symptoms.
-
Complications can include skin ulcers, infections, and scarring if not properly managed.
-
Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist or rheumatologist are crucial for ongoing care.
-
Lifestyle modifications like a healthy diet and regular exercise can improve overall well-being and reduce flare-ups.
-
Research is ongoing to better understand the underlying mechanisms and develop more effective treatments.
-
Awareness and education about lymphocytic vasculitis can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes for patients.
Final Thoughts on Lymphocytic Vasculitis
Lymphocytic vasculitis, a condition marked by inflammation of blood vessels due to lymphocytes, can be tricky to diagnose and manage. Symptoms like skin rashes, ulcers, and pain often lead to confusion with other ailments. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. Understanding the triggers, such as infections or autoimmune disorders, helps in managing the condition better. Treatment usually involves corticosteroids or immunosuppressants to reduce inflammation. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure the condition remains under control. Staying informed and proactive can make a significant difference in the quality of life for those affected. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with any medical condition. Stay curious, stay informed, and always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
