Hereditary Hyperuricemia is a genetic condition where the body produces too much uric acid or fails to eliminate it efficiently. This excess uric acid can lead to painful gout attacks, kidney stones, and other health issues. Understanding this condition is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. In this blog post, we will explore 40 fascinating facts about hereditary hyperuricemia, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and treatments. Whether you or a loved one is affected, or you're simply curious, these facts will provide valuable insights into this often misunderstood condition. Let's dive into the world of hereditary hyperuricemia and uncover what you need to know.
Key Takeaways:
- Hereditary hyperuricemia is a genetic condition causing high uric acid levels, leading to gout and kidney stones. Lifestyle changes and medication can help manage the condition effectively.
- Understanding the causes and risks, along with early detection and proper management, can prevent serious complications and improve the quality of life for those with hereditary hyperuricemia.
What is Hereditary Hyperuricemia?
Hereditary hyperuricemia is a genetic condition where the body produces too much uric acid or has trouble eliminating it. This can lead to various health issues, including gout and kidney stones.
- Genetic Basis: Hereditary hyperuricemia is caused by mutations in specific genes that affect uric acid metabolism.
- Uric Acid: Uric acid is a waste product formed from the breakdown of purines, substances found in many foods and drinks.
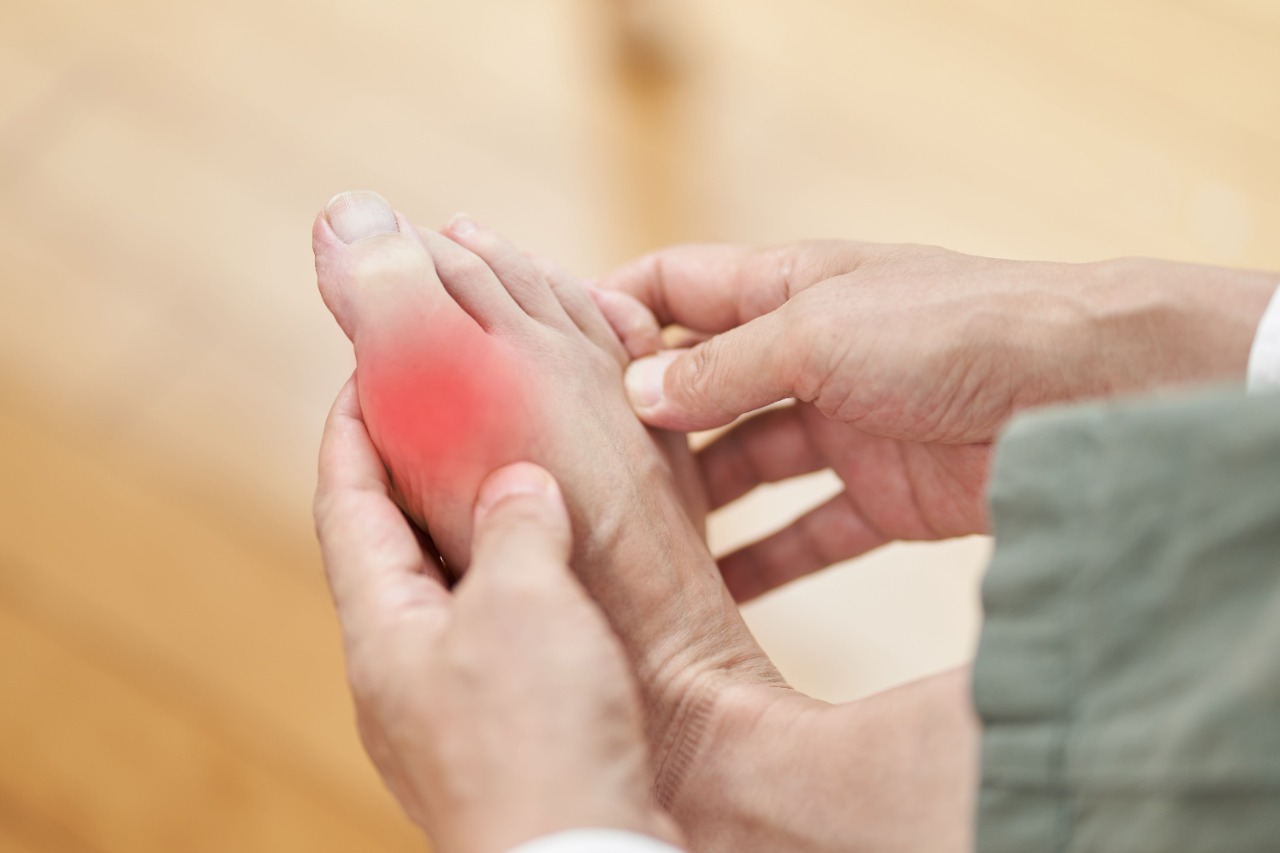
- Gout: High levels of uric acid can lead to gout, a type of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in joints.
- Kidney Stones: Excess uric acid can form crystals in the kidneys, leading to painful kidney stones.
- Xanthine Oxidase: This enzyme plays a crucial role in the production of uric acid. Mutations affecting this enzyme can lead to hyperuricemia.
- Inheritance Pattern: The condition is often inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning one copy of the altered gene is enough to cause the disorder.
- Prevalence: Hereditary hyperuricemia is relatively rare, affecting a small percentage of the population.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and redness, particularly in the big toe.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests measuring uric acid levels are typically used to diagnose the condition.
- Family History: A family history of gout or kidney stones can be a strong indicator of hereditary hyperuricemia.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in managing hereditary hyperuricemia more effectively.
- Diet: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat and seafood, can exacerbate the condition.
- Alcohol: Alcohol, especially beer, can increase uric acid levels.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of developing hyperuricemia.
- Medications: Certain medications, like diuretics, can raise uric acid levels.
- Age and Gender: Men are more likely to develop hyperuricemia, and the risk increases with age.
- Renal Function: Impaired kidney function can lead to decreased elimination of uric acid.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes are associated with higher uric acid levels.
- Dehydration: Lack of fluids can concentrate uric acid in the blood, increasing the risk of crystal formation.
- Lead Exposure: Chronic lead exposure has been linked to higher uric acid levels.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can identify specific mutations responsible for hereditary hyperuricemia.
Treatment and Management
Effective management of hereditary hyperuricemia involves lifestyle changes and medical treatments.
- Medications: Drugs like allopurinol and febuxostat can help reduce uric acid production.
- Dietary Changes: Reducing intake of purine-rich foods can help manage uric acid levels.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess uric acid.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help manage weight and improve overall health.
- Avoiding Alcohol: Limiting or avoiding alcohol can help keep uric acid levels in check.
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests can help monitor uric acid levels and adjust treatment as needed.
- Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain during gout attacks.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Stress management and a balanced diet can contribute to overall well-being.
- Medical Supervision: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for managing the condition.
Complications and Prognosis
If left untreated, hereditary hyperuricemia can lead to serious complications.
- Chronic Gout: Repeated gout attacks can lead to chronic gout, causing permanent joint damage.
- Tophi: These are lumps of uric acid crystals that can form under the skin and around joints.
- Kidney Damage: Persistent high uric acid levels can lead to kidney damage over time.
- Heart Disease: High uric acid levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
- Hypertension: Hyperuricemia can contribute to high blood pressure.
- Diabetes: There is a link between high uric acid levels and an increased risk of developing diabetes.
- Early Detection: Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent many of these complications.
- Quality of Life: Proper management can significantly improve the quality of life for those with hereditary hyperuricemia.
- Research: Ongoing research aims to better understand the genetic basis and develop more effective treatments.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing the condition.
Final Thoughts on Hereditary Hyperuricemia
Hereditary hyperuricemia, a genetic condition, affects uric acid levels in the blood. This can lead to gout, kidney stones, and other health issues. Understanding the genetic factors helps in managing the condition better. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and staying hydrated are crucial. Medications can also help control uric acid levels. Awareness and early diagnosis make a significant difference. Genetic counseling might be beneficial for families with a history of hyperuricemia. Knowledge empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health. Remember, while hereditary factors play a role, lifestyle choices also impact the condition. Stay informed, consult healthcare professionals, and take charge of your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
